This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Binh - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Binh has more than 20 years of experience in the field of anesthesia and resuscitation.Horseshoe kidney is a birth defect in the kidneys. Horseshoe kidney malformation can cause many bad effects for unfortunate people, especially children. A horseshoe nephrectomy is necessary when this defect causes serious complications that affect the patient's health. The anesthetic method commonly used in laparoscopic horseshoe nephrectomy is endotracheal anesthesia.
1. What is a horseshoe kidney?
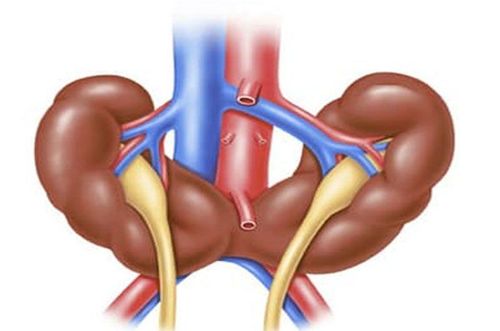
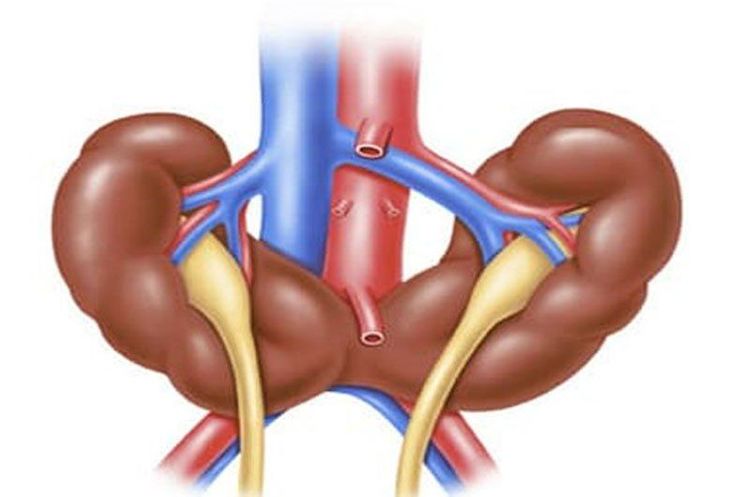
Horseshoe kidney, also known as super kidney, is a birth defect with an incidence of 1/500 people, more common in men than in women. In this malformation, the patient's two kidneys are connected by a false isthmus in the middle, forming a horseshoe-like shape during fetal development. Called the pseudo-renal isthmus because this junction is very small and is only a soft parenchyma, with absolutely no function. More than 90% of cases are adhesions at the lower poles of the 2 kidneys, only less than 10% are adhesions at the upper poles.Also because the two kidneys are connected by a pseudo-renal isthmus, this condition is also called two-kidney fusion. However, the two kidneys are not completely fused because they still have two renal pelvises, two urethras or, in a word, they still have two separate urine drainage routes.
2. Is horseshoe kidney malformation dangerous?
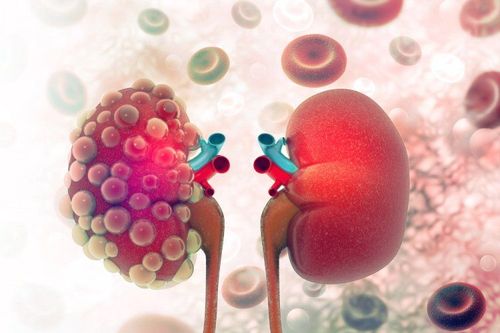
The presence of an additional pseudo-isthmus not only does not contribute to kidney function, but it can also cause many other medical conditions. There are many complications that appear in people with this malformation such as hydronephrosis, kidney stones, urinary tract infections, kidney cancer,...Common complications of horseshoe kidney malformations are: :
Urinary tract obstruction: about 35% of people with horseshoe kidney have this complication. The reason is that the prosthetic isthmus has pushed the junction of the ureter and the renal pelvis higher than normal. This makes it impossible for urine to completely exit the kidneys, resulting in urinary retention and urinary tract infections. Kidney stones: about 20-60% of people with horseshoe kidney defects have kidney stones. Urinary tract infections: about 30-40% of people with horseshoe kidney have urinary tract infections. Renal cancer: up to 45% of renal carcinoma patients have horseshoe kidney malformation.
3. Anesthesia in endoscopic horseshoe nephrectomy
It is not easy for people with horseshoe kidney defects to detect the condition on their own. They are often discovered by accident or discovered during medical examination because of the complications mentioned above.Treatment of horseshoe kidney is treated with isthmus nephrectomy indicated when the thick isthmus of the kidney compresses the ureter causing hydronephrosis. Relative contraindications of horseshoe nephrectomy are: the patient is old and weak, in poor physical condition, in a severe general condition,... unable to tolerate surgery.
Previously, the horseshoe nephrectomy was often an open surgery with many potential risks. Today, thanks to the development of science and technology, the laparoscopic method of horseshoe nephrectomy with many outstanding advantages has replaced the previous open surgery method.
Endotracheal anesthesia is a technique of general anesthesia through endotracheal tubes for the purpose of controlling breathing during surgery and resuscitation after surgery for patients. This method requires medical facilities to have all the necessary modern equipment, and the operator must be trained and proficient in techniques.
3.1. Steps to conduct endotracheal anesthesia laparoscopic horseshoe nephrectomy Check records Check the patient Perform the technique: The general steps are: Patient position: supine, oxygen 100 % at a rate of 3-6 l/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Install the tracker. Set up transmission. If necessary, pre-anesthesia can be performed. Induction of anesthesia: Sleeping pills Pain relievers Muscle relaxants The condition for intubation is that the patient must sleep deeply and have enough muscle relaxation. Carrying out oral intubation: insert the endotracheal tube through the mouth, put the cannula in the mouth to prevent the patient from biting the tube (if necessary). Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics, and muscle relaxants (if needed). Control the patient's breathing with a machine. Criteria for extubation: The patient is awake, following the doctor's orders. Patient can raise head for more than 5 seconds, TOF >0.9. The patient is breathing on his own, the respiratory rate is within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Temperature > 35 degrees C. The patient had no complications of anesthesia and surgery. 3.2. Complications and management in endotracheal anesthesia laparoscopic horseshoe nephrectomy 3.2.1. Reflux of gastric juice into the airways Gastrointestinal fluid is found in the oral cavity and airways. At that time, it is necessary to immediately aspirate the fluid, place the patient in a low lying position, and tilt the head to one side. Place the endotracheal tube quickly and clear the airways immediately. Then it is necessary to monitor for lung infections. 3.2.2. Hemodynamic disorders Patients with hypotension or hypertension, arrhythmia (tachycardia, bradycardia or irregular rhythm). Treatment depends on the specific symptoms and cause. 3.2.3. Incident due to intubation Unable to intubate: manage with difficult intubation procedure or switch to another anesthetic method. Wrong placement of endotracheal tube into the stomach: Auscultation of the lungs without alveolar murmur, EtCO2 cannot be measured. Reinsert the endotracheal tube. Vocal - tracheobronchial spasm: Difficult or impossible to ventilate, auscultation with rales or no hearing at all. It is necessary to provide adequate oxygen to the patient, use more hypnotics and muscle relaxants, ensure ventilation, and use bronchodilators and corticosteroids. If breathing cannot be controlled, a difficult endotracheal intubation procedure should be used. Trauma during endotracheal intubation: patients have bleeding, broken teeth or damaged vocal cords, foreign objects fall into the airways,... Depending on the injury, appropriate treatment is available. 3.2.4. Respiratory complications Possible folding or retraction of the endotracheal tube deep into one lung, collapse or opening of the respiratory system, lack of oxygen. Management: immediately ensure ventilation and provide 100% oxygen, find and resolve the cause. 3.2.5. Complications after extubation Patients may experience respiratory failure after extubation. The patient may have a sore throat and hoarseness. Patient has laryngospasm - gas - bronchi. The patient may have an upper respiratory tract infection. The patient may have laryngotracheal stenosis. Depending on the symptoms and cause, the doctor will have an appropriate treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.