This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc Vo Thien Ngon - Urologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Acute scrotal syndrome is a swelling of the scrotum accompanied by redness and pain in the scrotum, which may be accompanied by systemic symptoms. The disease can cause testicular necrosis, so in many cases, urgent surgery is needed to save the testicle.
1. Causes of acute scrotal syndrome
Causes of acute scrotal syndrome include:
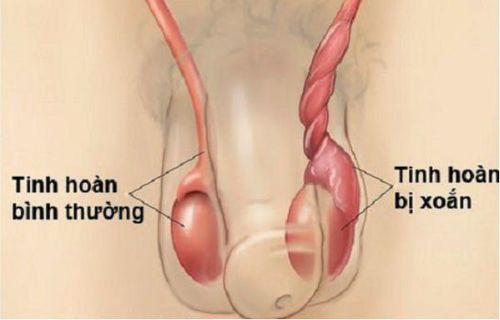
Torsion of testicular appendage, epididymitis, testicular trauma, inguinal hernia, acute hydrocele, testicular tumor, varicocele, testicular torsion, scrotal edema In which, testicular torsion accounts for a high rate and is the most dangerous pathology because it can cause irreversible testicular damage, threatening to cause irreversible testicular damage if the torsion lasts for more than 8 years. should now be followed up urgently until completely ruled out. Therefore, in acute scrotal syndrome, the physician and the patient must be monitored urgently until testicular torsion is ruled out.
2. Symptoms of acute scrotal syndrome
2.1. Physical symptoms Sudden, severe and gradually increasing pain, especially at night, should consider the cause of testicular torsion. Sudden severe pain in the groin or scrotum. Pain is localized or radiates along the inguinal canal to the ipsilateral iliac fossa. Pain makes children tend to flex their thighs and have little movement. Older children often locate pain on their own. With infants and breastfed babies, there is a lot of crying. Swollen large scrotum and inguinal canal, painful. If the illness is long, the skin may appear red. If fever is present, a UTI suggests epididymitis. 2.2. Physical symptoms The testicles are enlarged, lying high and the axis of rotation is horizontal, pulling the testicles down, causing more pain. An undescended testicle, the patient has pain in the inguinal canal, a bulge in this area, tenderness, and the ipsilateral scrotum is not palpable. There is a lump in the testicle and pain in the testicle or scrotum. Loss of scrotal reflex is a highly valued sign in testicular torsion. Pain limited to the upper pole of the testicle suggests torsion of the appendix; examination may reveal a blue dot sign that penetrates the skin of the scrotum. Bell-clapper deformity is caused by alteration of the seminal vesicles at the site of attachment to the testicle. In patients with this deformity, the testicle is transverse and has an anterior-posterior longitudinal axis. This distortion is always on the sides.
3. Identify acute scrotal syndrome
Differentiate acute scrotal syndrome from testicular appendage torsion
Scrotal skin reflexes persist and testicles remain mobile. Pain is localized in the upper pole of the testicle or epididymis, usually of gradual onset rather than acute and not accompanied by vomiting, regurgitation, or abdominal pain. The blue dot sign is specific for torsion of the testicular appendage, however, the “blue dot sign” is detected in only 20% of patients with testicular torsion. Testicular torsion does not require surgery if diagnosed correctly.
Differentiate acute scrotal syndrome from epididymitis
Pain has a gradual onset, fever and painful urination are often accompanied. Common between 9-14 years old. In younger children, patients with anorectal malformations or urogenital malformations.
Differentiate acute scrotal syndrome from orchitis
May be infectious or inflammatory, due to the direct effect of epididymitis. Infections that affect only the testicles are rare in children, as a result of the bacteria spreading through the bloodstream or after mumps.
Distinguishing acute scrotal syndrome from scrotal trauma
Scrotal trauma can cause hematoma in the scrotum, bleeding in the testicle or tearing of the epididymis, exposing the testicle to the scrotum. Ultrasound is the best diagnostic tool. If there is testicular rupture (tear the membrane) surgery is indicated.
4. What to do to avoid acute scrotal syndrome?

Mumps vaccination Prevent acute scrotal syndrome by immunizing children from an early age. Usually not long after the onset of mumps will appear orchitis because the virus directly enters the testicle. To prevent the disease, children under one year of age need to be vaccinated to prevent it. The effect of vaccines is to strengthen the body's immune system. Vaccination can be said to be the most effective measure in preventing mumps and orchitis in the future.
Form healthy habits Build good habits in life such as: do not smoke, do not drink alcohol, do not sit or stand for too long in one place, do not have excessive sex, do not abuse masturbation.
In addition, you should eat a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits and increase the amount of vitamins in your body, especially vitamin C to help increase immunity, and at the same time should limit hot and sour foods.
Test testicles The testicle massage method can be applied before sleeping or taking advantage of the bath. Gently press the testicle with your thumb clockwise, then counter-clockwise for 10 minutes at a time. If you feel strange pain during the massage, it is likely that you have swollen scrotum or epididymitis. At that time, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible for timely diagnosis and treatment.
If you have any questions or suggestions, you should consult your doctor or medical professional for the best answer.
Go to the emergency room right away if you develop sudden pain in the scrotum. Some conditions require prompt treatment to avoid permanent damage to the testicles. See your doctor if you find a lump in your scrotum, even if it's not painful or sensitive, or if you have other symptoms of a scrotal mass.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.