This is an automatically translated article.
Malaria is a blood-borne disease transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person by the Anopheles mosquito. If not treated in time, people with malaria will experience many dangerous complications.1. What is malaria?
Malaria is a disease syndrome caused by parasites. This is the most common infectious disease today, seriously affecting public health. The patient has typical clinical symptoms or atypical fever, does not have a blood test or the result is negative but has the following characteristics:Fever in the last 3 days or fever above 37.5 degrees Celsius. Find another cause of fever. The patient is in or has been in contact with a malaria-affected area within the past 9 months. Within 3 days, after being treated with antimalarial drugs, the patient had a good response.
Bệnh nhân sốt rét thường có biểu hiện sốt
Common malaria: Expressed by episodes of malaria
Primary fever: often atypical, high fever for several days. The following fevers are more typical than the previous ones. Typical fever: Typical malaria episodes have 3 stages (chilling phase, hot fever phase, sweating phase). Fatigue fever: the patient will only feel chills, fever spikes usually last from 1-2 hours. Patients with long-term malaria infection often experience this type of fever. Severe malaria - complicated malaria:
Cerebral-complicated malaria: When the patient has symptoms of consciousness disorder, high fever continuously, severe headache, diarrhea... this is a precursor sign. malignant. Mortality rates from cerebral malaria are between 20 and 50%. Hemoglobinuria complications of malaria: Severe form due to massive hemolysis, heart failure, kidney failure. Urine is red-brown, then turns coffee-colored, urine volume gradually decreases, and anuria. Hemolysis causes yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. Insufficient blood and oxygen supply. The number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is drastically reduced. Malaria with cold complications: Blood pressure drops, the whole body becomes cold, pale skin, sweating, headache. Malaria gastrointestinal complications: patients have abdominal pain, nausea, or diarrhea, low body temperature. Malaria with hepatobiliary complications: Patients have jaundice, yellow eyes, yellow stools and urine. The patient may also go into a coma.
2. Is malaria contagious?
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite. This disease is transmitted mainly by Anopheles mosquitoes. Mosquitoes suck malaria parasites in the blood of an infected person to a healthy person. Major modes of transmission include:Malaria transmitted by mosquitoes: This is the main mode of transmission. Malaria is caused by blood transfusions contaminated with the malaria parasite. due to sharing needles (needles contaminated with blood containing the malaria parasite). Malaria parasites do not exist in the external environment, only in the blood and in the body of the mosquito that transmits the disease.
Malaria, if diagnosed late, will cause dangerous complications, possibly death within 12 hours.
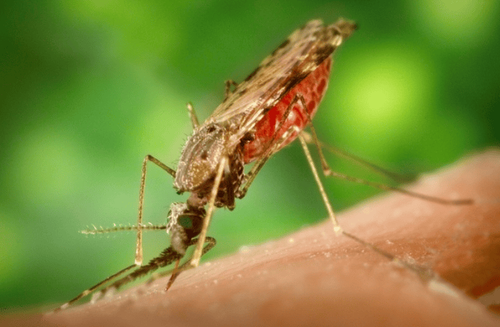
Bệnh sốt rét lây truyền qua muỗi Anopeles
3. At what stage does malaria spread?
A patient with malaria remains a source of transmission as long as there are gametocytes in the blood. If not thoroughly treated, the source of infection remains for 1-2 years.Mosquitoes infected with malaria parasites can transmit the disease for a lifetime
In Vietnam, the malaria season usually has a strong spread rate between April-May and September-October (beginning and ending of the rainy season). In June, July, and August, Anopheles mosquitoes are less developed, so the disease progresses more slowly. In the South, malaria occurs all year round and develops more in the rainy season.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.