This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Resident Doctor, Doctor Nguyen Hung Tien - Resident Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. Dr. Tien has more than 8 years of experience in the field of Pediatrics - Neonatology.Stridor is an important indicator of laryngeal fibrillation in children. We can notice this hissing sound from the first weeks to months of the baby, especially when the baby is eating, lying on his back or crying loudly. Although most cases go away on their own when the child grows up, parents still need to be alert when detecting signs of stridor in their children.
1. What is laryngeal softening in children?
Laryngeal laxity is a congenital abnormality of the larynx used to describe the softening of the laryngeal tissue and the inward collapse of the epiglottis, resulting in upper airway obstruction. stridor in children.In diseases classified as congenital abnormalities in the larynx, laryngeal fibrillation accounts for 60% of cases. Usually when the baby is about 4-6 weeks old, the disease will be detected, sometimes it can be as late as 2 months. Softening of the laryngeal cartilage in children causes stridor in clinical, 2 times more boys than girls.
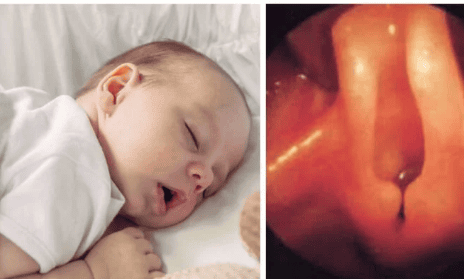
Mềm sụn thanh quản gây tắc đường hô hấp trên ở trẻ
2. Causes of soft laryngeal cartilage in children
Up to now, world medicine has not identified the exact cause of laryngeal softening in children. However, there are still a number of hypotheses about the pathogenesis that have been raised such as:Abnormal development of laryngeal cartilages Neuromuscular immaturity leads to respiratory organs in children having the ability to coordinate poor, whereby the airways are easily inflated.
3. Manifestations of soft cartilage in the larynx in children
Symptoms of laryngeal softening are persistent wheezing and wheezing in children. This is an indicator of laryngeal softening, not only that, adults will easily notice that when the child is lying on his back or crying, the breathing will be louder.Besides, it is also impossible not to be vigilant when the child shows the following symptoms:
The child has difficulty in eating or breastfeeding; Difficulty swallowing when eating, occurrence of choking; Breastfeeding time is prolonged, with weight loss or slow weight gain; Choking, coughing or vomiting frequently; Due to low oxygen levels in the blood, the child has cyanosis; Sudden stop breathing for a few seconds. In addition, cases of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) will accompany it, accounting for 80%. If the child has the above symptoms, especially the child wheezing, parents should take the child to a medical facility for examination and timely treatment.

Trẻ mềm sụn thanh quản thường xuyên bị nôn trớ
4. Soft classification of laryngeal cartilage
Through symptoms or flexible laryngoscopy, doctors divide laryngospasm in children into 3 levels: mild, moderate and severe.4.1. Mild laryngeal softening
At this level, the child will only have wheezing and no other symptoms. However, it will not affect the child's eating process and the disease usually resolves on its own after 12-18 months of age.4.2. Moderate laryngeal softening
On average, babies not only wheeze when they inhale air, but often have difficulty eating or nursing. This is also a period when babies are more prone to spitting up, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and mild or moderate thoracic spasms.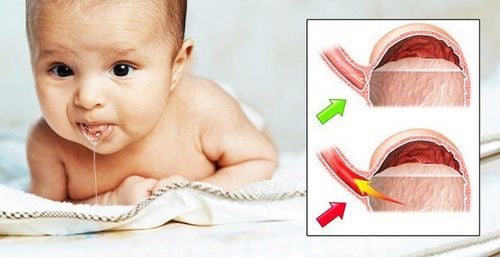
Mềm sụn thanh quản mức độ trung bình trẻ dễ bị trào ngược dạ dày
4.3. Severe laryngeal softening
This is a very rare case because about 99% of children with congenital laryngospasm will be classified as mild or moderate. If children unfortunately fall into this level, they will have serious symptoms such as difficulty breathing, difficulty eating, weight loss or slow weight gain, pauses for breathing for a few seconds or cyanosis of the body.5. How is the diagnosis process of laryngeal soft tissue in children?
The doctor will base on the status of stridor and the symptoms of the disease in the child to diagnose laryngeal softening as well as the extent of the disease.In case the child is mild, the doctor will recommend that the parents continue to closely monitor the symptoms of the disease. Basically, most cases will go away on their own as the child gets older. In cases where the child is more severe, the doctor will ask the parents for the child to perform a number of tests to determine the exact condition that the child is having. Nasopharyngeal-laryngoscopy is the main test used to diagnose laryngospasm in children. The doctor will perform a laryngoscopy and rely on the images collected through the camera to have a better overview of both the health and structure of the patient's larynx.
As soon as there are suspicions that the child has laryngospasm, the doctor may ask the family to let the child do other tests such as X-rays of the neck and chest to give the most accurate assessment of the condition of the baby. larynx.
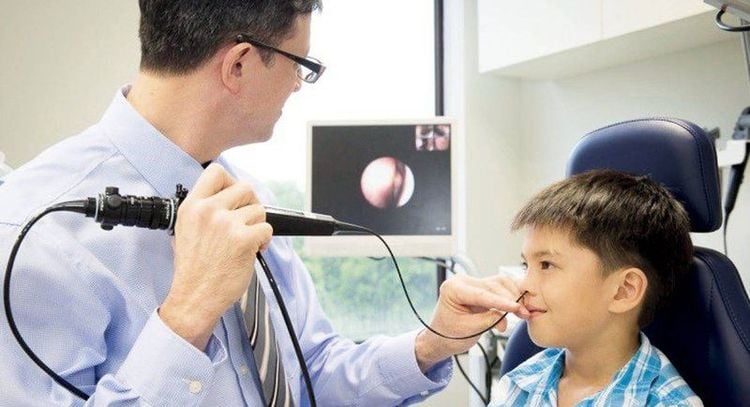
Soi mũi - hầu - thanh quản là một trong những biện pháp chẩn đoán mềm sụn thanh quản
6. Soft treatment of laryngeal cartilage in children
Medical treatment and surgical treatment are two methods used to treat soft laryngeal cartilage in children.Medical treatment: Because most cases of laryngospasm can improve on their own without treatment. Surgical treatment: Applied to severe cases, however, it is very rare to have to apply surgery to treat soft cartilage in the larynx in children. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and laryngeal softening in children are two related diseases, in order to avoid this disease becoming worse and affecting the other, doctors will treat reflux. gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) as needed.
Mềm sụn thanh quản tự cải thiện mà không cần điều trị.
7. Home Remedies
With cases of laryngeal softening, you can go home to monitor and do not need surgical intervention, you and your family can still continue with normal activities. However, adults also need to carefully monitor the baby for any other serious symptoms to promptly take him to the doctor.When taking care of the baby at home, you can keep the following points in mind:
Limit the baby lying on his back: Raise the baby's head slightly and let the baby sleep on his side. This will help reduce wheezing because the airway is less prone to the laryngeal cartilage tissue. Cleaning the nose and throat for children before sleeping: Before going to bed, you need to use physiological saline solution to clean the baby's nose and throat. In addition, parents can apply lip balm to prevent the baby's lips from drying out and chapping due to frequent breathing through the mouth. Smaller meals throughout the day may be possible if feeding or nursing is difficult. Build a really reasonable and nutritionally complete weaning diet. This will help children strengthen their resistance as well as ensure the baby's weight. It is necessary to periodically re-examine according to the doctor's orders until the disease is completely cured. Breastfeeding properly: Because when the laryngeal cartilage softens, the baby will have difficulty in breastfeeding. It can be seen that children with laryngeal softening in most cases will heal on their own when they grow up. However, parents must always pay special attention to their child's case, especially the stridor, so that they can take the child to the doctor and get appropriate treatment. To ensure that children are examined and diagnosed with the most accurate laryngeal soft tissue, parents need to choose reputable medical facilities.
With many years of experience in examining and treating diseases in children, now the Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital has become one of the major health care centers, capable of examining , screening and treatment of many specialized diseases in children. Therefore, if the child shows signs of wheezing and wheezing for a long time, it is likely that the child has laryngospasm. In this case, parents can take the child to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and receive support and advice from doctors.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.













