This is an automatically translated article.
Bleeding in the first half of pregnancy is a common phenomenon, most of which are light bleeding cases and do not affect health. However, sometimes bleeding in the first half of pregnancy is a sign of more serious conditions that threaten the health of the fetus and mother.1. What is bleeding in the first half of pregnancy?
Bleeding in the first half of pregnancy is all cases of pregnant women who have symptoms of vaginal bleeding during the first half of pregnancy. Vaginal bleeding can occur after trauma or it can happen spontaneously, regardless of any factors. Vaginal blood can be bright red, dark red or black, blood can be more or less, lasting. When bleeding may be accompanied by other symptoms such as dull or intermittent abdominal pain, abdominal pain localized or the entire hypogastrium.Vaginal bleeding in the first half of pregnancy is a common phenomenon, the rate of pregnant women having bleeding in the first trimester is 15-25%. The majority of cases are minor bleeding, not pathological cases. Like bleeding in the second month of pregnancy in the form of small brown or pink blood spots, this can be a sign that a fertilized egg has implanted in the uterus.
During pregnancy, hormone changes in the body make the blood flow to a woman's uterus greatly increase, the cervix is very easy to bleed, especially after sex or gynecological examination. However, in some cases, vaginal bleeding is a sign of serious medical conditions, so when pregnant women have signs of vaginal bleeding, they need to go to medical facilities for timely treatment. In those cases where interventions are needed to keep the pregnancy, there are cases where the pregnancy must be removed as soon as possible.
Dangerous conditions when bleeding in the first half of pregnancy are: threatened miscarriage, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, pregnancy.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
2. Threat of miscarriage
As one of the common causes of bleeding in the first half of pregnancy, it is common in women with abnormalities in the uterus such as patients with uterine fibroids, bicornuate uterus, double uterus, ...Threatened miscarriage is a condition in which the fetus is still alive, partially removed from the lining of the uterus. Pregnant women have symptoms of missed periods and signs of pregnancy, bright red vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain or dull pain in the lower abdomen. On physical examination, the cervix is long and closed; uterus corresponding to gestational age. Laboratory tests are positive for hCG, ultrasound shows pregnancy in the uterine cavity, there may be fetal heartbeat.
Patients will be instructed to rest, avoid vigorous exercise, eat light meals, and prevent constipation. Treated with smooth muscle relaxants, anti-infective antibiotics, hormone drugs such as Progesterone, Dydrogesterone,... to maintain pregnancy. Find the causes of threatened miscarriage for treatment, the causes can be due to systemic disease, uterine fibroids, uterine isthmus, genetics, endocrine,...
3. Miscarriage phenomenon

3.1 Having a miscarriage
Miscarriage is the next development of the phenomenon of threatened miscarriage if not successfully managed, miscarriage is the natural death of the fetus, usually bleeding at 13 weeks gestation.When you are having a miscarriage, the mother has symptoms of severe abdominal pain in the lower abdomen, blood is more and more, red blood mixed with blood clots, the patient may be shocked because of a lot of blood loss. On vaginal examination, the cervix has been cleared and opened, and the placenta, fetus or gyrus can be seen because the inner hole and the upper part of the cervix have dilated and enlarged because the fetal mass has descended to the lower segment.
The patient will be treated with abortion as soon as possible, using uterotonics (Oxytocin, Ergometrin) to stop bleeding, antibiotics to fight infection, infusion of isotonic solutions (NaCl 0.9) % or Ringer lactate) for shock resistance.
3.2 Complete miscarriage
Complete miscarriage is common in the first 6 weeks of pregnancy. After abdominal pain, the patient bleeds, the whole fetus comes out, then the blood becomes less. On physical examination, the cervix is closed and the uterus is small for gestational age. During ultrasound, if the uterus is clean, no need to aspirate, give the patient antibiotics if there is a risk of infection.3.3 Incomplete miscarriage
Symptoms when the patient has an incomplete miscarriage (replacement of the placenta) is that after the miscarriage, the patient has prolonged bleeding and abdominal pain. On examination, the cervix is dilated and the uterus is enlarged. The patient will be treated with antibiotics, if there are many abnormal echoes in the uterus, use Misoprotol (every 3-4 hours for 200mcg sublingually, up to 3 times). The next day, if the ultrasound does not improve, the uterus is aspirated, injecting a tube of Oxytocin 5UI intramuscularly before aspiration.3.4 Miscarriage died
A stillbirth is a condition in which a fetus dies at a gestational age of less than 22 weeks, remaining in the uterus. The patient has symptoms of pregnancy, then vaginal bleeding, morning sickness ceases, breast may secrete colostrum, no fetal movement, no fetal cardiac activity. On examination, the cervix is closed, there is black blood, the uterus is smaller than gestational age. The hCG test is negative if the fetus has been dead for a long time, ultrasound shows a distorted amniotic sac margin, no fetal cardiac activity.The patient will be managed with Misoprotol, aspiration, and antibiotics after the procedure. Vital signs and bleeding are closely monitored.
3.5 Infectious miscarriage
Usually occurs after unsafe abortion, sterility of the means of abortion or due to placental abruption. On examination, the uterus is soft, tender, and the cervix is dilated. The patient has fever, fatigue, malaise, heart palpitations, prolonged vaginal bleeding, foul odor, sometimes pus.Patient will be treated with high dose antibiotics. If there is a lot of bleeding, resuscitation and aspiration will be performed. If the bleeding is small, give the patient antibiotics for 4-6 hours, then aspirate the remaining placenta in the uterus. Intramuscular injection of the uterotonic Oxytocin before smoking. In cases of severe bleeding and infection, a total hysterectomy may be required.
4. Ectopic pregnancy
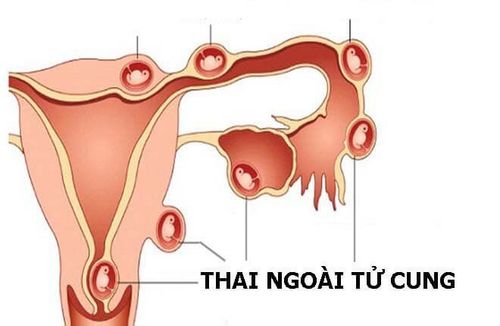
Women with ectopic pregnancy have symptoms of missed periods or menstrual irregularities, possibly morning symptoms. Dull abdominal pain in the lower abdomen, pain towards the fallopian tube with embryo implantation, sometimes sharp pain. Bleeding occurs, blood is a little long in the vagina with the characteristics of black blood, like coffee grounds, scattered many times a day.
On examination, the body of the uterus is slightly larger than normal, the side of the uterus has mass, the border is not clear, the pressure is painful, the cervix is closed. When the finger touches the cervix, the pain increases. The hCG test is positive, but ultrasound does not show the amniotic sac or echoes in the uterine cavity, but may show erratic echoes on one side of the uterus.
If the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured, the patient has sudden, severe pain, possibly shock due to blood loss, mild abdominal distention, abdominal wall reaction and peritoneal palpation, low percussion. The cervix is closed, there is little blood in the hand, the sacs are full, the posterior sac is bulging and when pressing the finger on the patient is very painful, the uterus moves like swimming in water.
Management of ectopic pregnancy:
If the ectopic pregnancy has not ruptured: the patient is operated on as soon as possible to avoid rupture causing bleeding. Depending on each case and conditions of the medical facility, it is possible to have laparotomy or laparoscopic surgery, choose the method of cutting or preserving the fallopian tubes. Medical treatment if indicated and monitoring conditions. If the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured: carry out shock resuscitation, quickly perform tubalectomy, remove all the dilute blood and blood clots in the abdomen, return blood can be re-transfused if eligible.
5. Egg pregnancy
Symptoms of ovulatory pregnancy are: amenorrhea like other pregnancies, morning sickness heavier than usual, vaginal bleeding a little, black blood, persisting for many days, night bleeding often more than three days. Uterine examination shows that the uterus is enlarged faster than gestational age, soft, not palpable parts of the fetus, not heard the fetal heart, hCG test is elevated, ultrasound shows the image of bread intestines, the patient may have edema, high blood pressure, proteinuria.
The patient should be removed early to avoid the risk of bleeding due to miscarriage. Depending on the patient's age and fertility needs, it is possible to only remove the eggs or remove the whole uterus to reduce complications of the disease. After removing the ovum, the patient needs to continue to be monitored on an outpatient basis for 2 years to detect glioblastoma complications early.
Due to the complexity and danger of possible medical conditions, when there are signs of bleeding in the first half of pregnancy, pregnant women need to go to medical facilities for timely examination and treatment. , even after the bleeding has stopped.
The first trimester is the most sensitive time throughout pregnancy, to help keep both mother and baby healthy from the very first days. Pregnant women need:
Distinguish between normal vaginal bleeding and pathological vaginal bleeding for timely intervention to maintain pregnancy; Periodic prenatal check-up Screening for fetal malformations at 12 weeks detects dangerous fetal malformations that can be intervened early. Screening for thyroid disease in the first 3 months of pregnancy avoids dangerous risks before and during delivery. Currently, Vinmec International Hospital is implementing a maternity package (12-27-36 weeks), in which a 12-week maternity package helps to monitor the health of mother and baby right from the beginning of pregnancy. early and timely intervention in health problems. In addition to the usual services, the maternity monitoring program from 12 weeks has special services that other maternity packages do not have such as: Double Test or Triple Test to screen for fetal malformations; Quantitative angiogenesis factor test to diagnose preeclampsia; thyroid screening test; Rubella test; Testing for parasites transmitted from mother to child seriously affects the baby's brain and physical development after birth.
For more information about the 12-week maternity package and registration, you can contact the clinics and hospitals of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.













