This is an automatically translated article.
Bilobular goiter is a term used to refer to any abnormal growth that forms a solid tumor in both lobes of the thyroid gland. In any case of detecting thyroid nodules with diverse features, the diagnosis and treatment always require aggressive, early intervention to prevent possible complications.
1. What is a 2-lobed nodular goiter?
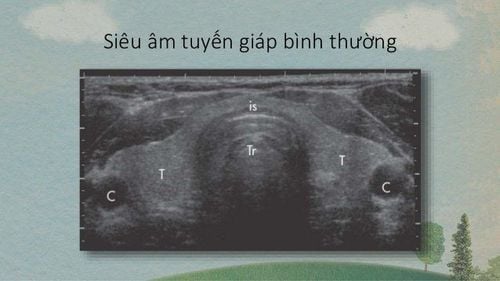
The appearance of nodules in the thyroid gland is quite common in the community. The risk of forming a palpable thyroid nodule is estimated to be 5-10%. However, a high-resolution ultrasound has shown an increased incidence of thyroid nodules in 9-68% of randomly selected individuals, and the condition affects women more than men. Accordingly, a 2-lobed nodular goiter is defined as the presence of nodules in both lobes of the thyroid gland. At this time, the characteristics of quantity and position are generally not affected by the characteristics of the nature and size of the nucleus. The nodules can increase the production and secretion of thyroid hormone into the bloodstream and cause hyperthyroidism. On the contrary, if the causes compress the surrounding organs, causing difficulty in breathing, swallowing and reducing thyroid hormone, leading to hypothyroidism is a remarkable thing.Furthermore, while thyroid nodules are commonly benign, thyroid malignancy accounts for 7-15% of nodules. At the same time, the incidence of thyroid nodules of thyroid malignancy has increased rapidly in recent years. However, if detected early and treated completely, the survival rate for thyroid cancer is still quite stable and satisfactory.
2. What are the factors suggesting a diagnosis of malignancy in a 2-lobed nodular goiter?
If the patient has a bilobular goiter, thyroid cancer is a diagnosis that cannot be ruled out but must be confirmed. Because it is very different from malignancies in other organ systems, if detected and properly intervened, the survival prognosis of patients with thyroid cancer is similar to that of normal people.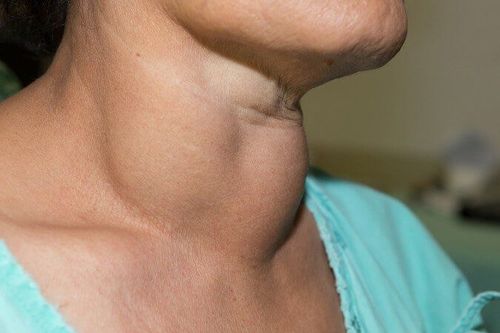
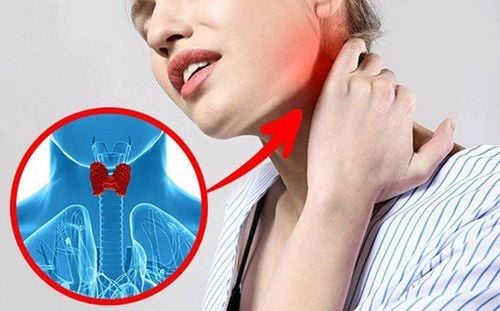
Hình ảnh bệnh nhân mắc bệnh bướu giáp nhân 2 thuỳ
Accordingly, the factors that suggest the diagnosis of malignancy in bilobular goiter include:
Age under 20 years old or more than 70 years old Male gender Having symptoms related to dysphagia, difficulty speaking or difficulty speaking breathing History of cervical irradiation History of thyroid carcinoma A palpable nodule of the thyroid gland is a firm, hard, or immobile nodule Presence of lymph nodes in the neck region Conversely, if the patient has the following factors: With the following suggestions, the likelihood of a benign diagnosis is higher:
Have a family history of autoimmune disease (eg, Hashimoto's thyroiditis) Have a family history of benign thyroid nodule or goiter thyroid hormone dysfunction (eg, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism) Neck pain or pain associated with the thyroid nodule Palpation of the thyroid nodule is soft, smooth, and mobile
3. How to diagnose 2 lobe nodular goiter?
Diagnosis of goiter is made depending on the reason for the patient's examination. However, in the majority of cases, the presence of a bilobular thyroid nodule is due to structural or radiographic examination. Patients will come to the clinic because they feel nodules in the thyroid gland themselves or when looking in a mirror, buttoning their shirt, or wearing a necklace.
On examination, the doctor will re-determine these abnormal structures by palpating the anterior neck area, assessing the size of the nodules, location and surrounding invasion, and detecting lymph nodes. An indication of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels is then used to screen for hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. In addition, measurement of both serum thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) levels may also be helpful. In most cases of bilobular goiter, the TSH level is normal.
In the case of isolated thyroid nodules and normal TSH values, no further diagnostic testing is needed unless an autoimmune disease such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis is suspected. Simultaneously, testing for serum antithyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies and antithyroglobulin (anti-Tg) antibodies are also needed to diagnose Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Một số loại xét nghiệm đặc biệt sẽ giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán bướu giáp nhân 2 thuỳ
4. How to treat 2-lobed goiter?
The treatment of 2-lobed goiter with surgery should soon be recommended for cases with 2-lobed goiter causing compression symptoms. At the same time, this will be the initial treatment for thyroid nodules that are malignant in nature, aiming to eradicate them in the early stages. In addition, if thyroid nodules do not cause thyroid dysfunction, medical treatment with T4 inhibitor therapy is still controversial. The role in possibly preventing the formation of new thyroid nodules remains unclear.Most bilobular goiters with other benign nodules will not require any specific intervention, unless there are symptoms of local compression during significant enlargement, such as difficulty swallowing, choking, trouble breathing, hoarseness or pain. These situations sometimes necessitate removal of the thyroid gland.
Radioiodine therapy (131-I) may also be an alternative for the treatment of toxic goiter. The indications for this treatment are when the bilobular goiter produces too much thyroid hormone, causing hyperthyroidism and cannot be controlled with medication. At this point, the only absolute contraindications to 131-I therapy are pregnancy and lactation.

Một số trường hợp, người bệnh có thể được chỉ định điều trị nội khoa
5. How to monitor the progress of 2-lobed goiter?
When growth from more than 50% of the original thyroid nodule is observed, repeat biopsies are indicated.Furthermore, even benign thyroid nodules require long-term follow-up because of the risk of false-negative results after initial biopsy, with an incidence of about 5%. Accordingly, if no more enlarged bilobular goiter is observed, a follow-up period of 3 to 5 years can be planned for the patient.
In summary, the way to diagnose and treat 2-lobed nodular goiter depends on the characteristics of the nodule, such as size, invasiveness, and ability to cause thyroid dysfunction. However, the most important feature is the possibility of malignancy. Accordingly, the patient's prognosis will be meaningfully positive if detected early and properly intervened.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its medical examination and treatment services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.