This is an automatically translated article.
Scientists find new and better ways to stop cancer cells from forming and detect disease before the tumor spreads. Medicine today is making great strides in cancer prevention, as are many advances in cancer screening.
1. Closely monitor personal medical condition
Finding out the risk factors associated with some cancers can help your doctor reduce your risk, as well as better prevent and screen for cancer.
Factors that contribute to an increased risk of cancer include:
Genetics; Surroundings; Obesity, diet, lifestyle, smoking habits and exercise. When a person knows that a patient is more likely to have certain types of cancer, the doctor will provide specific cancer prevention guidelines, as well as more accurate cancer screening and screening.

2. Advances in Cancer Screening
Similar to other medical conditions, the earlier cancer is detected, the better. Cancer is easier to treat if the malignant cells are killed before it spreads widely. However, finding and diagnosing cancer is not easy. Furthermore, cancer screening tests always come with some risks, such as:
CT scans expose the body to a small amount of radiation risk; Biopsy and endoscopy are invasive techniques, so they can cause side effects; Some results can be misleading, doctors call this a false positive; Sometimes, a cancerous tumor is found to be unable to grow (benign tumour), causing the patient to have more tests or unnecessary treatment. Today, with advances in cancer screening, tests are becoming more personalized. The doctor can assign the right people and the frequency of cancer screening when really needed. The cost and time spent is minimal, but ensures maximum efficiency.
3. New Cancer Screening Tests
3.1. Genetic and genomic testing
As an advancement in cancer screening, this test helps predict cancer risk and tumor activity by observing changes in the inherited genome.
For example, a genetic test will look for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Women with one or both of these genes are more likely to develop breast and ovarian cancer than those without.
Another home test kit also helps detect DNA changes in stool, thereby diagnosing colon cancer early. This test is completely non-invasive like a common endoscopic procedure. But if the results suggest you have something suspicious, an endoscopy still needs to be done to confirm the diagnosis.
In addition, there is a genetic test that looks at breast cancer genes, so that doctors can find the most effective treatment for a patient, as well as predict the likelihood of a tumor come back (recurrence of cancer).
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3.2. Biomarkers (Biomarkers)
Biomarkers are substances found in blood, urine and other body fluids that have the ability to screen for cancer. It also helps predict how the body will respond to certain therapies.
Similar to tumor markers , biomarker tests include:
Liver cancer : Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP); Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Gene ALK; Prostate cancer : Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) Thyroid cancer : Thyroglobulin (TG). Scientists are still studying more biomarkers for other cancers. For example, a new test hopes to measure levels of two proteins in the blood, thereby helping to diagnose pancreatic cancer early. However, more research is still needed to achieve perfect accuracy.
Biomarkers are also expected to be used to detect diseases other than cancer. Therefore doctors are still trying to figure out the best way to optimize the application of these tests.
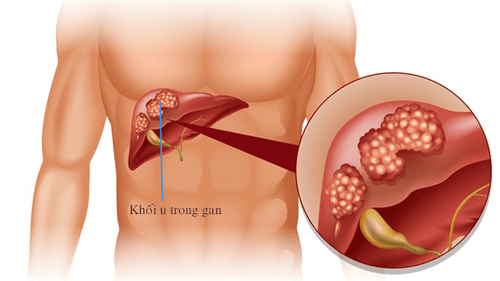
3.3. Liquid Biopsy
Researchers are looking at a blood test that can detect many different cancers. This technique, known as a liquid biopsy, helps detect cancerous DNA circulating in a patient's blood. The FDA approved the first liquid biopsy technique in 2016. Specifically, changes in the EGFR gene in the blood of patients with non-small cell lung cancer were detected.
Several other liquid biopsy tests are also being studied and conducted to screen for more cancers.
4. Medicines and vaccines to prevent cancer
4.1. Medicine
Although you can't prevent cancer by taking medicine every day, some of the drugs being studied have certain effects.
For example, a drug used to protect the heart can also prevent colorectal cancer. Health experts in the United States say that middle-aged people aged 50 to 59 at risk should take a daily aspirin to help prevent both heart disease and colorectal cancer. There is also a class of estrogen receptor blockers that reduce the risk of breast cancer in high-risk women. In addition, aromatase inhibitors are also used to prevent disease.
4.2. Vaccine
Cancer vaccines affect the immune system, just like the common measles and chickenpox shots. Some vaccines prevent cancer, others are used to treat the disease.
For example, the vaccine prevents the HPV virus that causes most cases of cervical cancer. Since its approval in 2006, the vaccine has lowered HPV infection rates in young women by 64%. Another vaccine also helps prevent hepatitis B, which contributes to a lower incidence of liver cancer.
Meanwhile, cancer treatment vaccines help strengthen the body's immune system's response to fight against malignant cells. For example, the sipuleucel-T (Provenge) vaccine may be used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Scientists are also working on more vaccines for other cancers, including colon cancer and melanoma.
In a nutshell, advances in cancer screening help you recognize your risk, which can be done to reduce your odds. Find out your personal and family medical history, then talk to your doctor. Actively working with medical professionals is the way to get the full application of the latest cancer screening and prevention techniques.
Cancer inherently does not spare anyone, it is estimated that every year in the world, a very large proportion of people die from cancer. In fact, if cancer can be detected at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment is very high, even if it is completely cured and not recurred. Therefore, cancer screening is essential, especially for high-risk patients.

Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been implementing cancer screening packages. At Vinmec, there are fully modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI..., blood marrow test, histopathology, immunohistochemistry test, gene test, lab test molecular biology, as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment. Multimodal cancer treatment from surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy in cancer treatment, new treatments such as autoimmunotherapy body, heat therapy...
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to patients. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the cancer treatment is effective or not.
Thanks to modern facilities, a team of qualified doctors and excellent medical services, have brought confidence, health and good quality of life to patients who come to visit and treat diseases at the hospital. Vinmec.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Reference source: webmd.com
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.