This is an automatically translated article.
The pain of labor is a sign that announces the birth of a baby. Therefore, pregnant mothers pay special attention to the characteristics of labor pain and labor progress, to prepare in advance for what is about to happen to them.1. Characteristics of labor pain
The pain of childbirth comes from uterine contractions, causing contractions that are not controlled by the mother. Uterine contractions progressed rhythmically, sometimes at rest, but not completely, like contractions before labor. The intensity of contractions is not too strong to be dangerous for the fetus and mother, nor is it too weak.Uterine contractions are the driving force of labor, the rhythm of uterine contractions also varies with each stage of labor. Abnormal uterine contractions can prolong labor or cause complications for the mother and fetus.
Characteristics of uterine contractions:
Uterine contractions occur spontaneously against the mother's wishes. Uterine contractions cause pain. Pain threshold depends on each woman. When the contraction pressure reaches 25-30 mmHg, the woman begins to feel pain. The pain appears late, after uterine contractions, and disappears before the contractions cease. The origin of uterine contractions is located in one of the two horns of the uterus. Usually in the right horn of the uterus. The propagation of uterine contractions is also from top to bottom. The speed of contraction is 1-2cm/sec. Uterine contractions are cyclical and regular, gradually increasing, lengthening, at the beginning of labor only 15 to 20 seconds long, then reaching 30-40 seconds at the end of cervical dilation. The intensity of uterine contractions also gradually increased. Contraction pressure at the beginning of labor from 30-35 mmHg gradually increases to 50-55 mmHg. Uterine contractions have a decreasing nature: the pressure of uterine contractions decreases from top to bottom, the time of contraction of the uterine muscles also decreases from top to bottom Number of uterine contractions during a labor varies from 70 to 180, depending on number of births, easy or difficult labor and quality of uterine muscle.
2. Labor progress

Diễn biến cuộc chuyển dạ diễn ra như thế nào?
The average labor time in the child is from 16 to 20 hours. In humans, labor time is shorter, averaging 8-12 hours. Prolonged labor is labor that lasts longer than 24 hours.
Labor goes through 3 stages:
The first stage: the cervix dilates The second stage: begins when the baby is pushed out of the uterus, will go through the cervix, through the vagina and out The third stage: placental abruption. Each stage is an important milestone for the progress of a fetus about to be born. Early signs of labor are a mother's pregnancy process that has reached the day the baby is about to be born. Possible signs:
Lower abdominal pain: appears by sudden abdominal pain, regular abdominal pain, abdominal pain lasts about 15-20 seconds, then rests for 3-5 minutes , then the pain repeats. Abdominal pain is caused by uterine contractions. That is the official sign of entering labor, the abdominal pain then reappears and so on, the time after the abdominal pain is more and the rest time is shorter. Uterine contractions help the lower uterine segment to form well and the progress of the fetus to be favorable. Signs of pink vaginal discharge: During pregnancy, the cervix is always closed and sealed by a cervical mucus plug. It is the cervical mucus plug that is a solid barrier that prevents all agents from the vagina from entering the uterine cavity. When there is early labor, under the effect of uterine contractions, the mucus plug is released, mixed with little blood by the rupture of some of the capillaries on the cervix, creating pink mucus. Signs of amniotic fluid: This sign is completely sudden and usually occurs at night, when the mother is sleeping, there is a feeling of wet pants and a strong fishy smell of amniotic fluid. This is a symptom of premature rupture of membranes, a sign of early labor. Normally, the water breaks at the right time when the cervix is fully dilated 10 cm, the fetal head is low, under the effect of the uterus contracting the broken amniotic membrane to help the fetus out. Rarely does labor go without pain for the mother. However, labor pain during labor occurs in each mother is different, due to the perception and level of tolerance of each mother high or low. When the mother enters the real stage of labor, the pain of childbirth creates a feeling of high pain for mothers, some people have good tolerance, only a slight cry and whisper. But on the contrary, if the mother's tolerance is low, when the labor comes, they often scream, cry and panic.
All of the above phenomena are caused by labor pain, manifesting the contraction of the uterine muscles to form a strong contraction to help the fetus fall into the pelvis, and at the same time, it will help the fetus in the process of rotation and birth. out of the mother's pelvis to be born. When uterine contractions occur, the pelvic nerves are constricted, which creates pain for the mother every time uterine contractions occur.
2.2 Changes on the part of the mother and fetus during labor
Tầng sinh môn trước của mẹ phồng to lên, vùng hậu môn - âm hộ dài ra gấp đôi
The time of cervical dilation takes place irregularly. In the first stage (Ia) from the time the cervix is cleared to the time it is 4cm dilated, it takes 8-10 hours. The later stage (Ib) time from 4cm to full opening is about 4-6 hours, the average opening speed is 1cm/1 hour. Cervical dilation is fast or slow depending on the following factors: the amniotic sac is more or less pressing against the cervix, the condition of the cervix is thick and hard, and old fibrous scars. Are uterine contractions synchronous and strong enough? Differences between schizophrenia and schizophrenia in cervical dilation. In humans, the cervix is completely erased and then dilated, and the lower uterine segment is established in the last months of pregnancy. In humans, the cervix is both dilated and dilated, and the lower uterine segment is only established at the beginning of labor. Cervical dilation time in humans is faster than in children. Lower segment is established: the lower uterine segment is established due to the dilation, elongation and enlargement of the uterine isthmus. From 0.5-1 cm, when the lower segment is fully established up to 10cm high.
Changes in the perineum: Due to the pressure of uterine contractions, the fetus descends into the pelvis. The pressure of the fetal position pushes the coccyx process backward, the diameter of the coccygeal process changes from 9.5cm to 11cm, equal to the diameter of the sacral process. Resistance of the muscles on the posterior perineal side pushes the fetal position forward.
Change in the perineum: The anterior perineum swells, the anal - vulva area doubles (from 3-4cm to 12-15cm). Due to the effect of uterine contractions and contractions of the abdominal wall, the posterior perineum is stretched by the fetal position, and the anal opening widens and erases all wrinkles. The syllable expands, changes direction gradually to horizontal. Progression of the fetal position often causes incontinence, and if there is still stool in the rectum, stool will exit the anus when the fetal position is low in the pelvis.
2.2.2 Changes in the fetal position When the lower segment is established, the fetal position also gradually descends to the lower segment, making the fetal position close to the cervix, creating favorable conditions for opening the cervix. bow. During labor, the fetus has some mold bending phenomenon.
Skull overlap phenomenon : The overlapping bones make the fetal skull reduce in size. The two parietal bones overlap, the occipital bone and the frontal bone descending below the parietal bone. The two frontal bones can also overlap.
Establishment of serous tumor : is the presence of edema seepage of the serum under the skin, sometimes very large. The location of serous tumours is usually located in the lowest part of the fetus, in the middle of the opening of the cervix. Serous tumors appear only after the rupture of membranes. Each fetal position usually has its own location of serous tumor.
2.2.3 Changes in the appendages of pregnancy Uterine contractions cause the placental membrane at the lower pole of the cervix opening to fall off, the amniotic fluid accumulates to form the amniotic sac or amniotic sac
Effect of the amniotic head:
Helps to clear and open the cervix during labor due to the amniotic fluid pressing on the cervix Protects the fetus from external trauma Avoids the risk of infection going upstream from the vagina into the amniotic cavity Forms of ruptured membranes:
Timely rupture of membranes is the rupture of membranes when the cervix is fully dilated Premature water breaks are the rupture of membranes that occur when the cervix is not fully dilated but labor is already in place Placental abruption and placental abruption: after pregnancy, uterine contractions continue to appear after a period of physiological rest, causing the placenta and placental membranes to peel off, descending into the mother's genital tract and passing out. Uterine contraction causes physiological embolism to form a safe mass to stop bleeding after placental abruption.

Sự tiến triển của ngôi thai thường gây đái són và nếu trực tràng còn phân thì phân sẽ thoát ra ngoài hậu môn
Respiratory changes: during uterine contractions there is hyperventilation leading to respiratory alkalosis. During delivery, pushing increases PCO2, and hyperventilation adds to metabolic acidosis. Changes in hemodynamics: the mother's supine position, the uterus is often tilted to the right, so the abdominal vena cava is compressed, reducing placental circulation leading to fetal distress. Putting the pregnant woman on her left side will eliminate this bad effect. Strong uterine contractions or strenuous labor will compress the abdominal aorta, leading to decreased placental circulation and fetal distress. A decrease in arterial blood pressure due to vasodilation or from vasomotor paralysis due to perispinal anesthesia can also lead to fetal distress. Maternal bleeding during labor reduces the volume of circulation and is accompanied by vasoconstriction, which also causes fetal distress. Changes in metabolism: maternal body weight decreased from 4-6 kg after delivery, including fetal weight, placenta, amniotic fluid, blood and secretions from skin, lungs, kidneys. Blood sugar also decreased due to increased consumption. The strained muscles during uterine contractions and labor can lead to acidosis, which can be transferred to the baby. The white blood cell count is also increased during labor. Anxiety and pain: during labor, increased secretion of cortisol and cathecholamines is caused by uterine contractions pain and anxiety, leading to vasoconstriction that aggravates acidosis. lactic. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce pain and calm the mind to reduce anxiety for pregnant women. On the fetal side
At this time, the fetus also has changes in response to the mother's change, the fetal heart changes during uterine contractions. The fetal heart rate accelerates slightly during uterine contractions, then slows down during uterine contractions. In addition to uterine contractions, the fetal heart gradually returns to normal
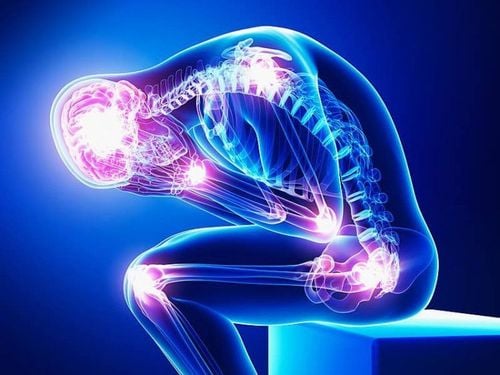
In short, the pain of labor and the course of labor causes the mother to suffer from pain. The severity of labor was compared with 20 broken ribs at the same time. Currently, medicine has made great progress, in parallel with the outstanding development of the anesthesiology and obstetrics industry. The application of anesthetics acting on the pelvic nerve to cut off labor pain has brought great results for mothers in labor with labor pain.
Mức độ đau đẻ được so sánh với gãy 20 cái xương sườn cùng lúc
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.