This is an automatically translated article.
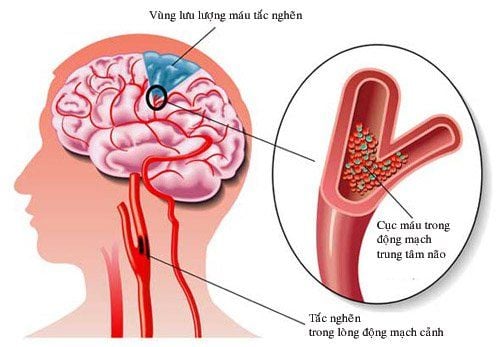
Stroke is a common disease with a high risk of death. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the location of cerebral ischemic injury, analyze the cerebral artery system, the culprit artery and locate the cerebral perfusion of each artery to have the best treatment and prevention direction.
1. Anatomy of cerebral perfusion
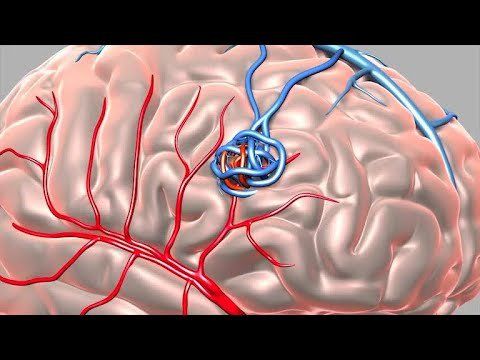
The central nervous system, like any other system of the body, needs a constant supply of oxygen and nourishment. The brain has an especially high need for oxygen - at rest, it accounts for one-fifth of the body's total oxygen consumption. The brain is very sensitive to hypoxia, which can lead to ischemic death within minutes. The brain is supplied with blood through 4 cerebral arteries including 2 internal carotid arteries forming the anterior cerebral circulatory system and 2 vertebral arteries forming the posterior cerebral circulatory system of the brain.
1.1 Anterior cerebral circulation The anterior cerebral circulation system consists of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and the middle cerebral artery (MCA) arising from the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery at the polygon of Willis.
Anterior cerebral artery (ACA): The anterior cerebral artery is the internal branch of the internal carotid artery, dividing a small branch is the anterior communicating artery connecting 2 anterior cerebral arteries on both sides, forming the anterior half of the polygon. Willis. After that, the anterior cerebral artery continues to divide into many branches such as the jugular artery and the frontal polar artery. The anterior cerebral artery supplies the motor and sensory cortex associated with the contralateral half of the body (mainly the leg) and the center that controls urination. Middle cerebral artery (MCA): The middle cerebral artery is the external branch of the internal carotid artery. The middle cerebral artery divides into perforating branches (thalamic-striatal artery), lens-striatal artery, and superficial branches (cortical-pleural branch). The middle cerebral artery supplies most of the rest of the cerebral hemispheres and the underlying subcortical structures. Cerebral perfusion regions include: Whole motor and sensory cortex (mainly for face and hands), expressive language area (Broca's area) for dominant hemisphere, visual ray, and language receptive area language (Wernicke region) for the dominant hemisphere. 1.2 Posterior cerebral circulatory system Posterior cerebral circulation system includes posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery and vertebral artery:
Vertebral artery: originates from subclavian artery, enters dura and arachnoid through great foramen occipital bone. The basilar artery: Due to the fusion of 2 vertebral arteries at the inferior border of the pons. Posterior cerebral artery: Formed by bifurcation of the basilar artery. 1.3 Willis polygon The Willis polygon is an anatomically constant anastomosis. The Willis polygon is formed from the anastomosis branches of the internal carotid artery and basilar artery, along with the anterior communicating artery, posterior communicating artery, and the proximal segment of the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries. .
Thiếu máu não thuộc vùng động mạch não sau gây ra bán manh đồng danh thị trường đối bên
2. The relationship between brain perfusion anatomy and symptoms of cerebral ischemia
Anterior cerebral artery: Cerebral ischemia in the area of control of the anterior cerebral artery, causing symptoms of weakness in the contralateral side (predominance of the leg is heavier than the hand), loss of sensation on the opposite side of the body, may be accompanied by occlusion. pee. Middle cerebral artery: Depending on the blocked cerebral artery, it causes different clinical symptoms such as weakness on the opposite side (mainly hands and face), sensory disturbance on the opposite side of the body, impaired speech ability. language or selling synonyms in the opposite market, impaired language comprehension. Posterior cerebral artery: Cerebral ischemia in the posterior cerebral artery region causes contralateral visual acuity hemolysis, which can cause oculomotor nerve paralysis. Basal artery: Total occlusion of the basilar artery often causes a severe clinical picture with a very high mortality rate (over 90%), including severe quadriplegia, coma, and functional paralysis of many parts of the body. cranial nerve. Cerebellar artery: Depending on the occlusion of the inferior cerebellar artery anterior, posterior inferior or superior cerebellar artery, there are characteristic clinical syndromes. Symptoms are usually cerebellar ataxia, Horner's syndrome, peripheral facial paralysis, decreased hemifacial sensation, decreased heat sensation along with dizziness, dysphagia,...
3. Imaging of brain perfusion anatomy
Neuroimaging plays an important role in the treatment of acute stroke by providing the information needed to accurately triage patients, accelerate clinical decision-making about treatment, and improve clinical outcomes. improve results.
Quick and accurate diagnosis is extremely important. The CT-scan of the brain enables time-critical decisions in stroke patients, informs decisions about thrombolytic therapy with tPA, and narrows the treatment time window.
MRI imaging of cerebral perfusion with contrast injection helps to assess the state of cerebral blood vessels in capillary beds.
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is an imaging method that combines X-ray and digital image processing to capture the vascular system. This is a minimally invasive technique for therapeutic intervention from within the blood vessel without the need for invasive surgery.
In summary, knowing the anatomy of the cerebral arteries, the cerebral perfusion function of each artery will help to better understand the pathologies of the cerebrovascular system as well as get the methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention. the best. Currently, advances in neuroimaging such as DSA, CT-Scan and MRI have greatly improved the treatment of stroke.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI System, which is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment by GE Healthcare (USA) with high image quality, allowing for a comprehensive assessment, without omitting the injury without leaving any damage. and reduce shooting time. Silent technology helps to reduce noise, create comfort and reduce stress for the client during the shooting process, resulting in better image quality and shorter imaging time. With the state-of-the-art MRI system With the application of modern methods of cerebral vascular intervention, a team of experienced and well-trained neurologists and radiologists, Vinmec is a prestigious address for stroke risk screening and screening. reliable goods.
In the past time, Vinmec has successfully treated and treated many strokes in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: Saved the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive brain strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of a stroke ;...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Source: Teachmeanatomy.info, emedicine.medscape.com