This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by BSCK I Le Thi Thu Hang, Dermatologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. Dr. Hang has over 10 years of experience in the field of dermatology. Her strengths are in the treatment of adult and pediatric skin diseases, sexually transmitted diseases, autoimmune and rare skin diseases.Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease. This pathology can be accompanied by other atopic diseases such as asthma, hay fever or allergic rhinitis... Symptoms of atopic dermatitis usually start very early, right from infancy, can be continues into adulthood or can appear at any point in life.
1. How to recognize atopic dermatitis?
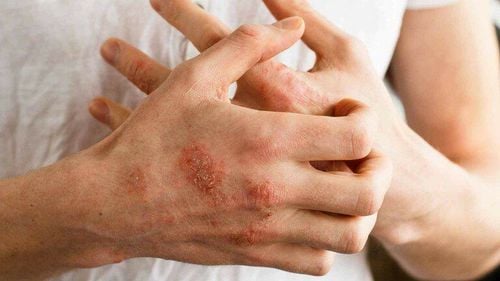
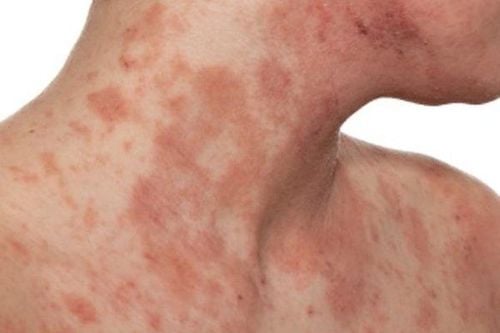
Atopic dermatitis can affect any area of the skin, but it is most common in the hands and in the folds (knees, elbows...). The symptoms flared up in waves, then subsided and after a while they would return. Therefore, this disease greatly affects the quality of life, making patients tired and uncomfortable.
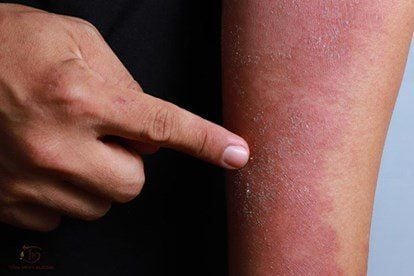
Atopic dermatitis often progresses in stages, in the acute episode, the patient sees an area of red and itchy skin. The degree of itching is sometimes very severe, especially at night, making it difficult for the patient to sleep. As the disease subsides, the skin will turn brown, gray, or leave thick patches of skin due to excessive rubbing.
Due to itching, many patients have to scratch, the diseased skin is very easy to scratch, can become infected, the lesion will be inflamed, pus-filled, and has a bad smell. Chronic itching and prolonged rubbing cause thickening of the skin. Skin characteristics of patients with atopic dermatitis are often dry, cracked.
2. What causes atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a familial allergic and immunological disease. The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is still unclear. Some hypothesize that because the skin is too dry and easily irritated, and at the same time, disorders in the innate immune system can also cause itchy rashes on the skin. Accordingly, this condition can have an early onset from infancy as well as many family members with asthma, allergic rhinitis ...
Several other factors are believed to have sex. dermatitis is more likely to trigger or worsen symptoms such as taking long or hot showers, soap changes, temperature changes, sweating, low humidity environments, wearing furry clothing sheep or man-made fabrics, wool, , exposure to dust, animal hair, tobacco smoke or eating certain foods that are susceptible to allergies such as eggs, milk, fish, soy or wheat... In general , in order to look for the cause, it is sometimes necessary to perform very in-depth tests, but it is not always definite. Therefore, patients are often recommended to avoid the triggers listed above, in order to limit the possibility of disease onset.

3. Is atopic dermatitis dangerous?
Because atopic dermatitis manifests itself in episodes, then self-resolves, with mild forms, most of which do not cause dangerous complications. However, if the patient is itchy and has to scratch a lot, long, pointed nails and poor hygiene can cause skin infections. The structure of the skin is broken, sores and skin cracks are infected by bacteria that live on the skin or even foreign bacteria. Therefore, when the wound on the skin heals again, it can leave bad scars, causing cosmetic loss.
The case of superinfection with the virus causing Kaposi-juliusberg syndrome (or eczema herpeticum) is quite severe, manifesting with fever, fatigue, skin blisters, organ damage... the mortality rate is 1- 1. 9%.
In addition, due to chronic diseases lasting many years, if treated incorrectly, overuse of topical or oral corticosteroids can lead to systemic redness. The patient's whole body is red, there may be episodes of fever, chills, frequent itching...
Atopic dermatitis in the skin around the eyes makes the patient uncomfortable, itchy, and the skin around the eyes is dark due to frequent scratching. affect aesthetics. Excessive scratching causes scratches on the skin that can become infected. Eye complications include persistent tearing, eyelid inflammation, and conjunctivitis. If eye complications are suspected, see a doctor as soon as possible.
4. What to do when you have atopic dermatitis?
When there are signs of atopic dermatitis as described, it is advisable to visit a dermatologist to confirm the disease as well as rule out other diagnoses. When you go to the doctor, you should let the doctor know how uncomfortable the signs are, when the disease started and how long it lasts.
In addition, it is also necessary to mention any factors that are thought to trigger the disease, such as changing weather, using soap, sweating, cigarette smoke... Besides, the doctor also needs to know you Do you have any food allergies or allergies, and are there any family members with similar illnesses?
5. How to cure atopic dermatitis?
The goal of treating atopic dermatitis is to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and prevent future flare-ups and complications. Accordingly, the drugs are often prescribed by the doctor in detail as follows:
Anti-itch cream: Apply to the skin with symptoms. However, if the patient's itching is so severe that it interferes with activities, sometimes an oral antihistamine is needed. With anti-allergic drugs that cause drowsiness, doctors often prescribe them to be taken at night.
Moisturizer: Combined with anti-itch cream to reduce discomfort. In addition to acute attacks, it is necessary to regularly moisturize the skin, soften the skin when the weather is cold and dry, and avoid letting the skin crack, which will easily cause itching.

Anti-inflammatory cream: Limiting the excessive local inflammatory reaction makes the symptoms better, the skin is less red, swollen, and itchy. However, the use of anti-inflammatory creams should be limited when the itching has subsided and other self-care therapies such as moisturizing and softening should also help control mild atopic dermatitis instead of medication. Because if used for a long time with anti-inflammatory, it will cause side effects such as discoloration of the skin, thinning of the skin, hair growth and easier skin infection. Anti-inflammatory creams with corticosteroids should only be used when prescribed by a doctor, depending on the nature of the lesion, the doctor will prescribe the active form from mild to severe.
Antibiotics: In case the patient has a skin infection, the treatment needs to add antibiotics for a short time to treat the infection. At the same time, if the wound is open and exudes fluid, the patient needs to cover with gauze, clean and change the bandage every day to avoid superinfection.
Limiting factors that trigger the onset of the disease: Many patients worry if atopic dermatitis is contagious because they are afraid that they have been infected by others or are afraid that they will spread it to their family members. However, the disease is caused by the body of each person, so it is completely non-contagious.
Accordingly, what needs to be done is to limit the factors that trigger the onset of the disease:
Avoid allergenic foods, clean the house, wash blankets, pillows, mattresses, carpets and curtains regularly, avoid smoke tobacco and dusty environment. Shower not too long; per shower, limit it to 15-20 minutes and use warm rather than hot water. Should use a perfume, soap fixed and mild detergent; If you want to make a change, you should test it on a thin area of skin first to see if it causes irritation. Limit scratching to a minimum; For young children, it is necessary to trim their nails and wear gloves at night. When it's hot, wear cool clothes. When it is cold and dry, it is necessary to nourish the skin with moisturizing creams and waxes. Drink enough water. Other treatment measures: Immunotherapy is gradually being applied in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in particular and diseases caused by other immune disorders in general. However, the long-term effectiveness and safety of these drugs are still unclear, so they are only approved for children over 2 years of age and for adults. Also, it should only be used when other treatments have failed or are completely intolerable.
Phototherapy: This method has also shown positive results, correcting disorders within and just below the skin structure; However, its wide applicability requires further study, as there is some evidence that it causes premature skin aging as well as an increased risk of skin cancer.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package of examination and advice on treatment of atopic dermatitis to help customers assess the overall condition of the disease and advise on measures to help prevent recurrence.
When registering for a package of examination and advice on treatment of atopic dermatitis, customers will receive: Dermatology specialist examination. Perform tests such as: quantitative IgE, fresh mycobacteria, specific IgE quantification with respiratory allergens - food (Panel 1 Viet), test Rida Allergy Screen (panel 1)...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.