This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Bui Le Phuoc Thu Thao - Radiotherapy Doctor - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Radiation therapy is a method of using high-energy ionizing radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy has been shown to reduce recurrence rates, reduce metastasis, and increase overall survival in breast cancer patients.
1. Factors to consider indications for radiation therapy for breast cancer
Initial tumor size Number of metastatic axillary lymph nodes Histopathological grade Histological grade Endocrine receptor status Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status Age. Breast cancer treatment is a multimodal treatment with methods: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, endocrine therapy and targeted therapy. Radiation therapy is a method of using high-energy ionizing radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is usually indicated after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy. At that time, radiation therapy has been shown to reduce the rate of recurrence, reduce the rate of metastasis and increase the overall survival time for breast cancer patients.
2. How is radiation treatment for breast cancer?
There are two main methods of radiation therapy in breast cancer:External radiation therapy: a machine that emits radiation from outside the body. This is the most commonly used method of radiation therapy in breast cancer. Brachytherapy: The radiation source is inserted directly into the breast tissue to close to the primary tumor site by placing ducts through the breast tissue. This method has the effect of delivering radiation precisely to the tumor site, avoiding affecting surrounding tissues. The technique requires modern equipment and high expertise of the radiologist. Radiation therapy is indicated in the treatment of breast cancer at most stages. This is an effective method to reduce the recurrence rate after surgery. In addition, symptomatic radiotherapy is also applied when the tumor has metastasized to other organs, for example, radiation therapy for pain relief for bone metastases, hemostatic radiotherapy - pain relief for large tumors. , broken skin bleeding is not favorable surgery.
3. Why is radiation therapy used in breast cancer?
Radiation therapy has the role of killing cancer cells, often indicated as adjuvant after surgery to help prevent disease recurrence. Radiation therapy also has a role in reducing pain and other symptoms in late-stage breast cancer with distant metastases.The following are some indications for radiation therapy in breast cancer:
Radiation therapy after breast-conserving surgery:
Breast-conserving surgery is surgery to remove the tumor and a small amount of surrounding healthy breast tissue (with a may be called a lobectomy). This postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy reduces the risk of recurrence of the disease. Usually after conservative surgery, the disease can recur after several months or years because of the remaining cancer cells after surgery. Radiation therapy will help destroy any remaining malignant cells. Breast-conserving surgery combined with radiation therapy is also known as conservative treatment. Comparing the 2 methods of conservative surgery alone and conservative surgery combined with radiation therapy, the second method has the effect of reducing the recurrence rate and has been shown to have the same therapeutic effect as total mastectomy. (emulsion). Radiation therapy after total mastectomy (mastectomy):
Total mastectomy does not completely eliminate the risk of recurrence of the disease in residual tissue in the chest wall or lymph nodes. In some cases adjuvant radiation therapy after total mastectomy is also indicated if the patient is at high risk of recurrence. Adjuvant radiation therapy after total mastectomy is usually given 5 days/week for 5-6 weeks. Adjuvant radiation therapy after total mastectomy is applied in the following cases: Axillary lymph node metastasis The tumor is larger than 5cm The surgical resection area is positive. Radiation therapy in locally advanced breast cancer:
Applicable cases include:
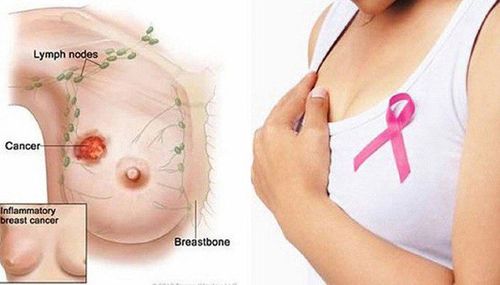
Inoperable breast cancer Inflammatory breast cancer: malignant cancer that invades the skin around the mammary gland. Patients with inflammatory breast cancer are often treated with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy, mastectomy, and then radiation therapy. Radiation therapy in distant metastatic breast cancer:
If the distant metastatic tumor causes pain and some other symptoms, radiation therapy works to shrink the tumor and relieve symptoms.
4. Complications in radiation therapy for breast cancer

Mild to moderate fatigue Skin irritation: itching, redness, pigmentation in the radiation area (similar to sunburn) Swelling of the mammary glands Changes in the sensation of Skin In addition, radiation therapy increases the risk of the following:
Swelling of the armpit: if radiation therapy to axillary lymph nodes Rib fracture (rare) Pneumonia or heart damage (rare) Secondary cancer: bone, muscles or lungs. Late side effects of radiation therapy for breast cancer :
The surrounding soft tissue is fibrosis, atrophy Pneumonia due to radiation therapy Myocardial ischemia due to radiation therapy for left breast cancer. After radiation therapy is over, check back periodically or when the following symptoms appear:
Persistent pain New tumor appearance Unexplained weight loss Persistent cough and fever Any other uncomfortable symptoms. Radiation therapy for cancer is a widely used method in medicine. Currently, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital has successfully applied this method to treat many cancer cases, helping to reduce clinical symptoms and limit cancer metastasis.
Oncology Center at Vinmec Central Park is fully equipped with cancer treatment modalities: From surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, radiation surgery .... pain treatment and palliative care. The diagnosis is made carefully: blood test, X-ray, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, myelogram, myelogram, biopsy, immunohistochemistry, biological diagnosis molecule.
Truebeam radiation therapy system at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital is integrated with HyperArc non-coplanar multidimensional radiosurgery function. Vinmec Central Park is the first place in Southeast Asia equipped with this HyperArc technology.
The treatment process is closely coordinated with many specialties: Center for Diagnostic Imaging, Laboratory Testing, Cardiology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Medicine. Nutrition, Pain Treatment and Palliative Care Department, in order to bring patients the optimal treatment regimen and the most reasonable cost.
Specialist II Bui Le Phuoc Thu Thao has nearly 15 years of experience in direct treatment of cancer patients, especially radiation oncology and care for terminal cancer patients, palliative care mild and pain-relieving. Dr. Thao has participated in many advanced training courses at home and abroad such as advanced radiation therapy in Singapore and Korea, and the National Palliative Care Instructor training course of Harvard University. Currently, Dr. Thao is working at the Center for Cancer - Radiation Therapy, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.