This is an automatically translated article.
Transverse myelitis is a disease that occurs in the nerve fibers causing the loss of nerve transmission from the spinal cord to organs throughout the body. So can transverse myelitis be cured?1. What is transverse myelitis?
Transverse myelitis is inflammation that occurs on both sides of a segment of the spinal cord and results in damage to the myelin sheath that covers nerve fibers. This disease has the ability to disrupt nerve signals from the spinal cord sent throughout the body, causing patients to experience pain, numbness, muscle weakness, sensory functions or bladder and bowel problems. subject.
Symptoms of transverse myelitis are often confused with neurological conditions such as spinal infarction and need to be differentiated from each other because each disease has a different treatment regimen.

Liệt chân hai chân do viêm tủy cắt ngang
2. Causes of transverse myelitis
The cause of transverse myelitis is still unknown and sometimes the exact cause cannot be determined. Some of the reasons explained are viral, bacterial or fungal infections. In most cases, the disease appears after an episode of infection.
Some viruses are associated with cross-sectional myelitis such as:
Herpes simplex virus capable of causing chickenpox and shingles measles and rubella Some diseases are associated with bacteria such as:
Lyme disease Syphilis Tuberculosis Actinomyces Pertussis Tetanus Diphtheria In addition some bacterial skin infections, gastroenteritis or pneumonia are also present can lead to transverse myelitis. It is very rare for fungal and parasitic infections to infect the spinal cord.
Several inflammatory diseases can also lead to transverse myelitis such as:
Multiple sclerosis: A disease related to the destruction of the nerves surrounding myelin in the spinal cord and brain. Multiple sclerosis is characterized by transverse myelitis as the first sign, and these manifestations occur only on one side of the body. This is a condition caused by the immune system destroying the nerves that surround myelin in the spinal cord and brain.
Myelitis - optic nerve This disease is also known as Neuromyelitis optica or Devic's disease. This is an inflammatory condition that destroys the myelin sheath surrounding the spinal cord and optic nerve, and affects both sides of the body.
In addition to symptoms of transverse myelitis, patients may present with optic nerve damage such as eye pain or temporary loss of vision. This may occur at the same time or separately from the disease symptoms. In addition, it is possible that the patient does not experience ocular symptoms but only has recurrent transverse myelitis.
Autoimmune diseases Several autoimmune diseases can be involved, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or Sjogren's syndrome, causing severe dry mouth and eyes.
Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a disease that causes inflammation to many parts of the body including the spinal cord and optic nerve. Symptoms may resemble neuritis but typical symptoms of sarcoidosis develop more slowly. The etiology of sarcoidosis is still unknown.
Bệnh sarcoidosis có thể dẫn đến viêm tủy cắt ngang
3. What are the symptoms of transverse myelitis?
Symptoms of transverse myelitis may occur within hours to days or may progress insidiously for weeks.
The disease usually affects below the affected area of the spinal cord. However, there are still some cases of lying on only one side of the body.
Typical symptoms of the disease include:
Pain: The pain of transverse myelitis usually occurs suddenly in the lower back, then the pain radiates down your legs, arms or around your chest and abdomen. Other pain sites depend on the area of the spinal cord affected. Sensory disturbances: Patients may experience tingling, burning, or numbness. Sometimes mild sensitivity to skin, clothing, temperature too hot or too cold. Weak movement of limbs: Some people find their limbs heavier than usual, prone to tripping or in many cases severe weakness causing total paralysis. Bladder and bowel disturbances: Frequent urination, urinary incontinence, painful urination or constipation. Patients with transverse myelitis usually only experience one episode of the disease, but complications can persist, including:
Pain: This is a long-term sequelae of patients with this disorder. Muscle spasticity: Common in the legs and buttocks with painful tightening manifestations. Total or partial paralysis of the arm. Sexual dysfunction: In men, erectile dysfunction or difficulty reaching orgasm in both men and women.
4. Means of diagnosing transverse myelitis
To diagnose transverse myelitis , the doctor will conduct an examination based on the medical history, symptoms and perform laboratory tests.
Laboratory tests to diagnose transverse myelitis and rule out other disorders include:
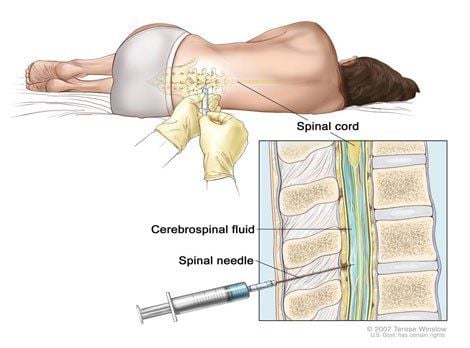
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This is a test that helps to indicate inflammation of the spinal cord and also detects inflammation of the spinal cord. other potential causes of the disease. Often there may be abnormalities in the blood vessels or spinal cord. Lumbar puncture: The doctor will use a specialized needle to draw out a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid, which is the protective fluid around the spinal cord and brain. In patients with cross-sectional myelitis, a CSF examination may reveal abnormally high levels of white blood cells or proteins that signal inflammation.
5. Can transverse myelitis be cured?
Treatment of transverse myelitis includes medical treatment and rehabilitation therapy. Prognosis is usually partially reversible, but in severe cases can lead to lifelong disability.
5.1. Medical Treatment Intravenous Steroids: Steroids given intravenously in the arm over several days can help reduce inflammation of the spine. Plasma exchange: Used in patients unresponsive to intravenous steroid therapy. This means that the plasma in the patient's blood will be filtered and replaced to improve symptoms and remove inflammatory antibodies. Antiviral drugs: For patients with viral transverse myelitis, this therapy may provide some relief of symptoms. Analgesics: Pain is a typical and common symptom of transverse myelitis. Patients may be prescribed common pain relievers such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen sodium. Medicines to treat other complications caused by the disease, such as muscle spasticity, urinary tract dysfunction, or depression. Medicines to prevent recurrent episodes of transverse myelitis such as corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressants to reduce the risk of developing transverse myelitis or developing optic neuritis.
Thuốc corticosteroid có tác dụng ngăn ngừa những đợt tái phát của viêm tủy cắt ngang
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: suckhoedoisong.vn, msdmanuals.com, youmed.com