This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Thi Vuong - Doctor of Microbiology - Laboratory of Laboratory - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Researching the formation and reproduction of bacteria is very helpful for applications such as antibiotic production, vaccine preparation for infectious diseases,...
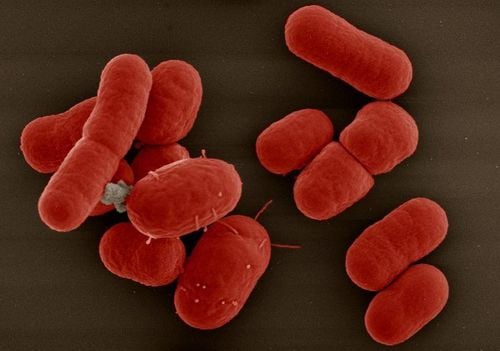
1. What are bacteria?
Bacteria (English name is bacteria, plural is bacteria). This is a group of single-celled microorganisms that are very small in size, can only be observed with a microscope and usually have a simple cell structure, without a nucleus, cytoskeleton or organelles.Bacteria have many forms but can be classified into 3 basic types: spherical (called cocci), straight (called bacilli) and curved (including bacilli - short curved, spirochetes - with many spiral). Bacterial size varies according to the type, and within a type, the size of bacteria also varies. The unit of measurement for bacteria is the micrometer (1 micrometer = 1/1000 millimeter). Most bacteria are 1 micrometer in size.
Bacteria are the group with the most abundant presence in the living world. They are present everywhere: In soil, water, hot springs, radioactive waste, and in symbiosis, parasitic with other organisms, even in manned spacecraft.
Bacteria play an important role in recycling nutrients such as: Fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere and causing the decay of other organisms, providing nutrients necessary for life. Besides, bacteria, yeast, and mold are also used to process fermented foods such as: Yogurt, cheese, pickled cucumber, vinegar, wine,...
However, there are many types. bacteria causing diseases to humans and animals and plants, causing serious harm to human health and production activities. And with the development of modern medicine, people have found ways to control the harmful effects of bacteria such as making vaccines, using antibiotics,...

2. Bacterial formation and reproduction
Bacteria reproduce only asexually, not sexually. More specifically, bacteria reproduce primarily by fission, or direct division. During mitosis, a parent cell is divided into 2 daughter cells by creating a septum that directly separates the parent cell in half. The rate of division depends on the type of bacteria. Specifically, TB bacteria have a slow multiplication rate of 18 hours/time; the average division rate of bacteria is 20-30 minutes/time; Cholera bacteria have a rapid division rate of 5-7 minutes/time.However, even without sexual reproduction, genetic changes (also called mutations) occur in bacterial cells through genetic recombination activities. Finally, the bacteria acquire a combination of traits from the two parent cells.
Types of genetic recombination include: Transformation, transduction and transduction:
Transformation: transfer of naked DNA from one bacterial cell to another through the external liquid medium; Transduction: Transfer of bacterial and viral DNA from one cell to another via phage; Transfer: Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another via a protein structure called a pilus (sex hair). After receiving DNA from one of the three methods above, the bacteria will divide and pass the recombinant genome to the next generation.

3. Application when studying bacteria
Bacterial plasmid structure: In bacteria, plasmid structure is a small circular DNA molecule that does not carry the main genome of the genome, carrying extremely important genes of bacteria. Plasmid plays an important role in the field of medicine - biology - agriculture - pharmacy and environment. They are reservoirs of antibiotic-producing genes; is the owner of a gene that produces products of antibiotic resistance in some pathogenic bacteria; at the same time is the owner of some toxin-producing genes and virulence-enhancing proteins for bacteria. Many plasmids are beneficial like plasmids in bacteria in legume nodules that allow the bacteria to capture nitrogen for protein production.In addition, there are many types of plasmids containing antibiotic-producing genes, which are used to produce antibiotics to treat diseases for humans and animals. Others contain genes that produce special yeasts, which help break down toxic organic compounds, chemicals, industrial waste, pesticides, disinfectants, etc., which contribute to environmental protection.
Bacterial growth: Includes 4 stages: Adaptation, growth, maximal and decline. In terms of application, when bacteria invade and cause harm, it is necessary to intervene early, right in the period when the bacteria are adapting to the environment and have not yet reproduced (for example, dressing, treating wounds early in the first 5-6 hours). to avoid infection). If you want to study the typical properties of bacteria, it is necessary to take bacteria cultured at a period of strong growth. In case you want to collect a lot of bacteria to make vaccines and antigens, it is advisable to collect at the maximum stage. Bacteria include beneficial bacteria and harmful bacteria. Humans need to exploit the benefits brought by bacteria and control the harmful effects of bacteria to improve the quality of life.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.