This is an automatically translated article.
Common treatments for cervical cancer include surgery, or a combination of chemotherapy and radiation, or surgery with radiation. When cervical cancer has spread beyond the cervix, targeted treatments may also be used. So, what factors will doctors rely on to determine which method is appropriate for each patient?
1. What is cervical cancer?
Cancer is a disease of cells and cells are the basic building blocks of the body. The body is constantly making new cells to help us grow, replace worn out tissue, and heal damage. Normally, cells multiply and die in an orderly fashion.Sometimes cells do not grow, divide and die in the normal way. This can cause the blood or lymph fluid in the body to become abnormal, or form a mass called a tumor. A tumor can be benign or malignant.
Benign tumor : the cells are limited to one area and are unlikely to spread to other parts of the body. This is not cancer. Malignant tumors: are made up of cancer cells, capable of spreading by traveling through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system (lymphatic fluid). The cervix is part of the female reproductive system, which also includes the fallopian tubes, uterus (womb), ovaries, vagina, and vulva (external genitals). The cervix, which connects the uterus to the vagina. It has an outer surface that opens into the vagina and an inner surface that points into the uterus.
Ung thư cổ tử cung là một trong những bệnh ung thư phổ biến nhất ở phụ nữ
Moisturises to lubricate the vagina, keeping it healthy Open to allow menstrual blood to flow from the uterus into the vagina Produces mucus that helps sperm travel to the tubes fallopian tube to fertilize an egg that has been released from the ovary Holds the developing baby in the uterus during pregnancy by closing it, then opening it to allow the baby to be born vaginally The cervix has a smooth surface The outer surface opens into the vagina (ectocervix) and the inner surface forms the cervical canal (hormonal). These two surfaces are covered by two types of cells: squamous and glandular.
Cervical cancer begins when abnormal cells in the lining of the cervix grow out of control.
Cancer usually starts in an area of the cervix called the transition zone, but it can spread to tissues around the cervix, such as the vagina or to other parts of the cervix. body, such as lymph nodes, lungs, or liver.
There are two main types of cervical cancer, named after the cells they start in:
squamous cell carcinoma. The most common type of cervical cancer, squamous cell cancer (often abbreviated as SCC) begins in the squamous cells of the cervix. This disease accounts for about seven out of ten or 70% of cases of cervical cancer. Adenocarcinoma (Adenocarcinoma). Adenocarcinoma is the less common type, accounting for about one in four cases or 25%. The disease begins in the glandular cells of the cervix. Adenocarcinoma is more difficult to diagnose because it occurs in the upper part of the cervix and the abnormal gland cells are harder to detect. Other, more rare cancers that can start in the cervix include small cell carcinoma and cervical sarcoma.

Ung thư thường bắt đầu ở khu vực cổ tử cung và có thể lây lan đến các mô xung quanh
2. Factors to consider before deciding on a treatment method
Because cancer treatments are often complex, hospitals use multidisciplinary health care teams (MDTs) to treat cervical cancer and tailor treatment to each individual.
MDT consists of a number of experts from different fields who will work together to make decisions about the best way to proceed with the patient's treatment. The cancer treatment team will recommend what treatments they consider the best treatment options, but the final decision will be yours.
In general, there are 4 main factors for this treatment team to develop a treatment plan for the patient:
Results of tests and diagnostic techniques The location of the cancer and whether it has spread Age and overall health of the patient Whether he or she wants to have children in the future In most cases, the treatment regimens will be:
For early cervical cancer, a neckectomy uterine cancer with part or all of the uterus, radiation therapy, or a combination of both For advanced cervical cancer, you will need radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy, and sometimes surgery also used Cervical cancer is often curable if diagnosed at an early stage. When cervical cancer cannot be cured, it is often possible to slow the progression of the disease, prolong life, and relieve any symptoms caused by the disease, such as pain and vaginal bleeding. This is called palliative care.

Ung thư cổ tử cung thường có thể chữa khỏi nếu được phát hiện và điều trị ở giai đoạn đầu
3. Can cervical cancer give birth?
When finding out that you have cervical cancer, many patients will have to think a lot, including what stage the cancer is in, how to treat it, how to overcome it and how the disease will affect it. for the patient's future. For those who are young or have not yet or have not had the desired number of children, there may be questions about how cancer will affect their fertility, and when to try. pregnancy and what you can do to maintain fertility.
The answer depends on a number of factors, including the stage of the cancer and the type of treatment used.
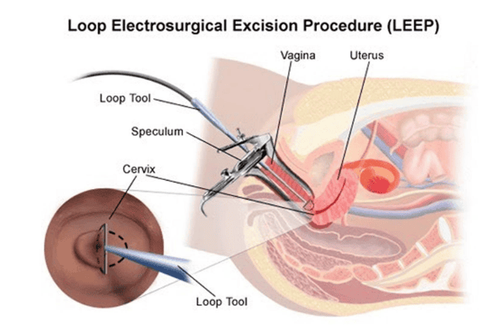
Conization If the cancer is limited to small growths in the cervix, the patient can be treated with a cone of the cervix.
First, the patient will be anesthetized during the procedure. The doctor then uses a scalpel to remove a cone-shaped area of your cervix, including cancerous tissue and some surrounding healthy tissue. This is to make sure there are no cancer cells left. The sick person should be able to go home later that day.
This treatment will help the patient get pregnant later. You may need to wait 6-12 months before trying to conceive. But there is a chance that you will have a higher risk of miscarriage or infertility. This is due to the potential changes and scarring in the cervix following this treatment.
Radical trachelectomy (removal of the cervix, upper part of the vagina, keeping the uterus) If the patient has a small tumor and is in the early stages of cervical cancer, the doctor may prescribe a treatment method. this value. This method removes most or all of the cervix, more so than a cone. This "radical" version can also remove some of the surrounding tissue, some of the upper part of the vagina, and nearby lymph nodes. As with conception, patients should wait 6 to 12 months to conceive after using this method. After that time, it is very likely that the patient will successfully conceive and carry a full-term pregnancy. The patient's chance of having a full-term pregnancy is 70%. However, pregnancy is still considered high risk and you will need to deliver your baby by cesarean section.

Bác sĩ có thể chỉ định tiến hành cắt bỏ cổ tử cung nếu khối u còn nhỏ
Freezing eggs or embryos If your doctor prescribes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a hysterectomy, you may want to consider freezing your eggs before these treatments. Some chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy can destroy eggs or damage your uterus, and hysterectomy is surgery to remove the cervix and uterus.
Egg freezing can allow you to conceive through IVF or other techniques and get pregnant (if you still have a uterus) or perform surrogacy.
Due to side effects, patients should avoid becoming pregnant during chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Doctors recommend that patients usually wait at least 6 months after finishing their last courses of treatment before trying to conceive.
In order to further improve the quality of diagnosis and treatment, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied the ThinPrep Pap Test for early detection of cervical cancer, this new method is currently being widely used in Vietnam. America, Europe. ThinPrep Pap Test has made a breakthrough compared to the traditional Pap smear method, through membrane controlled cell transfer technology, which increases the sensitivity and specificity in detecting precancerous cells. , especially adenocarcinoma cells, a type of cancer cell that is difficult to detect.
At Vinmec, the application of modern methods and procedures to ensure sterility helps to achieve the most accurate results. Screening results are returned to your home with specific advice and recommendations for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
The article references the source: cancervic.org.au, webmd.com