This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Huynh Vu Khanh Linh - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International Hospital
When a newborn baby is born, he or she will have a health check to make sure that his health is normal. Midwives will use the Apgar scorecard to assess the baby after 1 minute and 5 minutes of life. These scores will be recorded in the medical record.
In addition, the baby will be checked for other health indicators, including:
1. Baby's weight
After the Apgar assessment, the baby was weighed. This is an indicator you are often asked when telling family and friends about your baby. Newborns are usually 2.5 - 4.5 kg. Newborn babies are also measured for length (about 50cm) and head circumference.
Kiểm tra cân nặng để đánh giá tình trạng trẻ sau khi sinh
2. Check the external characteristics
After weighing the baby, the midwife will evaluate some additional external characteristics. Check the baby's head for serous tumours, check the lips and pharynx (cleft palate - cleft palate), count the fingers and toes, check the baby's adhesions, spine (spondylolisthesis), baby's temperature, whether the baby has meconium or urine, external genitalia as well as a few other abnormalities.
3. Other tests
The baby will have a follow-up check in a few days such as eyes, ears, heart, hips, primary reflexes and internal organs. Before you go home from the hospital, the midwives and pediatricians will do a complete exam of your baby.
4. Newborn screening
Currently, Vinmec hospital has implemented newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases (G6PD enzyme deficiency, congenital hypothyroidism, congenital adrenal hyperplasia and some other congenital metabolic disorders) through blood drops. heel, hearing test...

Lấy máu gót chân để thực hiện sàng lọc sơ sinh tại bệnh viện Vinmec
5. Vitamin K injection
Vitamin K deficiency Bleeding (VKDB) - Bleeding due to Vitamin K deficiency.
There are 2 types of VKDB: Early bleeding in the first week and late bleeding when the baby is 1-12 weeks old. Symptoms may appear as unexplained bruises, nosebleeds, bleeding around the umbilicus, and in more severe cases, brain hemorrhage. Jaundice that persists for more than 2-3 weeks can be a sign of liver disease, or it can also be caused by internal bleeding. Vitamin K has a particularly important role, helping to form the prothrombin complex needed for blood clots to prevent bleeding. Babies are born with breast milk, a valuable nutrient, but vitamin K content in breast milk is low (2-5 mcg/liter). Vitamin K stores in newborns are also very low because vitamin K naturally does not cross the placenta. The bacteria in the intestines of children have not yet developed, so they cannot synthesize vitamin K, leading to vitamin K deficiency in children. Therefore, children are prone to bleeding, especially cerebral hemorrhage - meninges often leave severe sequelae.
Vitamin K injection for newborns is an active preventive measure, avoiding the phenomenon of cerebral - meningeal haemorrhage, which is common in children at about 1 month of age. Vitamin K only needs a small dose to help the baby's blood clotting process effectively.
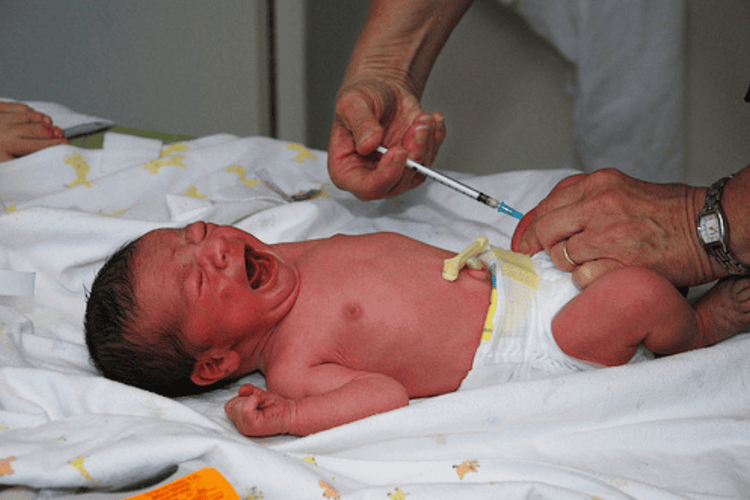
Tiêm vitamin K cho trẻ mới sinh là biện pháp dự phòng bệnh cùng quan trọng
6. Postpartum vaccination
Children will be examined and advised on vaccinations for common diseases:
BCG vaccine : This is a tuberculosis vaccine and should be given as soon as possible after the baby is born.
Hepatitis B vaccine neonatal dose : Hepatitis B vaccine is used to prevent hepatitis B and should also be given to babies within 24 hours of birth.
After discharge from the hospital, the child will be given a vaccination record and instructions on scheduled immunizations.
To learn about assisted reproductive methods at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE.