This is an automatically translated article.
Infection, bleeding or pneumothorax are complications that can occur if the intravenous catheter is placed incorrectly. Currently, placing a central venous catheter under ultrasound guidance offers many outstanding advantages, limiting the risk of complications.
1. What is a central venous catheter?
1.1 Definition The term “catheter” refers to a small, long catheter made of thin, flexible plastic. Catheters are used to infuse drugs, fluids, nutrients, or blood into a patient's body over a period of several weeks or more.
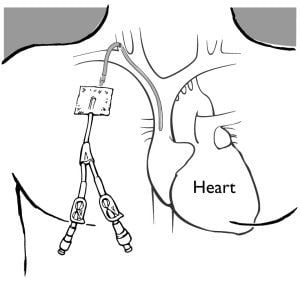
What is a central venous catheter? This is a technique of inserting a catheter from a vein in the arm, chest, or neck so that the end of the catheter is in the central vein near the heart. Currently, central venous catheterization is widely applied in the emergency and surgical departments of large hospitals.
This method has many advantages over direct injection into the central vein, namely:
High success rate. Patients with coagulopathy can still perform. Compression may be used to stop bleeding if there is bleeding at the injection site. Patient and family easily accept.

1.2 Indications and contraindications for implementation Intravenous catheterization techniques are indicated when needed:
Measure pressure in the central venous, cardiac chambers and pulmonary arteries. Transfusion of various fluids during emergency. Nutritional infusion for patients unable to eat by mouth. Long-term drug infusion. Pacing or cardiogenic shock. Hemodialysis. Central venous catheterization is contraindicated in patients with the following characteristics:
Platelets less than 60,000/mm3. Severe coagulopathy. There is a blood clot in the central vein. 1.3 Preparation for implementation Before performing the technique, it is necessary to undergo a careful preparation process:
Directly performing team: Including 1 emergency care specialist, 1 treating doctor and 1 nurse . All healthcare professionals performing central venous catheterization require extensive training and expertise. Equipment: The facilities to perform this technique include a 2- or 3-bore catheter set, a minor surgery set, a 5ml syringe, a local anesthetic, a needle to fix the catheter, a vial of 0.9% NaCl solution, a set of tools. infusion line and disinfectant. Patient: The patient and family will be thoroughly explained about the procedure and signed a consent form. They will also prepare medical records and conduct some tests. During the procedure, the patient will lie on his back, with a pillow to support his shoulder and turn his head to the side opposite the side of the needle or may be anesthetized. 1.4 Procedures There are three common routes of central venous catheterization:
Elevation: The intersection of the transverse thyroid cartilage and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Subclavian vein catheterization: Inner jugular vein Catheter area (According to Daily Line): Triangle of clavicle and sternum

2. Place a subclavian venous catheter
2.1 Definition The subclavian vein is located below the clavicle, close to the subclavian artery and the apex of the lung. Placement of a subclavian venous catheter is a procedure that is a procedure to insert a polyethylene catheter into the subclavian vein, aiming to rapidly infuse the patient's body with a volume of fluid, drugs, nutrients,...
There are 4 ways to enter the patient's body. Subclavian veins around the clavicle include: Aubaniac, Wilson, Testart, and Yoffa lines. The advantages of the subclavian vein catheterization method are:
Easy to identify anatomical landmarks The path and direction are favorable for pushing the catheter into the vena cava The diameter of the subclavian vein is quite large, not collapsing despite the disease. Patients suffering from vascular collapse, which makes the success rate high. Location is easy to fix, cover, care and convenient for patients to live. Fewer infections due to veins located deep in the chest Low blood pressure should not cause hematoma when having to inject many times 2.2 Two methods of placing subclavian intravenous catheters Method of catheterization: Applied with a single-bore catheter with the advantage of simplicity and ease of implementation. Seldinger method: Pass the catheter through the wire in any position. This is an improved technique with many advantages over other methods commonly used in the past, such as: Small needle size suitable for small basilar veins in children Increase success rate higher Less injection site bleeding Less catheter occlusion from large catheters Ease of central venous pressure measurement
3. Advantages of guided ultrasound
Currently, ultrasound-guided is the mandatory standard for central venous administration in order to increase the success rate, reduce the number of needle punctures as well as bleeding complications, tissue damage and infection.
The ultrasound guide kit includes an ultrasound machine with a Linear transducer, with a sterile nylon sheath covering the transducer, and two types of ultrasound gel, normal and sterile. During patient preparation, the physician or nurse practitioner should perform the technique under intravenous ultrasound guidance.
Placement of a central venous catheter under ultrasound guidance has the following advantages:
Ultrasound helps identify veins, avoids injection of the wrong artery Measure basilar vein diameter and vein depth Determine location and the direction of the needle, limiting bleeding at the injection site Checking the correct position of the catheter tip Detecting venous thrombosis in the presence of clinical signs Central venous catheterization technique in general, or specifically the method of catheterization subclavian vein , is quite complicated with strict adherence to the procedure and complications can still occur. Therefore, placing an intravenous catheter under the guidance of ultrasound will help prevent and prevent risks, increase the accuracy of the operator as well as the success rate of the procedure.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.