This is an automatically translated article.
Postpartum thrombophlebitis is one of the common postpartum diseases. Pregnant women should be wary of this complication because if not treated promptly, the disease can cause pulmonary embolism, kidney disease and easily lead to death.1. What is thrombophlebitis?
Veins are blood vessels in the body that carry blood from the limbs and organs back to the heart. Phlebitis is an inflammation of the veins. If a blood clot is the cause of the inflammation, it is called thrombophlebitis. When a blood clot forms in a deep vein, the condition is called deep thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
2. Postpartum thrombophlebitis - common complications
The risk of thrombophlebitis persists throughout pregnancy, especially peaking in the postpartum period.
One of the most dangerous complications of venous thromboembolism is pulmonary embolism (12-15% mortality), which arises from deep vein thrombosis. Three causes of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women are superficial vein thrombosis, venous thrombosis due to genital infections, and ovarian vein thrombosis. Most deep vein thrombosis occurs between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis include both congenital and acquired factors (obesity, prolonged immobility, trauma, inflammatory disease, polycythemia vera, sickle cell disease, varicose veins of the lower extremities. ,...). If these factors appear in the postpartum period, the risk of venous thrombosis leading to postpartum phlebitis will increase. The risk factors for obstetric-related morbidity are circulatory stasis, multiple births, advanced maternal age, gestational age less than 36 weeks, delivery with procedural support or cesarean section, pre-eclampsia, hemorrhage, and labor. prolonged, vascular circulation (venous system) is obstructed, fibrin proliferation,...
3. Postpartum thrombophlebitis symptoms
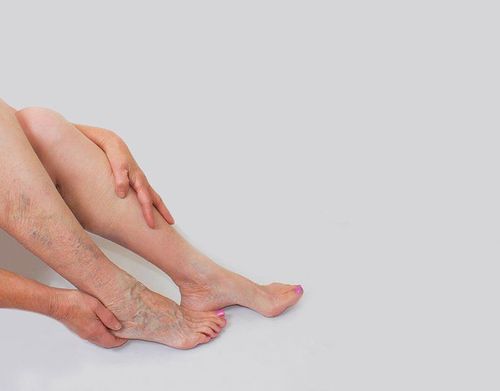
Symptoms usually appear late, about 12-15 days after giving birth; Mild fever, chills, rapid pulse; If thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities, the mother has symptoms of leg swelling, white, hot, painful when pressed, the heel cannot be lifted from the bed; If not detected and treated promptly, the disease can lead to pulmonary embolism, kidney and death.
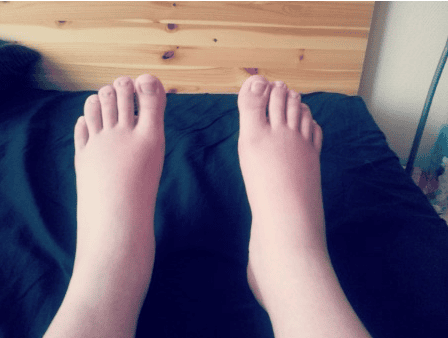
Phù chân - Triệu chứng viêm tắc tĩnh mạch sau sinh
4. Diagnosis of postpartum thrombophlebitis
Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms; Ultrasound of the affected limb: A method that uses sound waves to show blood flow through veins and arteries; D-dimer level test: A blood test to check for substances released in the body when a blood clot dissolves; Computed tomography scan, MRI scan to check for the presence of blood clots; If a blood clot is found, your doctor may take a blood sample to test for clotting disorders that cause the clot.
5. Postpartum thrombophlebitis treatment
Blood tests, blood clots, Quick time and Prothrombin ratio to monitor disease progression and response to treatment; Immobilize the extremity with thrombophlebitis for at least 3 weeks after the patient is afebrile; Using systemic antibiotics in combination with corticosteroids after a few days of antibiotic use; Use of anticoagulants: Heparin 25,000 UI/kg body weight/24 hours intravenously or intravenously. Dicoumarol 2 - 10mg/24 hours can also be used (vitamin K antibiotic, slow acting). Simultaneously monitor treatment results with Howell, Quick time test.
6. Prevention of postpartum thrombophlebitis
In order to prevent deep vein thrombosis causing thrombophlebitis in obstetrics, pregnant women as well as medical staff should pay attention to the following issues:Pregnant women with a history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, have deep vein thrombosis before pregnancy, need to be treated with anticoagulants from the time of pregnancy; Treatment of inflammatory foci during pregnancy such as urinary tract infections, genital infections; Pregnant women need to elevate their legs and wear compression stockings; Use the drug as prescribed by the doctor, avoid excessive weight gain; Avoid dehydration and prolonged immobilization during the antenatal, labor and postpartum periods; Prevention of amniotic infection and prolonged labor; During childbirth: Do not leave vegetables, strictly adhere to the indications for uterine control and sterilization and hygiene regimes; After giving birth: Avoid holding the delivery, clean and take care of the perineum properly

Sử dụng thuốc theo chỉ định của bác sĩ
Postpartum thrombophlebitis can cause many dangerous complications, even death. Therefore, women with a history of venous thromboembolism, at risk of disease or showing symptoms of the disease should immediately seek medical advice from a doctor in the prevention and treatment of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.