This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Nguyen Van Anh - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.And Master, Doctor Le Hong Chien - Doctor of Diagnostic Imaging - Intervention - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging and interventional radiology (endovascular intervention and extravascular intervention).
Salivary gland ultrasound is the first diagnostic tool, although it is simple, it is effective in diagnosing and distinguishing parotid salivary gland inflammation from other diseases.
1. What is parotid salivary gland disease?
The salivary gland system around the oral cavity has many important functions for the body such as: helping to digest food and regulating the oral environment, helping with excretion and preventing fermentation. In particular, in saliva, there are enzymes such as lysozyme, bacteriolyzyme that help fight inflammation by inhibiting the growth of staphylococcus, meningococcal, Salmonella bacilli and other intestinal bacteria.Parotid salivary gland inflammation is a disease that can appear at any age, especially common in winter and spring when the weather changes suddenly. Parotid gland inflammation is divided into two types and acute and chronic gland inflammation. In acute parotid gland inflammation is divided into acute serous gland inflammation (also known as mumps) and acute nonspecific glandular inflammation. Common clinical symptoms of the disease are swelling of the parotid salivary glands, swelling spreading around, the skin in the swollen gland is red and painful. It is very painful for the patient to speak and swallow. In general, patients often have fever, nausea, and fatigue.
Mumps virus: Mumps is a disease caused by the Paramyxoviridae virus. This is a systemic disease but manifests locally in the parotid gland. After being exposed to mumps virus 14-24 days, the patient has discomfort, poor appetite, fever, sore throat, pain under the jaw. After that, the parotid gland gradually enlarged in 3 days and then gradually decreased in about 1 week. The parotid gland may be enlarged on one or both sides. Mumps can cause many serious complications such as ovarian inflammation, orchitis, meningitis, pneumonia, polyarthritis,... Parotid inflammation caused by mumps accounts for 24% of all causes. Causes of parotid salivary gland inflammation Bacteria such as Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Parainfluenza, Coxsackie,.... Inflammation of the salivary glands caused by bacteria usually occurs after oral infections, temporomandibular joint diseases. , otitis media,... The disease usually only causes lesions in the salivary glands and has a benign course, most of which resolves spontaneously, but there are a few cases where it turns to chronic inflammation of the gland. Because the patient is allergic to some drugs such as antidepressants, chemotherapy drugs, antihistamines,... In addition, some other causes such as: the patient has systemic diseases that cause depression Physical exhaustion affects the function of the salivary glands, inflammation of the salivary glands after surgery,...
2. Can ultrasound diagnose parotid inflammation?
Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands is a common disease that can cause many serious health complications and can be contagious. Therefore, early detection and diagnosis of diseases for timely treatment play a very important role in protecting the health of themselves and the community. Many imaging modalities can be used to diagnose parotid gland inflammation, in which salivary ultrasound is the first diagnostic tool, playing an important role in definite diagnosis as well as differential diagnosis. parotid salivary gland inflammation with other pathologies.The doctor will do an ultrasound of the entire neck to detect combined lesions. In terms of facilities, use an ultrasound machine with a linear transducer with a high frequency of 9-15MHz. Patients with salivary ultrasound do not need to prepare in advance as in endoscopic or abdominal ultrasound. To perform a parotid ultrasound, the doctor will instruct the patient to lie on their back with a pillow under their shoulders. Then, the doctor applies ultrasound gel to the transducer and uses the probe to survey around the nasopharynx along the salivary glands. Parotid ultrasound is a very simple, safe, and painless method for the patient.
3. Common images in salivary gland ultrasound
3.1. Ultrasound image of acute parotid salivary gland inflammation
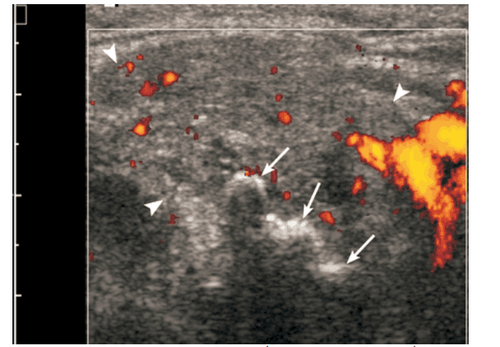
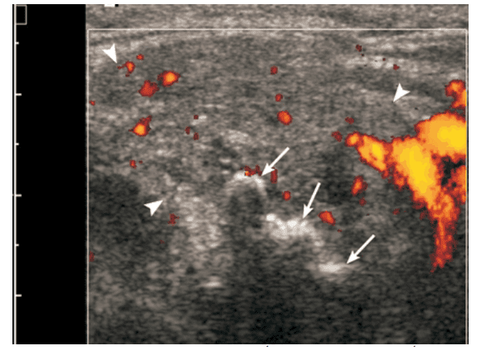
When salivary gland inflammation is acute, the ultrasound image is that the salivary glands are often enlarged and hypoechoic, the hypoechoic structure may be heterogeneous, and many small oval hypoechoic areas may appear. Image of enlarged lymph nodes with increased central flow, angiogenesis in the glandular parenchyma.3.2. Ultrasound image of chronic inflammation of the parotid salivary glands
The clinical feature of chronic parotitis is that the parotid gland swells repeatedly, causing pain. The sonographic image is normal or reduced salivary gland size, hypoechoic, heterogeneous, often without increased vascular flow on color Doppler ultrasound.
3.3. Ultrasound image of salivary gland abscess
Acute parotid gland inflammation can form an abscess. Salivary gland abscess presents with painful swelling of the salivary gland with redness of the skin, but it is difficult to detect on clinical examination. On ultrasound, the characteristic feature of a salivary gland abscess is a hypoechoic lesion or an echogenic drum with posterior echogenicity, with indistinct margins. The dots are hyperechoic due to small air bubbles visible inside the abscess. Central volvulus can be recognized as an avascular region or as mobile deposits. Organized abscesses may have a surrounding hyperechoic halo.The early detection and diagnosis and treatment of parotid gland inflammation contribute to improving the quality of life of individuals and communities. Ultrasound diagnosis of parotitis is a first-line method, simple and easy to perform at all medical facilities, including Vinmec International General Hospital to diagnose salivary gland inflammation, contributes to early diagnosis and treatment of disease, preventing possible complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.