This is an automatically translated article.
Acute tubular nephritis is a condition in which the interstitial tubules of the kidney are necrotic and damaged. Patients with acute tubular nephritis, if not detected and treated promptly, can experience dangerous complications of nephritis, even leading to death.
1. What is acute tubular nephritis?
Acute tubular nephritis, also known as acute interstitial nephritis, acute tubular necrosis, is a pathological condition in which the interstitial tubules are damaged and necrotic. Acute tubular nephritis is the cause of acute kidney failure, if not detected and treated, the disease causes serious complications and can lead to death.
2. Causes of acute tubular nephritis
Acute tubular nephritis caused by many causes, classified into 3 main groups as follows:
Acute tubular nephritis caused by anemia: Anemia in the kidney is the leading cause of tubular necrosis. Causes of long-term decreased renal perfusion leading to renal ischemia may be prerenal or renal. In which, prerenal causes include cardiogenic shock, shock due to hypovolemia (after surgery, trauma, burns, miscarriage, abortion), shock due to infection or toxicity. The cause in the kidney is mainly due to drug shock or drug components (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antihypertensive drugs, ...).

Các thành phần trong thuốc có thể gây ngộ độc tại thận
Acute pyelonephritis caused by poisoning: Poisoning by drugs (antibiotics of aminosides, neomycin, gentamycin, kanamycin, streptomycin; anti-tumor drugs cisplatin, cyclosporine, interferon; anesthetics;...), endogenous pigments , muscle pigment; chemicals (carbon tetrachloride, methyl alcohol,...), natural toxins (found in some seafood species and organisms such as toads, carp,...) can directly affect renal tubular cells or indirectly affect the vascular mechanism, causing renal ischemia and leading to tubular inflammation. Allergic acute tubular nephritis: Due to allergies to certain drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, cimetidine, methicillin, penicillin, ...
3. Signs of acute tubular nephritis
Acute tubular nephritis is a manifestation of acute renal failure, in some cases due to poisoning may be accompanied by acute hepatitis. In fact, the disease is often detected through some typical symptoms such as oliguria, anuria, or through complications of the disease such as high blood pressure, pulmonary edema causing extracellular fluid retention, or hyperuricemia syndrome. , electrolyte imbalance,...
Depending on the stage, the signs of the disease are different. Acute tubular nephritis progresses through the following 5 specific stages:
Infectious stage: Depending on the cause of the disease, the duration of the stage will be different. If due to shock, hemorrhage, the disease appears suddenly and acutely, if due to poisoning, the time will be slow and prolonged. Oliguria, initial anuria stage: This stage usually appears in about 1-3 days. At this stage, the patient has signs of extracellular fluid retention such as weight gain, dyspnea, labored breathing, and peripheral edema. After these signs are manifestations of digestive disorders, bleeding under the skin.

Dấu hiệu khó thở ở người bệnh suy thận cấp
Stage of oliguria, true anuria: If the disease is not detected and treated promptly at the initial stage, patients with acute tubular nephritis begin to turn to oliguria or true anuria. There are also typical signs of uremia syndrome. The progression time of this stage ranges from 7 to 21 days. Polyuria phase: This phase may appear earlier or in the third week of anuria. The sign of this stage is that the patient begins to have a large amount of urine, which increases gradually. Renal rehabilitation phase: The patient's kidney function recovered with the urea and creatinine levels reaching normal levels.
4. Complications of acute tubular nephritis
In the course of progression, acute tubular nephritis can cause a number of systemic complications such as:
Cerebral edema, convulsions Acute pulmonary edema Cardiovascular collapse However, some other cases have complications in the renal tubules with different degrees, due to damage in different segments. Mild complications that may be encountered are flattening, dilatation of renal tubules, especially in the distal tubules, tubular intercellular necrosis, tubular cell necrosis, loss of protoplasm and nucleus. Severe complications can be necrosis or rupture of each renal tubule.
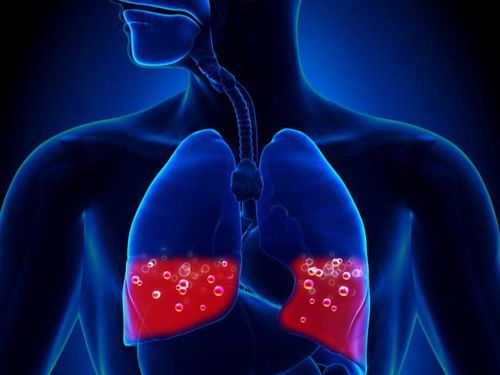
Phù phổi cấp do biến chứng của viêm ống thận cấp
Patients with acute tubular nephritis need to be detected and treated promptly. During and after the treatment, it is necessary to follow the instructions of the treating doctor to quickly recover health.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disease transmission? Symptoms of kidney failure in men 5 stages of chronic kidney disease