This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Diem Thi Yen - Doctor of IVF Lab, Reproductive Support Center - Vinmec Times City International HospitalThalassemia is the most common recessive genetic disease in the world accounting for about 4.8% of the global population. In Vietnam, the rate of carrying the disease gene in Kinh people is 2 - 4%. This rate is very high among the Muong, Tay and Thai ethnic groups 22%; over 40% of the Ede and Stieng ethnic groups. This is an inherited disease, the father and/or mother pass the gene to the child. The disease occurs in both men and women.
1. What is Thalassemia (Congenital Hemolytic Syndrome) and how to prevent it?
Diseases related to genetic defects that impair the function of red blood cells. There are two main types of the disease, alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia. Patients with the disease will have frequent hemolysis leading to chronic anemia, requiring lifelong blood transfusions and iron chelation.
Early detection and screening have an extremely necessary role in relation to treatment prognosis. If both husband and wife carry the gene, there is a 25% chance that the child will have the disease.
Therefore, couples who are about to become pregnant, especially families who have had Thalassemia patients, should go for screening to detect timely and take appropriate preventive measures thanks to the PGT-M technique ( preimplantation genetic testing for monogenetic gene disorders).

2. What is the PGT-M technique or testing for genetic diseases caused by a single gene disorder?
PGT-M technique is also known by another familiar name, PGD (Preimplantation genetic diagnosis) - preimplantation genetic diagnosis. PGT-M is being applied in many modern centers around the world, including Reproductive Support Center, Vinmec Times City Hospital.
With this technique we can examine the embryo's genome at a very early stage, thereby detecting abnormal segments on a specific gene that is inherited from the parents.
From there, embryos that are homozygous for the disease gene will be removed before being transferred to the mother's uterus. The effectiveness of this method has been proven to help limit the number of babies born with the disease as well as the need to terminate the pregnancy halfway when the fetus has severe anemia abnormalities.
Not only effective in diagnosing Thalassemia, PGT-M method also helps diagnose many other single-gene diseases in embryos such as hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, X-linked genetic diseases ...
Besides, in the future, this technique will also be applied in the treatment of siblings of children who have been born but have the disease. With PGT-M, it is possible to diagnose human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching of embryos with diseased siblings. Stem cells from umbilical cord blood of children born from embryos selected through PGT-M technique will help treat diseased siblings.
3. How is the PGT-M technique performed?
Basically, to perform PGT-M technique, couples need to have assisted reproduction by in vitro fertilization method. The generated embryos will be raised to day 5.
With the qualified day 5 embryos (blastocysts or blastocysts) biopsies will be performed (3-5 embryo cells are removed from the area where the cells will develop into the placenta. later pregnancy). Cell samples after biopsy will be applied special testing methods to detect disease-carrying genes.
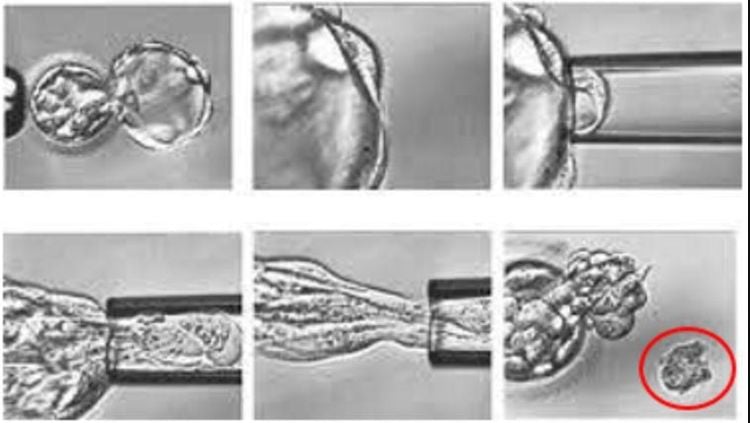
Hình ảnh sinh thiết phôi trong kỹ thuật PGT-M
Today, with modern medicine, it is also possible to perform Ni-PGT-M (non-invasive PGT-M) technique on embryo culture medium samples without needing embryo biopsy.
With this technique we no longer have to worry about possible effects on the embryo during the biopsy, but instead only need to take a small amount of culture medium about 10-20μl. currently diagnosed.
However, this is a relatively new research direction and there is still not much scientific evidence to prove the superior efficiency and reliability of the Ni-PGT-M method compared with conventional PGT-M. .
4. What risks can be encountered when applying the PGT-M technique?
Before being assigned to PGT-M technique, patients should be consulted about possible risks as follows:
No embryos on day 5 : by far, PGT-M method is the best diagnostic method. is still on day 5 embryos, while the percentage of embryos developing from day 3 to day 5 is only around 60%. Thus, it is possible that the patient will not have day 5 embryos for genetic diagnosis, or may have day 5 embryos but the quality of embryos is not qualified to conduct this technique. Results after genetic diagnosis, none of the embryos can be transferred to the uterus: the results after genetic diagnosis can fall into three possibilities (completely diseased embryos, heterozygous diseased embryos, unaffected embryos) sick). Thus, there is still the worst possibility that all the embryos are completely diseased and cannot be transferred into the uterus. Embryos that are mosaic or carry abnormalities other than the diagnosed gene: The PGT-M method only helps in preimplantation diagnosis of abnormalities related to a specific gene, known to be inherited from the parents, but cannot diagnose detect abnormalities in other unscreened genes as well as mosaicism. Therefore, it is still possible for embryos to be screened for diseases related to 1 known gene but still have abnormalities in other genes because of not being screened and diagnosed. Embryo growth stopped after biopsy: because the most common PGT-M method being applied today is on biopsied embryonic cell samples, the biopsy process can have the effect of stopping embryo development. . However, with the advancement of embryo biopsy techniques today, this possibility is rare.
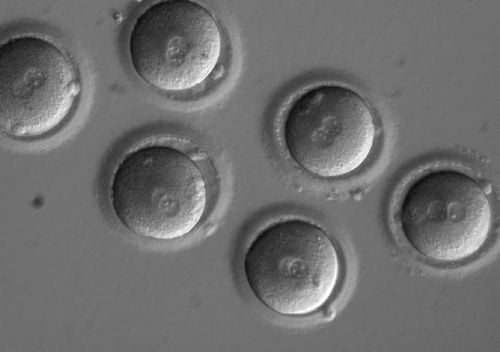
Kỹ thuật PGT-M có thể gây ra một số rủi ro nhất định đối với phôi thai
5. How does Vinmec deploy the PGT-M method to screen for Thalassemia?
Based on all available knowledge and information about single-gene diseases, especially Thalassemia, we need a proactive prevention strategy to reduce the number of children born with the disease, reduce disease burden for the community thanks to PGT-M technique.
Currently, the PGT-M method is being carried out in most modern assisted reproductive centers in the world, including Vinmec Times City Fertility Center. In particular, the success rate of couples doing assisted reproductive technology combined with PGT-M to screen for Thalassemia at IVF Vinmec Times City is up to 75%.
The center is equipped with the most modern equipment and system of culture cabinets for continuous monitoring in the world, the successful rate of embryo culture on day 5 of Vinmec Times City IVF is always above 60%, reducing the relationship The initial concern was that there was no day 5 embryo for the patient.
In addition, a team of doctors and specialists who are well-trained in both professional and technical skills at leading universities in Vietnam (Hanoi Medical University, University of Natural Sciences), are regularly sent Professional updated training in the US, Australia, Spain, France.... patients can be assured of the safety of the techniques as well as the accuracy of the diagnostic methods. genetic prediction.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.