This is an automatically translated article.
Biliary ischemia is one of the common biliary tract diseases. If not detected and treated early, people with biliary anemia may face unwanted complications.
1. What is biliary ischemia?
The biliary tract is a system of tubes, divided into many branches, to carry bile from the liver to the small intestine, to aid in the digestion of food. Outside of meals, when not needed, bile is stored in the gallbladder.Biliary ischemia is a condition in which the biliary tract is locally damaged due to interrupted blood flow from the hepatic artery through the network of arteries adjacent to the biliary tree. Common causes of biliary ischemia include:
Vascular injury due to laparoscopic cholecystectomy or during local liver transplantation; Effects of radiation therapy; Injury from liver transplant rejection (most common); Influence from chemical cleavage method; Thrombosis - consequences of hypercoagulable disorders.
2. Symptoms and complications of biliary ischemia
Common symptoms of patients with biliary anemia are: Itchy skin, dark urine and pale stools. From tests and imaging tests, your doctor can detect biliary tract disease.
Biliary ischemia causes necrosis, damage to the bile ducts, leading to cholecystitis, cholangitis or biliary stricture (often repeated).
Ngứa da là một trong các triệu chứng thường gặp của bệnh nhân mắc thiếu máu đường mật
3. Diagnosis of biliary ischemia
Doctors may order patients to perform the following methods to diagnose biliary anemia:
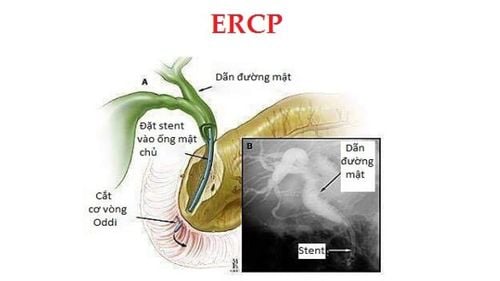
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) : This technique uses a magnetic resonance machine to create images. of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts and pancreas. This is a valuable technique in investigating biliary-pancreatic pathology, supporting the detection of gallstones, biliary obstruction, biliary ischemia,...; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): An endoscopic duodenal technique combined with X-ray, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of a number of diseases in the bile and pancreas. Through the endoscope, the doctor will insert a catheter into the biliary or pancreatic duct and then inject contrast material into these tubes. X-rays are taken after the contrast is injected, capturing the bile ducts and pancreas. The obtained images help doctors accurately diagnose diseases in the biliary tract such as biliary ischemia, cholangiocarcinoma, bile duct stones or biliary stricture,... The doctor can choose to perform one of the following procedures. 2 methods above or both to diagnose biliary ischemia.
Physicians should consider the diagnosis of cholestasis in patients at high risk for biliary ischemia, especially after liver transplantation. Ultrasound is the first imaging test for cholestasis, but two additional tests are needed to rule out other causes such as pancreatic cancer or gallstones.
4. How is biliary ischemia treated?
The treatment of biliary anemia depends on the cause of the condition. Specifically:
If the cause is the effect of liver transplant rejection, anti-rejection therapy should be used and a liver transplant can be performed; For the cause is biliary stricture, it is necessary to treat by endoscopic balloon dilatation, combined with stenting When diagnosed with biliary ischemia, the patient should absolutely follow the doctor's instructions. to ensure the most effective treatment process.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.