This is an automatically translated article.
Atbet pneumonitis (asbestos) is a form of interstitial lung fibrosis, caused by exposure to asbestos dust. Diagnosis is based on history and chest x-ray or chest CT. Treatment is supportive. So is pneumococcal disease dangerous? The following article will give you information about this disease.
1. What is atbet (asbestos) dust?
Asbestos pneumonitis is pulmonary fibrosis, with or without pulmonary fibrosis and the formation of particles such as silicon granules. Atbet pneumoconiosis and silicosis are two completely different diseases, caused by breathing in atbet dust or asbestos dust. The fibrous lesions in this pathology do not form granules on X-ray and GPBL images as in silicosis.
2. Causes and risk factors of pneumoconiosis atbet
Due to occupations in the environment that have to be exposed to asbestos such as mining, or the manufacture of certain products whose raw materials are asbestos.
Asbestos mining and industry can also disperse asbestos dust over long distances, polluting the environment and therefore people living in polluted environments are at high risk of Atbet pneumoconiosis.
Do some of the following occupations that may expose you to asbestos and get sick:
Producing construction materials for asbestos roofing. Drilling, smashing, mining ore or rock containing asbestos. Crushing, crushing, sieving and dry handling of asbestos ores or rocks. Combing, spinning and weaving of asbestos fabrics; insulation with asbestos. Dismantling construction works using asbestos. Making furniture in the asbestos-cement manufacturing industry; manufacturing all kinds of auto brake pads parts, paperboard with asbestos...

Hình ảnh thực tế của amiăng
3. Symptoms of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos)
The disease usually appears after a long time of exposure (from 10 to 20 years). The clinical symptoms ranged from difficult to recognize to easy to recognize based on the degree of pulmonary fibrosis. Common symptoms that can be seen are:
Shortness of breath: This is the most basic sign, the patient at first only feels short of breath with exertion, later on, continuous shortness of breath. Chest tightness, cough, sputum production: this symptom appears earlier like chronic bronchitis. Auscultation: A reduced or coarse alveolar murmur is heard, with or without crackles at the base of the lung. However, this sign is not typical. When the lung has fibrosis, the vital capacity of the lung, or the total capacity of the lung, is reduced to varying degrees. In practice, clinical signs cannot be relied on to identify this pathology, because clinical signs are often atypical, and appear late. The correct diagnosis should be based on occupational, clinical and laboratory exposure factors.
4. Diagnosis of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos)
Diagnosis of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos) is based on the following factors:
History of exposure. Clinical symptoms. X-ray, HRCT. Computed tomography (CT Scan), an X-ray of the lungs, can help doctors see the shape and damage caused by the disease. Pulmonary ventilation measurement. Identification of fibers/asbestos in sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid or lung biopsy fragments
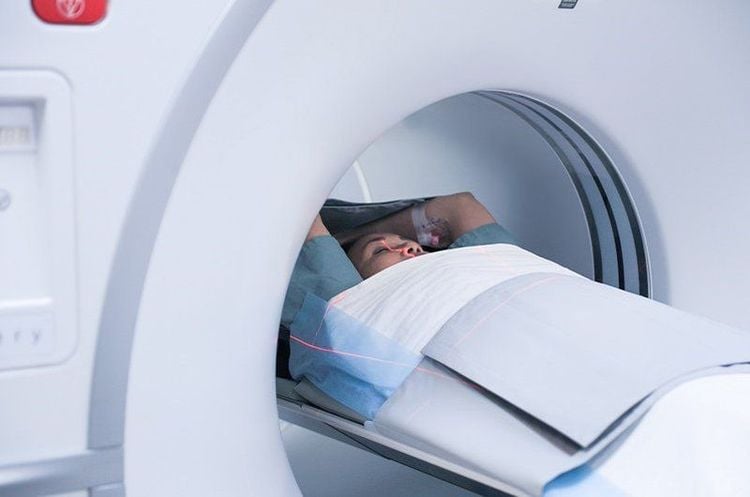
Chụp cắt lớp vi tính (CT Scan) giúp chẩn đoán bệnh bụi phổi atbet (amiăng)
5. Possible complications of pneumococcal disease
The disease usually progresses slowly, the pulmonary fibrosis and pleural lesions are permanent and irreversible and tend to develop with exposure time.
If not detected early and treated promptly, the disease can cause dangerous complications:
Chronic heart failure: Due to diffuse pulmonary fibrosis leading to right heart failure. Bronchitis and emphysema: Also common in patients with pulmonary fibrosis due to asbestos dust. Bronchiectasis due to contraction of fibrous tissue. Lung cancer: There is an association between people with asbestosis and lung cancer. In workers with this disease, the rate of lung cancer increases.
6. Treatment of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos)
There is no specific treatment.
Treatment is mainly symptomatic, there is no treatment to stop or slow down the development of the disease.
Prophylaxis by labor protection is key:
Stop smoking. Early detection. Prevention of influenza and pneumococcal infections and timely treatment of bacterial infections.

Kiểm tra sức khỏe định kỳ hoặc khi có dấu hiệu bất thường, giúp phát hiện sớm và điều trị kịp thời bệnh bụi phổi atbet (amiăng)
7. Prevention of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos)
7.1. Lifestyle habits that can help you limit the progression of atbet pneumonitis (asbestos) Follow your doctor's instructions for treatment. Regular check-ups to monitor health status and disease progression. Maintain an active lifestyle and limit stress. Contact your doctor immediately when there are body abnormalities during treatment. 7.2. Effective disease prevention method Replace asbestos raw materials with other materials. Prevent dust formation at the place of production, use and exploitation. Performed in a closed cycle, not to disperse dust into the surrounding environment. Ventilate regularly, humidify the air, the floor Wear a mask or mask when working to prevent dust from entering through the respiratory tract. Wear protective clothing, change clothes when leaving. Monitor environmental sanitation closely and regularly Organize annual health check-ups to detect people in poor health to change jobs. suspected sick people must be isolated, treated or transferred.
Periodic health check-ups help to detect diseases early, so that there are treatment plans for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy.
Results of the patient's examination will be returned to the home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.