This is an automatically translated article.
The kidney is an organ located in the urinary system, which plays many important roles in the body. Everyone should understand the anatomy of the kidney and urinary tract to understand kidney function.1. Overview of kidney characteristics and function
The kidney is a major excretory organ of the urinary system. Each person has 2 kidneys, which perform many different functions. Some of the functions of the kidney can include:Excretion of waste: The kidneys excrete waste products (hydrogen, potassium, uric acid, ...) and reabsorb substances (water, sodium, amino acids, etc.) glucose,...). Waste is converted into urine, which flows down the ureters to the bladder; Substance conversion and synthesis: The kidneys convert vitamin D precursors to calcitriol, synthesize the hormones erythropoietin and renin; Whole-body homeostasis: The kidneys are involved in whole-body homeostasis, regulating acid-base balance, blood pressure, extracellular fluid volume, and electrolyte concentrations. The kidneys ensure this function independently, in coordination with other organs in the endocrine system; Hormone secretion: The kidneys secrete many hormones such as calcitriol (promotes intestinal calcium absorption and phosphate reabsorption in the kidney), renin (regulates angiotensin and aldosterone levels) and erythropoietin (stimulates erythropoiesis in the blood). bone marrow); Other functions: blood pressure regulation, acid-base balance, plasma osmosis regulation,...
2. Kidney Anatomy: External Shape of the Kidney
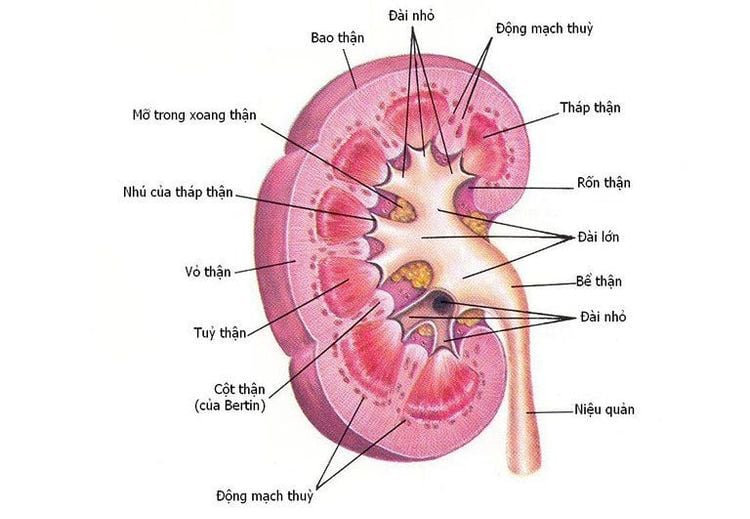
The kidney is a reddish-brown bean-shaped, located in the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneum, in the angle of the 11th rib and the lumbar spine anterior to the lumbar muscle. The right kidney is located about 2cm lower than the left kidney. The surface of the kidney is smooth, encased in a fibrous capsule that is easy to remove. The kidney has 2 faces, 2 poles and 2 banks. The anterior surface of the kidney is convex, looking anteriorly and outwardly. The back of the kidney is flat, looking back and inward. The outer margin is convex, the inner margin is convex in the upper and lower parts, and the center is concave (called the renal hilum - where the arteries, veins, and ureters pass). 2 poles including upper pole and lower pole.
Each adult kidney weighs about 150 - 170g, is about 10 - 12.5cm long, about 5-6cm wide and about 3-4cm thick. On the X-ray, each kidney is as tall as 3 vertebrae.
Hình ảnh giải phẫu thận
3. Renal anatomy: Renal fascia features
The kidney and adrenal gland are on the same side enclosed in the renal fascia. The renal fascia has 2 leaves anterior and posterior. Between the renal fascia and the fibrous capsule is a layer of fat (peritoneal fat). Outside the renal fascia, there is another layer of fat (perirenal fat).
4. Anatomy of the kidney and urinary tract: The surrounding organs
4.1 In front of the kidney Right kidney: Located behind the peritoneum, almost above the transverse mesenteric root. The upper end and the inner upper part of the kidney are related to the right adrenal gland. The medial margin and right renal peduncle are related to the descending part of the corolla. The anterior aspect of the right kidney is related to the liver, small intestine and right colonic angle; Left kidney: Located behind the peritoneum, with a transverse mesenteric root crossed in front. The superior and superior medial margins of the kidney are related to the left adrenal gland. The lower part of the kidney is connected to the stomach by the omentum sac connecting the intestines, spleen and pancreas, the angle of the left colon, the small intestine, and the upper part of the left colon. 4.2 Behind the kidney Physiological anatomy of the kidney the following parts:
Behind the 12 ribs are horizontal, divided into 2 floors: the thoracic and lumbar layers; The thoracic floor involves ribs 11, 12, the diaphragm, the diaphragmatic recess of the pleural cavity; Lumbar floor from the inside out is related to the lumbar muscle, the transverse abdominal muscle, and the lumbar square muscle.

Giải phẫu thận tiết niệu và các cơ quan xung quanh
5. Kidney Anatomy: Inner Body
5.1 Macroscopic kidney is enclosed in a fibrous capsule, in the middle is the renal sinus: Nerve blood vessels, renal pelvis pass through, filled with fatty tissue. Surrounding the renal sinus is the semicircular renal parenchyma.
Renal sinuses open to the renal hilum. Sinus wall convex, concave. The protrusion above the renal sinus has a conical shape, called the renal papilla. Renal papillae have many holes of the urogenital tubules, which are responsible for emptying urine into the renal pelvis. The renal sinus contains the renal pelvis, renal calyx, blood vessels and fatty tissue. Each kidney has about 7-14 small calyces. The small calyces form 2-3 large calyces. The large calyces make up the renal pelvis.
Renal parenchyma: Includes renal cortex and renal medulla. The renal medulla is composed of many conical masses (renal pyramids), the base of the pyramid is turned towards the renal capsule and the top of the pyramid is towards the renal sinus to form the renal papilla. The middle part of the kidney has 2 - 3 pyramids sharing 1 renal papilla, the 2 poles can have 6 - 7 pyramids sharing 1 renal papilla. The renal cortex consists of the renal column (the part of the parenchyma between the renal pyramids) and the cortical lobules (the part of the parenchyma from the base of the renal pyramid to the fibrous capsule).
5.2 Microscopy Under the microscope, each kidney is made up of renal units. Each kidney unit includes:
Renal corpuscle: There are 2 parts including 1 outer capsule and surrounded by capillary coils; Genitourinary system: Consists of proximal tubule, distal tubule, loop of Henle and income duct. In which, renal corpuscle, proximal tubule and distal tubule are located in the convoluted part; loop of Henle, the collecting duct is located in the renal cortex and medulla. Kidneys are one of the most important organs in the body. Understanding kidney anatomy and keeping it healthy is essential to maintaining good health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.