This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
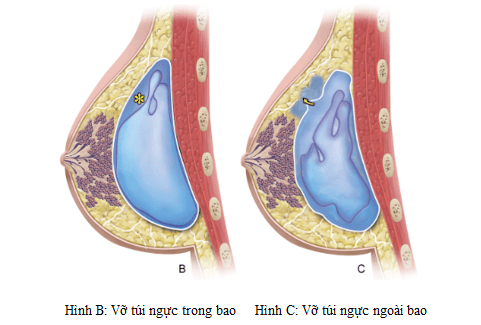
Breast implant rupture is a recognized complication of implant placement. It can be an internal or an external rupture. Intracapsular rupture occurs when the sheath of the breast implant (inner capsule) is broken but the capsule formed by the breast remains intact and the silicone does not escape freely. Extracapsular rupture is when the inner capsule breaks and the outer capsule is damaged, resulting in free silicone escaping.
1. Overview
Breast implant (breast implant) is a synthetic material used to change the size, shape, and contour of the breast. The breast implant is composed of an elastic silicone shell, inside containing an aqueous solution. salt or silicone gel. After implant placement, the body's response will form a thin fibrous capsule around the breast implant, completely enclosing the elastic shell of the breast implant. An elastic silicone sheath forms the internal capsule and the outer fibrous capsule forms the external capsule.
Intracapsular implant rupture has not yet altered the contour of the breast implant, making it difficult for clinical examination or mammography and is best seen on mammograms. Extracapsular rupture can lead to changes in the contour of the breast implant and can be detected on physical examination or mammography.
Intracapsular rupture is more common, accounting for about 85% of cases, and extracapsular rupture in about 15%.

2. Causes and symptoms of breast implant rupture
Causes of breast implant rupture can be due to normal aging of the breast implant, trauma, needle puncture during biopsy or other factors.
When a saline breast implant ruptures or its valve fails, saline leaks out very quickly often for a few days and the breast appears to be slightly deflated, so you know right away that it has ruptured. Salt water is absorbed by the body.
When a silicone implant is broken, the gel comes out more slowly because it is denser, so it may take longer for you to realize that the implant has broken or you may not realize it at all.
Liquid silicone gel breast implants made in the United States before 1992 are more likely to leak out of the sheath of the surrounding fibrous tissue if rupture occurs. Liquid silicone gel can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes or lungs. Your body may react to the silicone by forming more scar tissue, which can cause discomfort or cause your breasts to look distorted. In relatively rare cases, lumps called silicone granulomas can form in the arms, armpits, chest area, or elsewhere on the body.
Beginning in 2006, silicone breast implants made in the United States have had thicker shells and thicker gels. If these implants rupture, they tend to have a shell tear (also known as a “gel fracture”), which can affect the shape and appearance of the implants.
Signs that your silicone breast implant has ruptured can include changes in breast shape and size, and increased tenderness, firmness, and swelling over a period of several weeks. Breast implant rupture can also cause capsular contracture. A silicone implant rupture without causing any noticeable symptoms is known as a “silent rupture”.
3. When to screen for breast implant rupture?
FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) recommends that women with silicone breast implants be screened for breast MRI for "silent rupture" 3 years after the first implant surgery and 2 years once after that.
If at any time you think your implant may have ruptured, have your plastic surgeon check it out. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, can help determine if a breast implant is leaking. MRI is considered the most accurate method for this purpose.
Diagnostic Imaging
Mammography : Normal breast implants on mammography: oval, regular, very contrast-enhanced. The detection of breast implant rupture (especially silicone gel implant rupture) is difficult on mammography. Detecting ruptured silicone breast implants within the capsule is virtually impossible on mammography. However, mammography is very useful in detecting damage to the breast tissue around the implant.
It should be noted that breast implant mammography is different from conventional mammography, the mammogram technician will gently push the implant back into your chest wall and pull your breast tissue. You are forward to the scan showing as much breast tissue as possible so in the event you have implants please inform the mammogram technician before the scan.
Ultrasound : Ultrasound may show a “blizzard” sign of capsular rupture due to silicone escape from the sheath of the breast implant into the mammary gland tissue or a “ladder” sign of rupture in a capsule (normal breasts will not be echogenic on ultrasound). Ultrasound generally has poor sensitivity and specificity in the evaluation of breast implant rupture with sensitivity and specificity ranging between
59-85% and
55-79%
Mammal resonance imaging (MRI), respectively. breast) : Considered the most sensitive method for detecting breast implant rupture. To evaluate only for breast implant rupture, an MRI without contrast is usually required.
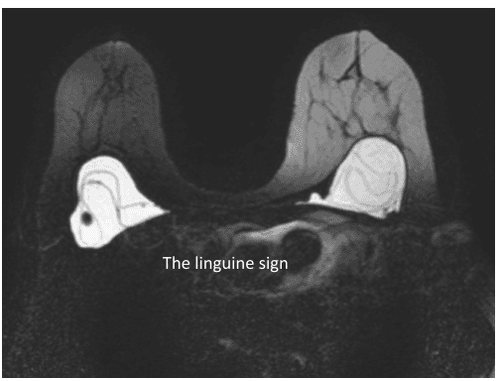
+ In intra-capsular rupture, the material inside the implant is covered by fibrous scarring, while the silicone sheath of the implant is flattened. When slightly deflated, it will manifest as a line parallel to the contour of the breast capsule, known as the “subcapsular line” sign. When it deflates significantly, it appears as a group of wavy lines, known as the “linguine sign”. Other signs such as the "keyhole sign", the "noose sign" or the "tear-drop sign" are the presence of silicone on both sides of a radial fold and also suggest implant rupture.
With the use of multi-plane imaging, MRI can also distinguish between radial folds or signs of true implant rupture.
+ In the extracapsular rupture, it is obvious that free silicone, separate from the implant, has spread outside the breast pocket into the mammary gland or axillary tissue. Free silicone has increased signal on STIR image, low signal on T1FS image, increased on silicone sensitive pulse, and cleared on suppressed silicone image.
4. Treatment of ruptured breast implants
The empty shell of a ruptured saline breast implant should be discarded. A ruptured silicone breast implant, whether intra or extracapsular, should be removed because interaction with surrounding tissue may occur and silicone leak may occur to local lymph nodes. Asymptomatic patients may consider breast implant removal, but overall safety in the long term should be emphasized and the risk of malignancy should be discussed with the patient. If an inner capsule ruptures, a cystectomy may be performed. If all the silicone has been cleaned up (and a new rupture has occurred), the surgeon may not be able to remove the capsule. If there is doubt about silicone retention, the surgeon may attempt to remove the entire capsule that has been infiltrated by silicone. A mastectomy will be necessary in the case of calcifications. If the rupture is extracapsular, multiple surgeries may be required to remove all of the silicone gel that has escaped, and replacement of the new implants may be slower in order to preserve the shape of the mammary gland.
Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with GE's 3.0 Tesla breast magnetic resonance imaging machine with mammography function that can survey and evaluate mammary gland abnormalities in patients with breast implants and evaluate Complications of breast implant placement.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
Breast Implant Rupture, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459308/ Breast Implant Rupture https://www.breastcancer.org/treatment/surgery/reconstruction/corrective/ implant-rupture Breast Implant Rupture https://radiopaedia.org/articles/breast-implant-rupture.