This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Van Quang - Ear, Nose Throat Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. BSCKI. Le Van Quang is an expert in the field of ENT with 15 years of experience.Patients with otitis externa and auricular hematoma may be indicated for a variety of treatments, including aspiration aspiration. This technique helps to drain the fluid, creating negative pressure to reduce the amount of fluid accumulated in the ear canal, supporting effective treatment.
1. Diseases that need to be treated with ear aspiration
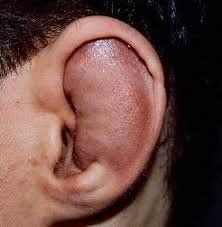
Patients with effusion, hematoma in the ear canal without infection will be indicated for aspiration of the ear canal. This technique is contraindicated with auricular cartilage abscess. The characteristics of the two pathologies are indicated for aspiration as follows:1.1 Cartilaginitis of the ear is an inflammatory condition secondary to an ear injury or a hematoma. The cause of otitis externa can be caused by trauma that damages the cartilage membrane in the ear canal, obstructing the blood flow to nourish the ear cartilage, leading to fluid secretion.
It may be a sterile fluid at first, followed by a secondary infection due to superinfection. The fluid is often located between the cartilage layer and the cartilage layer, hindering the maintenance of the ear cartilage. If not treated, timely aspiration can lead to necrotizing otitis media.
1.2 Auricular hematoma is a condition in which blood accumulates in the coronal area, mainly appearing after an impact injury. The mechanism of injury is to cause a rupture of the meniscus blood vessel, causing blood to flow, pooling between the cartilage layer and the meniscus layer, separating the cartilage layer from the cartilage. If this condition is not treated early, the hematoma will compress and cause inflammation and necrosis of the ear cartilage and lead to complications of the broccoli-shaped ear (cauliflower ear). This condition affects both aesthetics and can lead to tinnitus, hearing loss, headaches,...
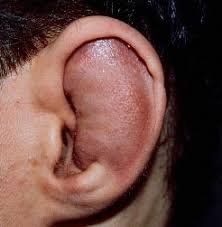
Viêm sụn vành tai tình trạng viêm nhiễm trùng thứ phát sau chấn thương va đập hoặc tụ máu vành tai
2. The procedure of aspiration of ear fluid to treat cartilage inflammation and hematoma of the ear canal
2.1 Preparation of personnel to perform: Ear - nose - throat specialist; Equipment: Surgical forceps, sharp knife, small scissors, needle-carrying pliers, suction probe, syringes of all sizes, gauze, bandages, bean trays, square towels,...; Drugs: Local anesthetic and iodine tincture 1%; Patient: Assigned to perform basic tests such as: Coagulation function, HIV, ... The patient is also instructed by the doctor on personal hygiene (bathing, shampooing,...), receiving instructions from the doctor. explanation of the treatment procedure. 2.2 Carrying out the procedure Disinfection in the ear area; Local anesthetic injection; Use a sharp knife to prick a small wound about 2-3mm in size, enough to drain the fluid, thread the drain wire under the skin of the ear lobe, make an incision in the lowest area of the swelling (hematoma); Place the drain in, the lead is located in the lowest area of the fluid collection block; Stitch the foot of the drainage tube, use a pump with a size depending on the amount of fluid to continuously aspirate; Disinfect, put gauze bandage and perform daily dressing change. 2.3 Monitoring and management of complications Monitor drainage failure, inadequate drainage or dizziness due to pain; Drainage is not tight: Need to sew up the foot of the drainage tube; Drug allergy: Properly manage according to allergy protocol; Pain: It is necessary for the patient to lie down, monitor and handle according to the specific situation; Inflammation of the ear cartilage: Treat as usual cases of otitis externa (using antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, cleaning, aspiration and pressure bandages,...).
Trường viêm tấy sụn vành tai, người bệnh sẽ được chỉ định dùng thuốc kháng sinh, chọc hút và băng ép,...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.