This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by doctor Biochemistry Test - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
Cirrhosis is a disease in which scar tissue replaces the normal tissue of the liver parenchyma. Cirrhosis has many causes and often progresses over many years. Cirrhosis usually does not cause clinical symptoms in the early stages. Damage caused by cirrhosis is difficult to reverse, but the right and timely treatment can stop or slow the progression of the disease.
1. Mechanism of cirrhosis of the liver
The liver is the largest organ in the human body with many special important functions such as: biochemical metabolism, digestion, detoxification and elimination of metabolic products from the body. The liver is involved in many functional activities such as excretion, synthesis, and metabolism. The liver is a unique organ that has a very important feature that is its ability to regenerate and restore. The liver has the ability to regenerate cells that have been destroyed by acute injury or disease. Chronic damage or long-term, repeated damage can create irreversible liver damage.
The metabolic activities of the liver occur in parenchymal cells (Parenchymal - Parenchymal cells make up 80% of the liver volume). The liver also contains Kupffer cells that act as macrophages capable of destroying bacteria, cell debris, toxins, and other substances.
The liver is a very rich vascular system: the hepatic artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart and supplies 25% of the blood supply to the liver; The portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the digestive system, supplying 75% of blood to the liver. The amount of blood through the liver is about 1500 mL/min. The excretory system of the liver starts from the bile capillaries, originates from the intercellular space between the liver cells, from which to form the intrahepatic bile ducts, forming the right and left hepatic ducts. The two hepatic ducts merge into the common hepatic duct and empty into the gallbladder, where the liver's excretion products are concentrated before emptying into the duodenum.

Gan là cơ quan lớn nhất trong cơ thể người và đảm nhiệm nhiều chức năng quan trọng
Due to many metabolic functions, as the gateway of substances into the body through the digestive system, the liver is a disease-prone organ. The prevalence of hepatobiliary disease is often higher than that of other organs and biochemical tests play a very important role in the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases of this system.
Cirrhosis is a disease in which scar tissue replaces the normal tissue of the liver parenchyma. Because scar tissue replaces normal tissue, it blocks blood vessels to the liver, causing liver problems. Cirrhosis usually does not cause clinical symptoms in the early stages. Damage caused by cirrhosis is difficult to reverse, and the right treatment can stop or slow the progression of the disease. Treatment depends on the cause of cirrhosis and on the individual patient.
2. Causes of cirrhosis
There are many causes of cirrhosis, known causes include:
Heavy drinking (alcoholic beverages), Infections: leading in this group are hepatitis B, C and or combined with hepatitis D virus. Other less common infections are Brucellose infection, Echinococcus, Schistosomiasis, Toxoplasmosis. Cirrhosis due to rare hereditary diseases: Hereditary hemoglobinopathy (increased serum iron, elevated ferritine and transferritine), Wilson's disease, copper cirrhosis (elevated serum copper), antitrypsin deficiency, porphyrinuria , hypergalactosemia, Gaucher disease, fructoseuria. Cirrhosis due to immune disorders: primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis. Mechanical cirrhosis (Secondary biliary cirrhosis - consequence of chronic primary biliary obstruction due to stenosis of oddi muscle, due to stones); vascular occlusion such as hepatic venous occlusion in Budd-chiari syndrome, long-standing right-sided heart failure, constrictive pericarditis. Cirrhosis due to the use of drugs Methotrexate, maleate de perhexilene, methyl dopa, oral contraceptives, oxyphenisatin, isoniazid, Other causes mentioned, but not proven include chronic inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, sarcoidosis . Some cases of cirrhosis have no known cause.

Lạm dụng rượu bia là nguyên nhân hàng đầu dẫn đến xơ gan
3. Stages of cirrhosis
Stage 1: The liver cells are inflamed, the liver corrects itself with scarring (fibrosis). This stage usually has no clinical signs because the fibrosis is not much, you may just feel tired. At this stage, with proper treatment, the liver can still recover and return to normal. Stage 2: More fibrous tissue appears. There have been manifestations of portal hypertension. At this stage, eliminating the cause of the disease can increase the chances of a cure. Stage 3: The tissues are very fibrous. The appearance of ascites (free fluid in the abdomen), collateral circulation, and many noticeable symptoms such as loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, yellow eyes, jaundice, anemia, edema (edema of the feet, ankles), itching, erratic rise and fall in blood sugar. At this stage when the liver cannot return to normal, a liver transplant is often suggested to cure the disease. Stage 4: Complete fibrosis of liver tissues. Symptoms that have been present since stage 3 are getting worse and worse, other signs such as drowsiness, red hands, fever, peritonitis, kidney failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, ... the final stage, this stage, liver transplantation is still proposed to cure the disease.
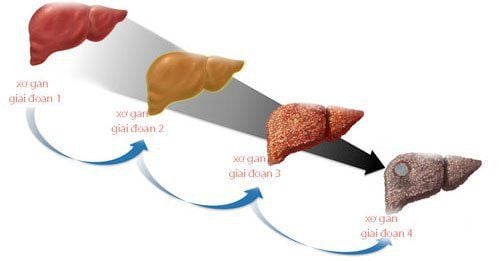
4 giai đoạn xơ gan
Possessing modern facilities, full of advanced equipment and machinery world leading, for high image quality, accurate and fast test results, maximum support for disease diagnosis and treatment. A team of leading specialists from major hospitals across the country helps the treatment process to be highly effective and shorten the treatment time. Professional, comprehensive examination and consultation service, examination space If you need to consult and visit Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.