This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the most common upper gastrointestinal (GI) disorder in the United States, defined as symptoms or damage caused by the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus. esophagus.
1. Anti-acids (PPIs) for reflux esophagitis
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), after activating acids to sulfonamides, covalently bind to cysteine residues on the luminous surface of proton pump H + / K + ATPase in pariocytes, blocking ion transport and acid secretion. Chemically, all PPIs are composed of a benzimidazole ring and a pyridine ring but differ in side ring substitutions. Although PPIs are currently the most effective treatment for GERD and its complications, up to 40% of patients with non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) remain symptomatic under standard treatment, and Approximately 10-15% of patients with erosive esophagitis (EE) do not have complete remission after 8 weeks of treatment.
Patients who continue to have symptoms despite PPI therapy are considered to have refractory GERD, usually defined as the persistence of typical symptoms unresponsive to stable, twice-daily doses of PPIs. every day for at least 12 weeks of treatment. Up to 30% of GERD patients have treatment-resistant GERD.

2. Potential causes of PPI treatment failure
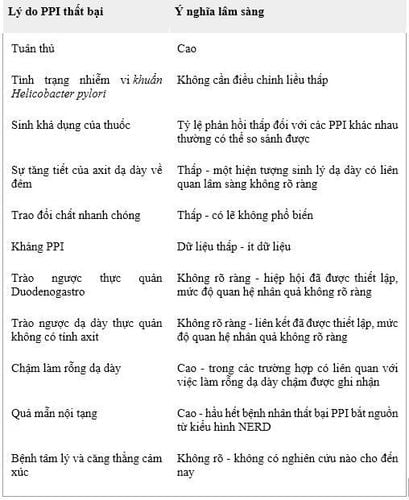
Several factors have been recognized that may contribute to the continuation of GERD symptoms despite PPI treatment. Some are clinically important, while others appear to be relatively uncommon and have only limited clinical value (Table 1). In addition, it is not uncommon that multiple causes of PPI failure can be recognized in a small subset of patients. It should also be emphasized that several proposed underlying mechanisms have demonstrated an association with PPI failure but the extent of causality and the true nature of the relationship are unknown.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Invite readers to refer to the following sections:
Causes of failure of antacids (PPIs) with reflux esophagitis (Part 1) Causes of failure of antacids (PPIs) with inflammatory bowel disease Reflux esophagitis (Part 2) Causes of failure of antacids (PPIs) with reflux esophagitis (Part 3) Causes of failure of antacids (PPIs) with reflux esophagitis (Part 3) Part 4)