This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Associate Professor, Doctor, Doctor Hoang Dang Mich - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
In the treatment of chronic kidney failure, currently in the world 3 popular methods are applied: kidney transplant, hemodialysis, and peritoneal dialysis. Depending on the stage of the disease and the patient's health condition, there are different treatment methods. So how is the treatment of chronic renal failure indicated for each stage? And is chronic kidney failure curable?
1. How many stages of chronic kidney failure?
Based on the level of kidney damage with changes in endogenous creatinine clearance, people divide chronic kidney failure into 5 clinical stages as follows:
Stage 1: Mild kidney failure Little kidney damage, glomerular filtration rate remains within the normal range; The direction of conservative treatment; Stage 2: Moderate renal failure The kidneys are slightly damaged, the glomerular filtration rate begins to decrease slightly, from 60-89 ml/min; The direction of conservative treatment; Stage 3a: Severe renal failure The glomerular filtration rate is moderately reduced (from 30-59 ml/min), anemia is present, bone and joint diseases such as back pain and knee fatigue may appear; The direction of conservative treatment; Stage 3b: Severe renal failure The glomerular filtration rate is severely reduced (from 15-29 ml/min); Direction of dialysis treatment; Stage 4: End-stage renal failure The glomerular filtration rate falls below 15ml/min, the kidneys are almost inoperable, the patient must undergo extra-renal dialysis or a kidney transplant; Treatment guidelines for mandatory dialysis or kidney transplantation.
2. Principles of treatment of chronic kidney disease
Depending on the patient's health status and disease stage to choose the most appropriate and optimal treatment methods. But regardless of treatment method, it is necessary to ensure the following principles:
Treatment of the cause combined with treatment of symptoms; Control and treat blood pressure; Control cholesterol during treatment to limit the risk of cardiovascular complications after kidney failure; Treat and limit complications after chronic kidney failure such as fluid retention, hyperkalemia, decreased protein...; Determine a reasonable diet according to the stage of kidney failure. Note to cases of end-stage chronic renal failure to choose the appropriate treatment: kidney transplant, peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis.
3. Treatment methods for chronic kidney failure
Currently there are many methods to support the treatment of chronic kidney failure, but the most commonly used in clinical practice are 3 methods:
Kidney transplant: Kidney transplant or kidney transplant, which is a process of transplanting a kidney. healthy for people with end-stage chronic kidney disease.
The kidney used for the transplant can be obtained from a living donor (with or without blood) or dead.
This method is indicated to apply to patients with end-stage renal failure when methods of peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis are not effective.
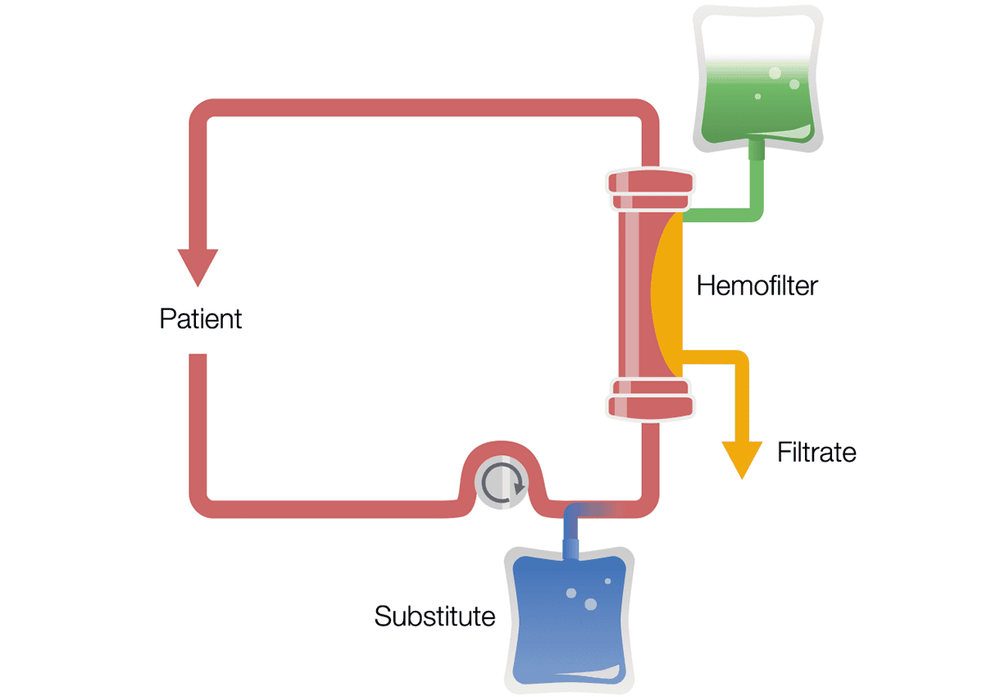
Hemodialysis: Hemodialysis is a treatment that filters blood outside the patient's body through a dialysis machine. Blood is drawn from the patient's bloodstream and passed through a synthetic dialysis device. At this point, the dialysis machine acts like an artificial kidney, the blood is cleaned and then returned to the patient's body.
Indications for hemodialysis in the following cases:
Patients with kidney failure have complications causing brain dysfunction; There are manifestations of hyperkalemia that do not respond to medical treatment; There are manifestations of acidosis that cannot be treated with medical therapy; Creatinine clearance decreased below 10ml/min/1.73m2 body. Hemodialysis is usually performed 3 times a week, each time for a minimum of 4 hours.
For hemodialysis to have the best effect, to ensure the filtering function, the patient needs a reasonable diet, rest, and activities.
Peritoneal dialysis: A method of dialysis that uses the body's natural filter instead of an artificial filter like in hemodialysis. The natural filter referred to here is the lining of the abdomen, also known as the peritoneum.
In the peritoneal dialysis procedure, 1-3 liters of dialysis fluid will be introduced into the peritoneal cavity including sugar, salt and some other substances. Here, toxins, products of metabolism in the body and water will be filtered and eliminated from the blood with tissues in the peritoneal cavity into the filtrate cavity based on diffusion and ultrafiltration by pressure. osmotic force with difference in concentration of solutes.
The dialysate is introduced into the abdomen through a catheter or a fixed tube. Here, the toxins in the blood are absorbed. After a while, this filtrate is discharged into a waste bag and replaced by a new filtrate. This insertion and discharge procedure can be performed in two different ways: either continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis (manual during the day), or automatic cyclic peritoneal dialysis (performed on a treadmill). automatically cyclically).
Indications for peritoneal dialysis in the following cases:
Acute renal failure with indications for acute dialysis with manifestations of increased blood urea, increased blood creatinine, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis and excess fluid; Difficulty choosing access route for hemodialysis catheter placement; Venous-arterial bridge occlusion; With chronic cardiovascular disease, the patient did not respond to emergency dialysis. Contraindicated peritoneal dialysis in the following cases:
Patients with infectious diseases or severe coagulopathy; Patient is pregnant; Patients who are obese, have a history of intestinal adhesions or fractures of the femur; The patient is on artificial ventilation. Chronic kidney failure, if detected early and treated promptly, using the right treatment method can limit the risk of complications occurring on other organs and at the same time prolong the life of the patient. patient.
However, in the late stages when kidney function is completely impaired and lost, complete recovery treatment is very difficult. At that time, it is necessary to apply supportive methods such as hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis. These methods will help ensure the body's reabsorption and elimination of toxins, thereby helping the body to be healthier and prolong life. In patients who are unable to perform these methods, the current indication is kidney transplantation.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.