This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Dinh - Head of Respiratory - Asthma - Allergy - Clinical Immunology Unit, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Asthma is a condition in which the bronchi are severely inflamed and constricted, causing the patient to feel short of breath, having to breathe quickly, hissing with long breaths, wheezing... Bronchial asthma often occurs in the early morning or late at night. . So is asthma a contagious disease?
1. What are the symptoms of asthma?
Symptoms of asthma are very diverse, patients sometimes have only a few symptoms at a certain time, for example, during exercise, or may have frequent symptoms because each person's body is different. Asthma symptoms include: Shortness of breath. Chest pain (Heaviness in the chest), insomnia due to wheezing, coughing or wheezing cough, difficulty breathing or wheezing, wheezing. Cough and wheezing are worse with respiratory viral infections, such as colds or flu.You should watch out for some signs of worsening asthma such as: symptoms come more often and more severe, shortness of breath increases, limit physical activity more, especially when limiting the activities of daily living or (increased shortness of breath) increased frequency of asthma reliever use...
The cause of asthma is unknown at this time, but may be due to a combination of both environmental factors and geographical factors. Factors that trigger asthma include:
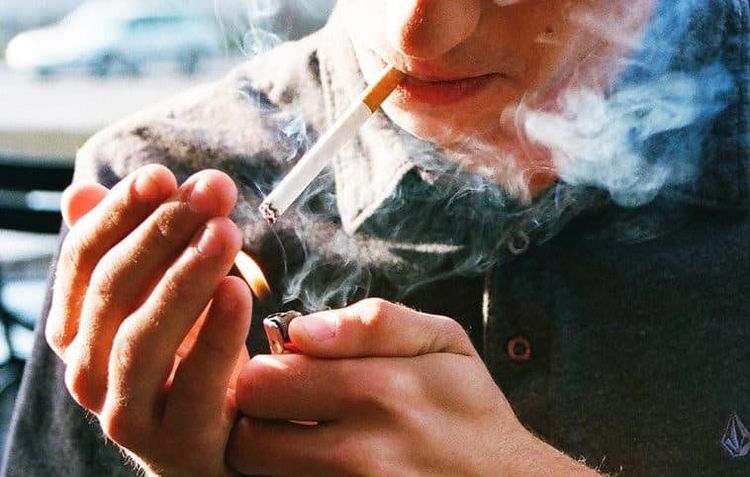
Small particles such as pollen, cement dust, animal hair... Factors that cause respiratory infections such as bacteria, viruses. Physical activity (increases severity of the disease if done incorrectly). Cold. Smoke. Some drugs such as Beta blockers, aspirin, ibuprofen. Stress, anxiety, emotion. Abnormal opening and closing of gastric pyloric cap Gastroesophageal reflux.
2. Is asthma contagious?
Asthma has a significant impact on people's quality of life. Therefore, many people worry that asthma will spread to other family members, especially when loved ones share common household items. However, in reality, asthma is not caused by a virus or bacteria, so it is not contagious.You don't need to worry about "is asthma contagious", instead, feel free to take care of and share daily living items with asthmatics.
Although asthma is not a contagious disease, it is hereditary. There are many factors that are thought to increase the likelihood of developing asthma including:
Having a close relative with asthma. Allergy history. Fat. Smoke. Passive smoking. Frequent exposure to chemicals.

3. Is asthma curable?
Because asthma still has no cure, the best way for patients is to improve quality of life and limit asthma attacks, so the best way to improve quality of life and limit asthma attacks bronchiectasis is adherence to treatment and periodic assessment of disease status. Asthma therapy for patients is relatively complex, patients need to recognize when an asthma attack is coming, avoid asthma triggers, use medication properly and have a reasonable working regimen. In many asthma attacks, patients may need quick-relief medications such as albuterol throat spray or nebulizer.In addition, depending on the patient, there will be different drug support devices. Common drug support devices such as inhalers, metered dose inhalers.
=>> See more: Breathing exercises for people with asthma
4. Certain medicines used in the treatment of asthma
Asthma treatment consists of two main purposes: to relieve acute asthma attacks and to prevent re-occurrence of acute asthma attacks (prophylaxis).Reliever medications include: Short-acting Beta-agonists (SABAs): These are bronchodilators and are used to relieve asthma attacks locally. The most common drugs are Salbutamol, Terbutalin and Fenoterol.
Medications to prevent bronchial asthma:
Inhaled corticosteroids: Inhaled corticosteroids are most commonly used in the treatment of asthma, especially allergic asthma. Due to its anti-inflammatory nature, the drug enters the bronchi and alveoli to reduce inflammation in the lungs, helping to reduce the risk of acute asthma attacks in patients.
Leukotriene antagonists: Suppress inflammatory substances caused by the immune system. Usually used for patients with poorly controlled bronchial asthma or bronchial asthma with allergic rhinitis.
Long-lasting Beta-agonists: Same as SABAs, but their effects last longer. Often combined with corticosteroids and used for the purpose of controlling and preventing asthma attacks.
Omalizumab (Xolair): Used in the treatment of allergic asthma. The drug binds to immunoglobulin E (IgE), reducing the amount of free IgE that triggers allergic reactions. However, this drug is quite expensive, so it is not used much in Vietnam.
Immunotherapy: The aim of immunotherapy is to help the body tolerate the allergens that trigger or worsen asthma attacks while these allergens cannot be completely eliminated in the environment such as: : house mites, pollen,...
Oral corticosteroids: Short-acting asthma medications and quick relief of acute asthma attacks. Long-term use can cause a lot of side effects.
Drugs Theophylline: Drugs are taken daily to dilate the bronchi. However, theophylline has many side effects while the benefits do not exceed other drug classes, so it is no longer used as much as it used to be.
Although medications help prevent and relieve symptoms, patients should still maintain a healthy and fit lifestyle, reducing the likelihood of asthma attacks. Ways for patients to manage their symptoms on their own, such as regular exercise; maintain a reasonable weight, proper work and rest regime, disease status,..
Asthma is a chronic and non-infectious disease. Because there is no definitive treatment, improving quality of life and reducing the number of asthma attacks is the best way to help people with asthma continue to live and work well.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.