This is an automatically translated article.
The uterus is an extremely important part of a woman. The cervix is also a structure that helps produce mucus, creating a favorable opportunity for the fusion stage, helping sperm penetrate deep inside the uterus to reach the fallopian tubes to fertilize. However, with that important role, the uterus is also the place where many obstetric and gynecological diseases occur that women need special attention.
1. Structure of the uterus
The normal uterus of a woman has an inverted pear shape, consisting of 3 layers from the outside to the inside: the serosa, the smooth muscle layer, and the endometrium. The endometrium is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is influenced by monthly sex hormones in the female body.2. Some benign diseases in the uterine lining and methods of treatment
The benign pathologies in the uterine lining include:
2.1 Endometrial polyps This is a benign form due to the growth of the uterine lining organization with different sizes. Polyps can be in one or more locations, even occupying the entire uterine cavity.
Common symptoms are menorrhagia, heavy bleeding, accompanied by a lot of white blood, in a few cases the patient has no symptoms and is only discovered by chance during physical examination or when taking a hysterogram for diagnosis. infertility.
Treatment of endometrial polyps is usually laparoscopic-guided surgical excision. Medical treatment can be combined with progesterone drugs to improve hyperestrogenic status.
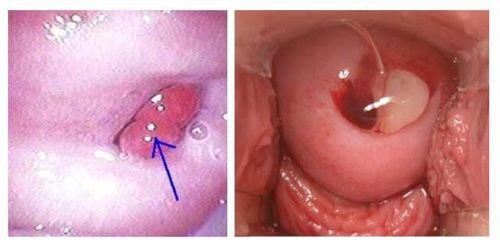
Polyp nội mạc tử cung
2.2 Endometrial hyperplasia This is the hyperplasia of the endometrium in both quantity and density of the endometrial lining.
Caused by luteal hyperestrogenic or hypo-progesterone status, which is common during puberty (proliferation of the uterine lining due to anovulatory cycles), or in perimenopause due to a decrease in luteal progesterone , and the postmenopausal group due to exogenous elevation of estrogen due to hormone replacement therapy.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia are usually irregular menstrual cycles, intermenstrual bleeding, menorrhagia, or hypermenorrhea. Ultrasound shows increased endometrial thickness, endoscopic images show irregular endometrial papillae, which requires curettage and biopsy to give accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is usually not necessary for girls, just adjust the nutrition and rest appropriately and in moderation.
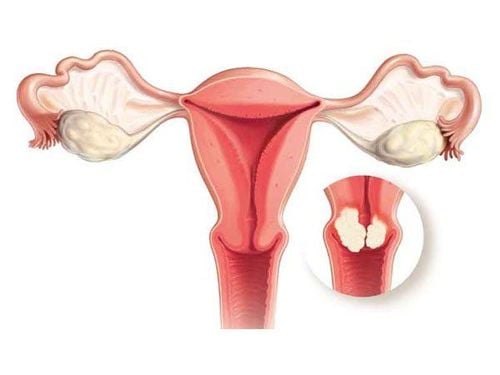
However, for the premenopausal age group, endometrial biopsy is required for pathology. If endometrial hyperplasia is atypical, high-dose progesterone can be given for 6 months and then re-examined. If results indicate atypical endometrial cell proliferation, complete hysterectomy should be performed.

Sinh thiết nội mạc tử cung để làm căn cứ chẩn đoán bệnh
2.3 Endometrial atrophy This is a condition that occurs in postmenopausal women due to a lack of hormones from the ovaries. Endometrial atrophy often accompanies the entire genitalia. Endometrial atrophy is also seen in women of reproductive age due to estrogen deficiency with secondary amenorrhea manifestations. Women who use combined oral contraceptives are also subject to endometrial atrophy. In these two cases, endometrial atrophy was simply not accompanied by atrophy of the sex organs. In the case of a problem with treatment only when abnormalities appear, then the doctor will usually prescribe low-dose estrogen in combination with antibiotics. If the treatment results are not satisfactory, the total hysterectomy should be considered. 2.4 Uterine adhesions It usually occurs after a trauma due to the adhesion of the uterine wall surface layer or after a curettage procedure, which results in partial loss of endometrial area. The morbidity rate is also increased when aspiration curettage is performed on the pregnant uterus, because at this time the endometrium is quite soft and congested, which can easily damage basal cells.
Mất một phần nội mạc có thể dẫn tới dính tử cung
In addition, the cause may also be due to curettage, biopsy, fibroid removal or lumen surgery. Common symptoms of uterine adhesions are oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea or amenorrhea, and abdominal pain when menstruating. Contrast-enhanced hysterosalpingography shows defects, atrophy, and narrowing of the uterine lumen. Treatment of uterine adhesions requires surgical excision of the adhesions combined with hysteroscopy, then a silastic lamellar is placed for 10-15 days and then replaced by an IUD. Medical treatment can be combined with a course of estrogen to stimulate the rapid regeneration of the endometrium after removal of adhesions. Customers with gynecological diseases can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. The team of gynecological specialists at Vinmec are well-trained, professional and experienced; system of modern equipment, meeting international standards; Professional service quality, high efficiency in diagnosis and treatment.
For detailed advice, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.