This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master - Doctor Le Van Binh - Doctor of Intensive Care Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Acetaminophen is a widely used antipyretic and pain reliever because it is safe, but can cause poisoning when overdosed or suicide.
1. Toxic Dose of Acetaminophen
Maximum concentration at the 4th hour. After oral administration, Acetaminophen overdose is metabolized in the liver to toxic substances, reduced Glutathione and necrosis of hepatocytes. Acetaminophen toxic dose > 150mg/kg.
2. Diagnosis of acute poisoning of the antipyretic drug acetaminophen
2.1 Clinical diagnosis
History: Acetaminophen overdose > 150mg/kg. Before 24 hours: Anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain. After 24-72 hours: Vomiting, elevated liver enzymes, prolonged PT. From 72 to 96 hours: Hepatocellular necrosis, jaundice, liver failure, encephalopathy - liver disease, coagulopathy, acute renal failure, multi-organ failure. From day 4 to 2 weeks: Progressive or reversible liver failure.
2.2 Determining the diagnosis of acute poisoning with the antipyretic drug acetaminophen
History: Acetaminophen overdose > 150mg/kg. Clinical: Anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain. Jaundice, enlarged liver. Test: Quantify Acetaminophen in the blood: Acetaminophen concentration > 140 μg/mL after the 4th hour. Or Acetaminophen concentration in the toxic hazard range.
2.3 Differential diagnosis of acute poisoning with the antipyretic drug acetaminophen
Viral hepatitis.
3. Treatment of acute poisoning with fever-reducing drug acetaminophen
Principles of treatment of poisoning with antipyretic acetaminophen are: Treatment of emergency situations; quickly remove toxins; specific antagonists and treatment of complications.3.1 Treatment of emergency situations
Respiratory resuscitation. Resuscitate shock with fluids and vasopressors.
3.2 Elimination of toxins
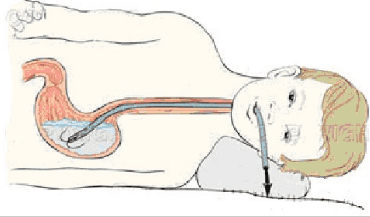
Gastric lavage.
Activated charcoal:
It is necessary to give activated charcoal as soon as possible after gastric lavage. Do not give activated charcoal when taking an oral N-acetylcysteine antagonist.
3.3 Specific N-acetylcysteine . antagonists
Glutathione replacement effect is lacking due to poisoning. N-acetylcysteine should be given early before the patient develops liver damage. Intravenous nutrition. Hemodialysis: although hemodialysis can remove Acetaminophen from the body, hemodialysis is usually not indicated even with high concentrations of Acetaminophen because most respond well to N-acetylcysteine. Therefore, hemodialysis is indicated in acute renal failure.
3.4 Treatment of complications
Hypoglycemia: Hypertonic glucose Electrolyte disturbances Coagulation disorders: Vitamin K1. Acute liver failure (see acute liver failure protocol).
4. Follow up
Vital signs. Jaundice, liver size. Blood sugar, electrolytes. Liver ultrasound. Liver function.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.