This is an automatically translated article.
The most common type of head injury in children is a concussion after a fall. This type of injury can cause brain damage and even brain bleeding. Concussion may or may not include loss of consciousness. So what to do when a child has a concussion after a fall or a strong impact?1. Head Injury in Children
A head injury is any type of injury to the scalp, skull, brain, or other tissues and blood vessels of the head. Head trauma is also known as traumatic brain injury, depending on the extent of the injury. A head injury can be as mild as a bump, bruise, or a small cut on the scalp. Sometimes it can be a concussion, a deep cut, an open wound, a skull fracture, internal bleeding, or serious brain damage. Head trauma is one of the most common causes of disability and death in children.Types of head injuries in children include:
1.1 Concussion This is a type of head injury that can make a child's brain unable to function properly for a short period of time. Sometimes this can lead to loss of consciousness or a lack of alertness for a few minutes to a few hours. In many cases, there are so few concussions that they are so mild and brief that parents don't even know the trauma has happened to their child.
1.2 Cerebral Hematoma A cerebral hematoma, also known as a bruise on the brain, is a congestive condition that causes bleeding and swelling inside the brain around the area where the child's head was impacted by an external force.
In some cases, a seizure can occur on the opposite side of the head due to the brain hitting the skull. This injury can result from a direct blow to the head, severe shaking of the child, or trauma resulting from a motor vehicle accident. The impact of the brain on the side walls of the skull can tear the lining, tissues, and blood vessels inside the brain.
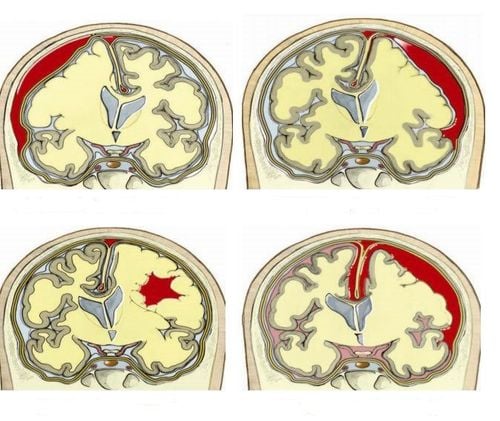
Tụ máu não hay còn gọi là vết bầm trên não là tình trạng xung huyết gây chảy máu và sưng bên trong não xung quanh khu vực mà đầu trẻ bị tác động bởi ngoại lực
Linear skull fracture: A fracture of the skull but the bones do not move or move. Children may be closely monitored in the hospital for short periods of time. Your baby can also return to normal in a few days without the need for medical intervention. Depressive skull fracture: With these fractures, part of the skull becomes indented where the bone is broken. This can happen with or without open wounds on the scalp. If the inside of the skull presses on the brain, this type of skull fracture needs surgery to realign it so it doesn't put pressure on the brain. Diastolic skull fractures: These are fractures that occur along the sutures in the skull. These are serrated lines between the plates of the skull and will merge as the child grows. Injuries to the brain can cause these serrations to split wider than they should. This type of cranial diastolic fracture can only occur in infants and young children. Basal skull fracture: This is a break in the bone at the base of the skull. Basal skull fractures can be a serious type of skull fracture. Children with this type of fracture often develop bruises around their eyes or bruises behind their ears. Fluid may also come out of your baby's nose or ears. This is because part of the cerebral cortex is torn. A child with a basilar skull fracture may need to be closely monitored in the hospital for an extended period of time, at least until the symptoms of the condition improve.
2. What is a concussion in a child?
A concussion occurs when a child experiences a blunt trauma to the head area. That is, an injury in which an impactor does not penetrate the skull causes a change in the normal functioning of the brain. An injury that can be caused by a strong blow, by a fall or even just some strong shaking can cause a concussion in a child's brain because the skull is not strong enough to withstand external forces.Children with a concussion may lose consciousness or have problems with vision, memory or balance. This may sound scary, but in most cases these effects are minor, temporary, and the child fully recovers afterward.
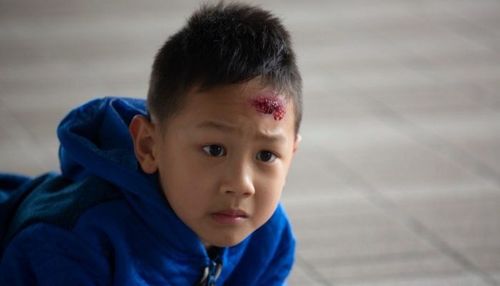
When a child falls and hits his head against the wall, he may or may not have a concussion. So how do parents or caregivers know if a child has a concussion? In the case of brain related problems, your baby may show one or several early symptoms including:
Loss of consciousness Drowsiness, daydreams Dizziness Confusion Vomiting Irritability, crying a lot Discharge from the nose, mouth, and ears, which may be clear or accompanied by blood. If your baby falls and hits his or her head against a wall or a sharp object and begins to breathe irregularly, convulses, or loses consciousness, call an ambulance immediately. Do not move the baby's body except in the case that if he continues to lie there, he will experience other injuries. Perform CPR immediately if the child shows signs of stopping breathing. In case the wound is open and bleeding, cover the wound with a clean cloth to stop the bleeding.
Khi trẻ bị ngã đập đầu vào tường có thể bị chấn động não hoặc không
3. When should parents call the doctor?
It is inevitable for babies to fall and hit their heads. However, if the child is unconscious, call an ambulance immediately. Sometimes, even a slight collision can cause serious brain damage.Parents should also take their child to the doctor immediately if the child falls and hits his or her head against a wall or other hard object and a day or two later the child has the following symptoms:
The child is vomiting continuously. Your child may feel nauseous and vomiting after a fall, but if it persists after that and doesn't stop, it could be a sign of serious brain damage. The child seems unusually sleepy during the day or cannot be awakened when he sleeps at night. Parents should try waking their child a few times the first night after a fall to make sure the baby can wake up normally. The child is physically weak or constantly confused, has problems with coordination, vision, or verbal communication.

Nếu sau ngã đập đầu trẻ nôn mửa liên tục, hãy đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ ngay
4. Can concussions cause permanent brain damage?
In rare cases, even minor concussions can cause permanent brain damage in a child. In addition, consecutive concussions, such as a second concussion that occurs before the symptoms of the first have ended, can be dangerous, causing brain damage or even death. So if a child's recent fall has shaken the brain to the point of unconsciousness, doctors will advise parents to monitor their baby more carefully for the next few days or even weeks.Head trauma is any type of injury to the scalp, skull, brain, or tissues and blood vessels near the head. A head injury that affects anything is called a concussion. The risk of concussion is higher and usually occurs during the spring or summer months when children are active and participate in many outdoor activities such as biking, rollerblading or skateboarding.... Children play sports. Sports such as football, basketball or volleyball also have a higher risk of concussion, so parents need to be very careful when allowing their children to participate in the above sports activities.
Children need to provide enough elemental zinc/day for them to eat well, reach the correct height and weight and exceed the standard. Zinc plays a role in affecting most biological processes taking place in the body, especially the breakdown of nucleic acids, proteins... Organs in the body when zinc deficiency can lead to a There are a number of diseases such as neurological disorders, irritability, etc. Therefore, parents need to learn about the role of zinc and guide them to appropriate zinc supplements for their children.
In addition to zinc, parents also need to supplement their children with other important vitamins and minerals such as lysine, chromium, B vitamins,... errands.
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.
Reference sources: babycenter.com, health.harvard.edu