This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Hoang Thanh Nga - Ophthalmologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Laparoscopic orbital decompression surgery is endoscopic surgery to remove the inner wall of the eye to reduce the pressure inside the orbit. Surgery can reach the top of the orbit.
1. Overview
Basedow's eye disease remains a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge to date. It is an autoimmune disease and is also the most common manifestation of hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. On the other hand, Graves' disease can also be seen in euthyroid or hypothyroid patients, making it difficult to diagnose.
Although the pathophysiology of Graves' eye disease is still not completely clear, the treatment of Basedow needs to combine the treatment of thyroid hormone disorders and orbital diseases.
For these patients, orbital decompression surgery is the only effective treatment. The purpose of orbital decompression surgery is to relieve intraorbital pressure to release compression by cutting the orbital bone wall and removing hypertrophied orbital fat to increase orbital volume.
2. Indications for orbital decompression surgery based on treatment
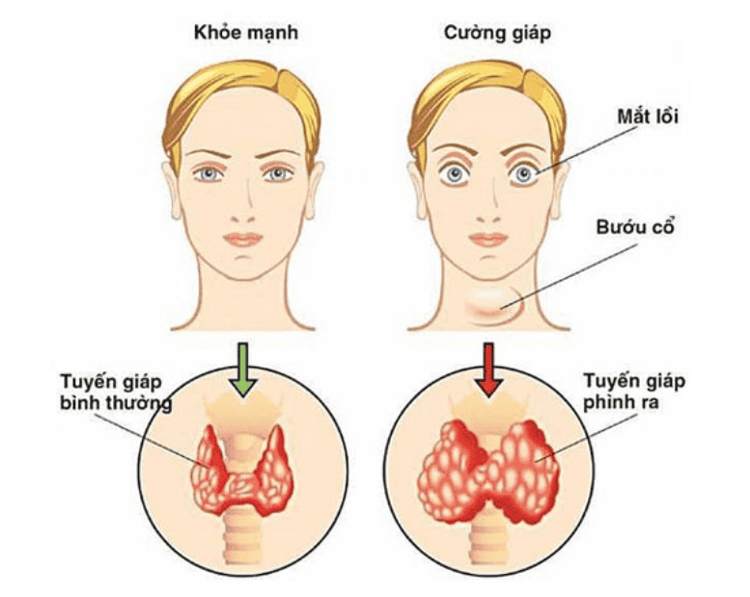
Tuyến giáp phình ra là yếu tố bị lồi mắt
- Orbital hypertension due to edematous hematoma after trauma, inflammation, ..
- Eye protrusion due to thyroid disease
Techniques to reduce orbital pressure (to reduce convexity and release nerve compression) vision) by removing the thin bone - the paper bone in the inner wall of the orbit and the ethmoid cells so that the orbital organs are released.
Surgery allows to clearly see the bone wall to be removed, can reach the top of the orbit, so it is effective in releasing compression of the optic nerve in particular and reducing orbital pressure in general. The surgery causes little bleeding from the top of the orbit, does not increase the pressure on the optic nerve and the organization in the orbit during surgery (the factor is believed to contribute to the decrease in postoperative visual acuity). The incision does not leave scars, does not cause edema of the orbital organization, so it has aesthetic advantages. Surgery can be performed in conjunction with external or inferior wall decompression to increase the effectiveness of the thyroid in cases of large convexity.
3. Preparation steps
3.1. Performers Otolaryngology specialists with master's degrees, specialty II and above are trained in-depth in endoscopic sinus surgery.
3.2. Means - Nasal endoscopic surgery kit, optic 0o and optic 45o, long diamond drill and water pump device to reduce heat of the abraded bone.
- Anesthetic: Lidocaine and adrenaline 1/10,000. Use vasoconstrictor drugs such as naphazolin, oxymetazolin.
3.3. Patients Patients can:
+ Perform routine tests
+ Preoperative examination as usual.
+ Endoscopic examination of otolaryngology.
+ Take computed tomography film of the nose and sinuses in 2 coronal and axial positions.
4. Implementation steps
Gây mê toàn thân
4.1. Methods of anesthesia, anesthesia Surgery can be performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
4.2. Technique The patient lies on his back with a round pillow under his head. Use a nasal wick impregnated with vasoconstrictor drugs: naphazolin, oxymetazolin, .. put in the nose. Use a rice knife to cut the hook tip from front to back or back to front with reverse cutting pliers. Use reverse cutting pliers to widen the maxillary sinus opening. Open the ethmoid balloon with Blakesley forceps or a curettage to drain the anterior ethmoid sinuses. Open through the medial lamina propria to the posterior ethmoid cells for cleaning and drainage, exposing the bony bony. Cut paper bone with trowel. Use the punching pliers to gradually gnaw the paper bone in the direction down, up and back. Paper bones can also be gnawed from back to front with reverse pliers, but we need to stop the manipulation when approaching the hard bone area to avoid injuring the tear duct. The assistant must press on the eyelid so that the surgeon can see how much of the orbital sheath has been exposed. The bone connecting the inner wall and the lower wall of the orbit is very thick, so we should not take this bone wall because this movement can cause double vision. Use a sclera knife after the entire orbit has been decompressed. First make a horizontal incision starting posteriorly on the fascia, then make several parallel incisions and then make vertical incisions to form a mesh. Be careful not to make a deep incision, which will damage the internal rectus muscle. After the choroidal incision is completed, the assistant uses the hand to press the eyeball to make the sclera fragment completely separate and the orbital fat can easily pass through the newly created opening into the nasal cavity. In total orbital decompression surgery, a diamond drill is used to remove bone at the top of the orbit (this bone is very hard and strong). While drilling, water must be regularly pumped to avoid the heat effect caused by the friction transmitted to damage the optic nerve
5. Post-operative care

Sử dụng thuốc kháng sinh để cầm máu
Use antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, pain relievers, hemostasis. Drop the nose with physiological saline.
6. Complications and treatment
Periorbital cellulitis: The patient's symptoms of swelling and pain in the eyes gradually increase. Treatment: Use antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, pain relievers. Antibiotic eye drops. If you are experiencing vision problems, go to a medical facility immediately to be examined and treated by a doctor as soon as possible. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has vision-related service packages such as:
Refractive error screening package Cataract surgery consultation and examination package Ortho-K package
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.