This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master - Doctor Le Thai Bao - Critical Care Doctor - Intensive Care Unit - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Plasma exchange is a technical method using a filter to remove drugs or toxins circulating in the blood plasma .... helping to improve disease status and patients to recover quickly.
1. Plasma exchange technique in the treatment of liver failure
Plasma exchange (PEX) is a technical method using a filter to remove a part of plasma and plasma substances such as: autoimmune antibodies, immune complexes, cryoglobulins, substances attached to the plasma. proteins, endotoxins, exotoxins, bilirubin, drugs or toxins circulating in the plasma .....
A new amount of plasma is re-transfused with an equivalent volume, helping the patient improve the disease and quick recovery.
In liver failure we replace plasma with fresh frozen plasma.
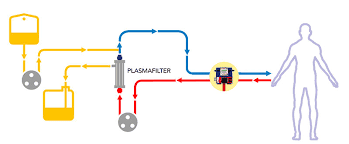
2. Advantages and disadvantages of plasma exchange with fresh frozen plasma
2.1 Advantages
Easy to make, low cost because frozen plasma is often available.2.2 Cons
The possibility of mild or severe allergic reactions, or the risk of infection with certain transfusion-related diseases due to plasma collected from many people (despite previous screening), should be considered implement this method.
3. Indications for plasma exchange in liver failure
3.1 Acute liver failure
Due to viral hepatitis (hepatitis A, hepatitis C), toxicity, vascular causes (Budd Chiari syndrome), autoimmune hepatitis, hepatitis in pregnancy (HELLP syndrome, acute fatty liver disease) ..)... has the following symptoms:
Hepatic encephalopathy above grade II Increased intracranial pressure Hepatobiliary syndrome Progressive intrahepatic cholestasis Bacterial peritonitis, sepsis.
3.2 Exacerbation of chronic liver failure
On the background of chronic liver disease with the following manifestations:
Serum Bilirubin > 15 mg/dl (250 μmol/l) Hepatorenal syndrome Hepatic encephalopathy above grade II.
4. Contraindications to plasma exchange in liver failure
Cases of severe shock that cannot raise mean blood pressure > 55 mmHg with measures, fluids and vasopressors.
Progressive bleeding Severe coagulopathy, disseminated intravascular coagulation Grade 4 hepatic encephalopathy.
5. Drugs used in plasma exchange
Anticoagulant Heparin: As indicated for each patient Calcium chloride 2gram: Inject 1gram intravenously into PEX (replacement of soy sauce) 30 minutes and 30 minutes before the end of PEX). Methylprednisolone 80mg IV 30 minutes before PEX for the purpose of preventing allergic reactions.
6. First aid equipment to prepare
Endotracheal intubation set Anaphylactic shock equipment Ambu ball, oxygen system Monitor monitor vital functions: Heart rate, SpO2, breathing rate, blood pressure.

7. Prepare Patient Before PEX
Explain to the patient, the patient's family the benefits and side effects of PEX. The patient lies on his back with his head raised 300 (if there is no hypotension). Legs on side of IV catheter: Straighten and rotate outward. If TM is placed in the internal scene: Head flat, face to the opposite side. Check medical records: Check anticoagulation process (risk classification and anticoagulation according to protocol).
8. Steps to take
Set up the extracorporeal circulation Connect the extracorporeal circulation with the patient Set the parameters for the machine to work End the plasma filtration process.
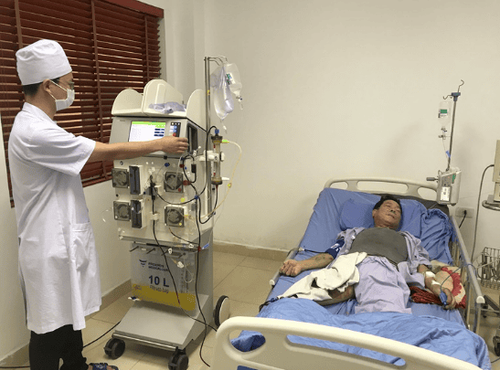
9. Monitoring during plasma filtration
Consciousness, pulse, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate, SpO2. Ventilator parameters. Allergic reactions: pruritus, urticaria, dyspnea, anaphylaxis. Bleeding complications: Bleeding under the skin, mucous membranes, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, brain, foot intravenous catheter. Check the dose of heparin. Monitor the parameters on the plasma dialysis machine. Arterial pressure (pressure into the machine). Intravenous pressure (pressure returning to the patient). Pre-membrane pressure. Transmembrane pressure.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Hepatodialysis (MARS) in the treatment of acute liver failure Diagnosis, treatment and complications of acute liver failure What is plasmapheresis?