This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Phuong - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. Dr. Le Thi Phuong has 29 years of experience in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.Forceps childbirth is a commonly used assisted delivery method in obstetrics. However, not many women know about this procedure as well as the risks that can be encountered when having a Forceps birth.
1. What is the technique of placing Forceps?
For women who give birth vaginally, labor has 3 stages. In the second stage is the pregnancy loss stage, this is the most important stage, the mother with the contractions of the uterus combined with the contractions to expel the fetus.
The time allowed at this stage only lasts for 30 minutes, if the labor lasts longer, it will be detrimental to the fetus, the baby will be born asphyxiated, which is very dangerous or in extreme cases. In case of medical conditions, the mother has heart failure, asthma, if the mother has an old incision, if she keeps pushing, the risk of maternal complications will be more severe.
Therefore, with difficult births, the doctor will consider using birth control methods to support the mother such as giving birth by suction or using Forceps forceps.
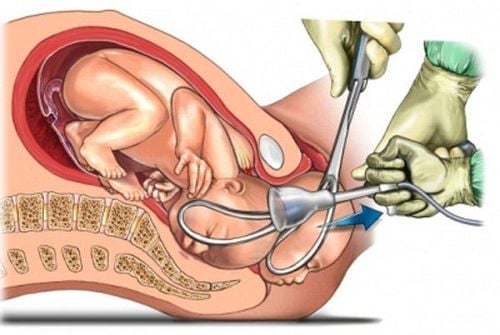
Forceps delivery is a procedure that uses an instrument to pull the fetus through the vagina, by placing a force on the head of the fetus without causing trauma to both the fetus and the mother. The doctor uses an instrument called a forceps, which consists of two separate branches like a hollow spoon, when placed on the head of the fetus, these two branches will fit together by a lock. When they fit together, the doctor uses his hands to clamp, rotate and pull the baby out with the condition that the fetal head is low, the mother's cervix is fully open, and the mother pushes for delivery.
The doctor performs forceps placement, checks that the two branches have matched, and pulls gently by hand according to the birthing mechanism of the fetal position. When the baby's head is out of the vulva, we will remove the forceps and continue the birthing stages, followed by shoulder birth, trunk birth, and the lower two limbs of the fetus come out easily.
2. Indication for delivery with Forceps
2.1 On the mother's side, I pushed hard. Mothers have contraindications for pushing: medical diseases (heart, lungs, kidneys, nerves), uterus with old surgical scars, severe preeclampsia, eclampsia.. Perineum solid, not dilated. 2.2 Fetal side Fetal failure. Forceps head back in the ass. 2.3 Conditions for performing the Forceps procedure The person performing the procedure must have experience with instrumental births, with the following conditions:
The cervix is fully dilated. Amniotic fluid has broken. The fetus has entered. The position and type must be clearly defined. The weight of the fetus and the mother's pelvis are proportional (avoiding the risk of shoulder entrapment). Sufficient pain relief. Empty bladder. The patient's consent was obtained. There is an operating room. Stop the procedure when:
Difficulty placing the instrument. The fetal head does not descend easily when pulled. No abortion after 3 pulls.
3. Contraindications
Fetal pathology: osteogenesis imperfecta, connective tissue disease (Ehlers-Danlos and Marfan syndrome), blood disease (hemophilia, alloimmune thrombocytopenia). The head does not pass or penetrates asymmetrically. Abnormal throne (face, forehead).
4. Possible risks when delivering with Forceps
The use of Forceps for assisted delivery may pose a risk of injury to both mother and baby.
4.1 Possible risks to pregnant women Pain in the perineum – the tissue between your vagina and anus – after delivery. Perineal trauma: The most common complication after forceps intervention. For lower waist forceps, the rate of grade 3 and 4 perineal tears accounted for 13% of urinary incontinence. Bladder or urethral trauma. Uterine rupture - when the uterine wall tears, it can cause the baby or placenta to be pushed into the mother's abdominal cavity. Weakens the muscles and ligaments that support the pelvic organs. Blood loss: this is often the result of severe perineal trauma after forceps intervention. Postpartum infection. Although most of these risks are also associated with vaginal delivery in general, these risks are more likely to occur for women who receive forceps assisted delivery.
The doctor may also have to perform an episiotomy - an incision of tissue between the vagina and anus - before the forceps are placed.
4.2 For the fetus Forceps delivery can cause serious complications for the mother but has little adverse effect on the fetus. Possible complications include minor superficial trauma due to forceps, subscalp hematoma, cranial nerve VII palsy, brachial plexus palsy.
Small scratches on a baby's face after birth with forceps are normal and temporary. Serious injury to a newborn after birth with forceps is rare.
5. How is forceps delivery performed?
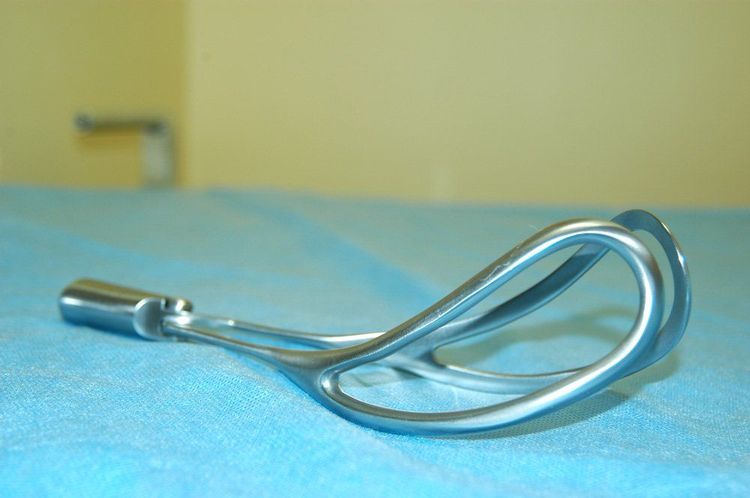
Determine position, potential, position, reach and conditions for forceps. Place two branches of forceps. Joint branches and scissors. Join the two branches together. Pull slowly according to the mechanism of giving birth by the strength of the forearm, best in contractions combined with the mother's pushing, unless there are contraindications to pushing. Cut the perineum between two forceps branches. Remove the forceps: When the maximum diameter of the fetal head (biparietal) passes through the vulva, stop pulling to remove the branch. Branches placed behind are taken out first, branches placed in front are taken out later. Support the fetus like a normal delivery. Check for cervical and perineal lesions. Suture the perineum and lacerations. Postpartum monitoring
Maternal status: blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, temperature. Blood loss, usually from trauma to the genital tract.
6. Notes for women after giving birth with forceps
If you had an episiotomy or a vaginal tear during delivery, the wound may hurt for several weeks. Larger lacerations take longer to heal. If there are unusual signs such as more pain, fever, signs of infection, bowel incontinence, see a specialist for a specific health check.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package Maternity Care Program for pregnant women right from the first months of pregnancy with a full range of antenatal care visits, periodical 3D and 4D ultrasounds and routine tests to ensure that the mother is healthy and the fetus is developing comprehensively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: mayoclinic.org