This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Cong Trinh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan allows your doctor to see your organs, bones, and tissues inside your body without having to do surgery. This test can help diagnose disease or injury.
1. What is an MRI scan?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses computer-generated magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in your body.
Most MRI machines are large, tubular magnets. As you lie in the MRI machine, the magnetic field temporarily rearranges the water molecules in your body. Radio waves that align these atoms produce a faint signal, which is used to generate cross-sectional MRI images.
The MRI machine can also produce 3D images, viewed from different angles.
2. How does an MRI work?
An MRI machine is a large, cylindrical (tubular) machine that creates a strong magnetic field around the patient and pulses of radio waves are sent from the scanner. Radio waves knock the nuclei of atoms in your body out of their natural positions. When the nuclei rearrange into the appropriate positions, they send radio signals. These signals are received by a computer that analyzes and converts them to form a two-dimensional (2D) image of the body part being examined. This image then appears on a viewing screen.
Some MRI machines look like narrow tunnels, while others are more spacious or wider. An MRI scan can last from 30 minutes to two hours.
Hình ảnh máy MRI
3. Applications of MRI in cardiovascular, brain, spinal cord, bone, internal organs
MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic method that helps your doctor examine your organs, tissues, and skeletal system. This method produces high-resolution images of the inside of the body that help diagnose a variety of problems.
In orthopedics, MRI can be used to examine bones, joints and soft tissues such as cartilage, muscles, and tendons due to injury or the presence of structural abnormalities or some other condition, such as mass tumors, inflammatory diseases, congenital abnormalities, osteonecrosis, myelopathy, and herniated or degenerative discs of the spinal cord. MRI can be used to evaluate the outcome of orthopedic surgery. Joint deterioration caused by arthritis can be monitored using magnetic resonance imaging.
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend an MRI of bones, joints, or soft tissues.
3.1 MRI of the brain and spinal cord MRI is the most frequently used imaging test of the brain and spinal cord. MRI is often done to help diagnose:
Brain aneurysm Disorders of the eye and inner ear Multiple sclerosis Spinal cord disorder Traumatic effects Tumor Concussion Trauma A special type of MRI - Functional MRI of the brain (fMRI), which can create images of blood flow to certain areas of the brain. It can be used to examine brain anatomy and determine which parts of the brain are handling important functions.
This helps identify important language and movement control areas in the brains of people being considered for brain surgery. Functional MRI can also be used to evaluate damage from head trauma or from disorders such as Alzheimer's disease.
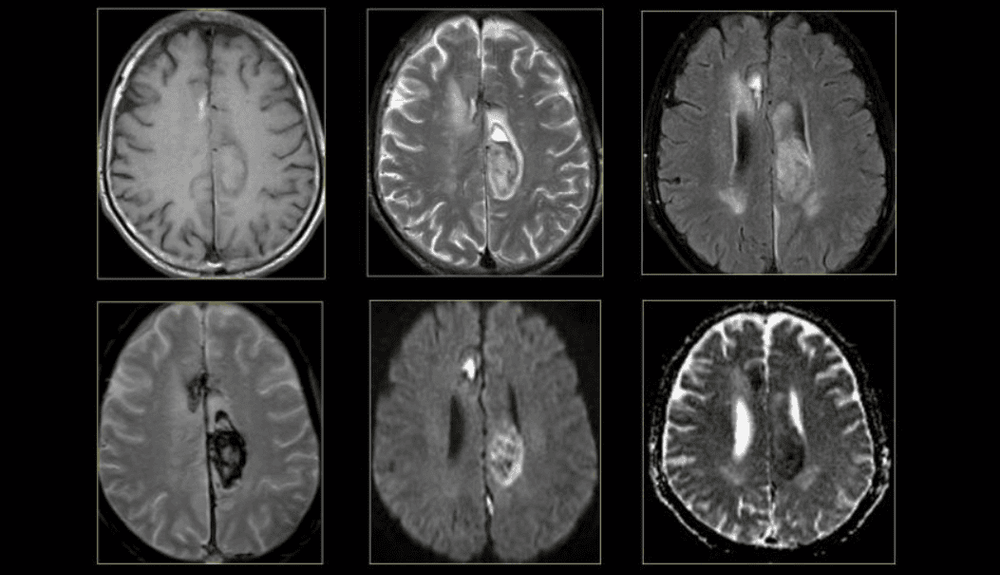
Hình ảnh não bộ trên MRI
3.2 MRI of the heart and blood vessels An MRI that focuses on the heart or blood vessels can evaluate:
Size and function of the heart chambers Thickness and movement of the heart walls Degree of damage from a heart attack or heart disease Structural problems in the aorta, such as aneurysm or dissection Inflammation or blockage in blood vessels 3.3 MRI of other internal organs MRI can check for tumors or other abnormalities of many organs, including:
Liver and bile ducts Kidneys Spleen Pancreas Uterus Ovaries Prostate Prostate 3.4 MRI of bones and joints MRI can help evaluate:
Joint abnormalities caused by trauma or repetitive, such as torn cartilage or ligaments Disc abnormalities in the spine Bone infections Bone and soft tissue tumors 3.5 MRI of the breast MRI can be used with mammography to detect breast cancer, especially in women with dense breast tissue or those at high risk for the disease.
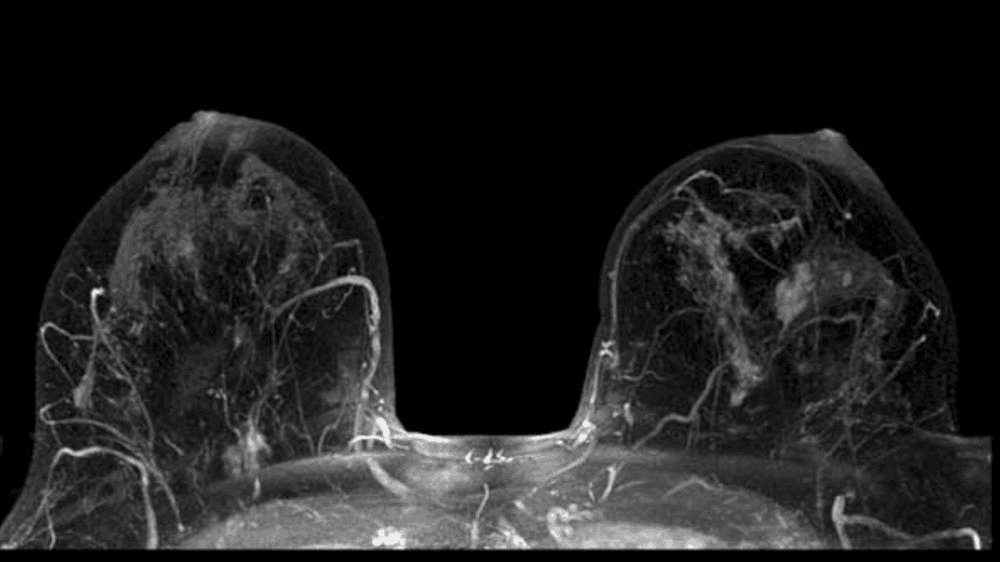
Kết quả chụp MRI vú giúp phát hiện ung thư vú
4. Risks of MRI
If you are pregnant or suspect that you may be pregnant, you should inform your doctor in advance. To date there is no information to show that MRI is harmful to the fetus, however MRI testing during the first trimester is not recommended. Patients with allergies or sensitivities to contrast dye or iodine should notify their physician or technician. If you have severe kidney disease or are on dialysis, there is an increased risk of a "systemic fibrosis of renal origin" from the contrast dye. You should discuss this risk with your doctor before the test. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF) is a very rare but very serious complication caused by the use of contrast dye for MRI testing in patients with renal disease or renal failure. If you have a history of kidney disease, kidney failure, a kidney transplant, liver disease, or are on dialysis, you must tell the MRI technician or doctor before using the contrast medium. The contrast mechanism of MRI can cause a number of other conditions in the patient, such as allergies, asthma, anemia, hypotension, kidney disease, and sickle cell disease. There may be other risks depending on your specific medical condition when having an MRI. You should discuss any concerns with your doctor before this procedure.

Phụ nũ mang thai không nên chụp MRI
5. What do you need to prepare before taking an MRI?
Before your MRI test, eat and drink normally and continue taking your usual medications, unless otherwise directed by your doctor. Usually you will be asked to remove things that can affect the magnetic image, such as:
Jewelry Hairpins Eyeglasses Watch Wigs Dentures Hearing aids Bras Cosmetics containing metal particles Previous when you have an MRI, find out why your doctor chooses this test. You might ask the following questions:
Why do I need an MRI? Is an MRI the best way to check on my condition? How will the results affect my treatment? What are the possible risks? Do the benefits of having this test outweigh the risks to me?
Hệ thống máy chụp cộng hưởng từ 3.0 Tesla công nghệ Silent tại Vinmec
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit to put into use the 3.0 Tesla Silent Resonance Imaging machine, bringing outstanding advantages. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at Vinmec will have the following outstanding advantages:
High imaging technology, first-class safety by accuracy, non-invasiveness and no radiation. High image quality, allowing doctors to comprehensively evaluate, not miss even the smallest lesions in organs Minimize noise, create the most comfort for patients when taking pictures, reduce stress, this helps better image quality and shortens the maximum scanning time. MRI with Silent technology is especially suitable for the elderly and children, people with weak health, and patients undergoing surgery. .. MRI at Vinmec can take 3-D vascular reconstruction without injection of magnetic contrast, can reconstruct and handle motion disturbances of the patient To register for examination and treatment at General Hospital Vinmec International Department, customers can call Hotlines of hospitals or register online HERE.
MORE:
Why do you need a breast MRI? Cardiac MRI: What you need to know Applications of CT, MRI