This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Le Van Binh - Pediatric Intensive Care Doctor - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Children are always curious and explore their world with all their senses, including taste. As a result, the home and its surroundings can be a dangerous place for children to inadvertently ingest toxins. Every year, thousands of children are hospitalized because of poisoning. The forms of poisoning vary by age group, type of material exposed, and the nature and dose of the poison.
1. General
Acute poisoning (NDC) is when poison enters the body in a short time causing damage to organs and causing danger to the body. If not treated in time, it can cause death.Every year, about 6 million children around the world suffer from food poisoning. In which, children under 5 years old account for 60-80%.
Poisoning tends to increase due to the arbitrary use of chemicals and drugs, the causative agents of NCDs are many, so it is difficult to identify. Children under 5 years old have a limited ability to fight and eliminate toxins, so when they are poisoned, they often need emergency care. When the disease is severe, it can easily cause death. However, today, with advances in diagnosis and resuscitation techniques, the mortality rate due to IBD is decreasing.
2. Approach to acute poisoning diagnosis
The diagnosis can easily be based on testimonies or items brought. However, there are many cases where it is very difficult, even with toxicology test results. Because the clinical manifestations of acute poisoning in children have many symptoms similar to other causes.Definitive diagnosis is based on: medical inquiry, clinical examination and toxicology test.
2.1. Asking about the disease Asking the patient is a very important job because 90% of the cases can be based on testimonies and family items to determine the cause. Some questions can be asked such as:
What do children eat and drink? How much is the food intake? How long does it take to eat? What is the first symptom? Do other people eating and drinking with the same symptoms as children? What first aid measures did you take before going to the hospital?

| Triệu chứng | Chất gây độc |
|
Hô hấp: Ức chế Tăng hô hấp Phù phổi |
Rượu, thuốc ngủ, thuốc phiện, Amphetamin, Aspirin, Hydrocarbon, P. hữu cơ,... |
|
Tim mạch: Nhịp tim nhanh. Nhịp chem. Tăng huyết áp. Hạ huyết áp, choáng. |
Atropin, theophylline, Aspirin. Digital, thuốc ngủ, nấm độc, P. hữu cơ |
|
Thần kinh trung ương: Co giật. Hôn mê. Mê sảng, ảo giác. |
Amphetamine, Aspirin, P. hữu cơ, Barbituric, nọc rắn, Penicillin,... |
|
Đồng tử: Co thắt. Giãn. |
Thuốc phiện, Pilocarpine, Nicotine, Prostigmin, Muscarin, Atropin, Belladon, rượu, thuốc ngủ, thuốc mê,... |
|
Tiêu hoá : Tăng tiết nước bọt. Khô miệng. Nôn, đau bụng, ỉa chảy. Vàng da, xuất huyết. |
Lân hữu cơ, thuốc chuột, muối kim loại nặng, Atropin, kháng Histamin, ngộ độc thức ăn, Paracetamol, nấm độc,... |
| Hô hấp có mùi rượu | Ethanol |
| Aceton | Cồn Methanol, Salicylate |
| Hạnh nhân trắng | Cyanide |
|
Da: Vết cắn, phỏng Vã mồ hôi Ban đỏ Tím niêm mạc |
Rắn, côn trùng đốt, Muscarin, Pilocarpine, Insulin, C.O, Penicillin, ngộ độc sắn, Met Hb,... |
| Tổn thương răng | Muối kim loại nặng: Pb, thuỷ ngân,... |
| Tổn thương tai: Điếc | Ngộ độc Streptomycin, kanamycin,... |
| Tổn thương thận: Suy thận | Muối kim loại nặng, Paracetamol,... |
| Rối loạn nước - điện giải |
| Nhẹ | Vừa | Nặng | Rất nặng |
|
Không có triệu chứng. Không có nguy cơ nguy hiểm. |
Lành tính. Tác dụng độc. Tự khu trú. |
Có rối loạn tinh thần. Có triệu chứng độc. Có đe doạ tính mạng. |
Đe doạ chức năng sống. |
| Hội chứng | Triệu chứng | Nguyên nhân |
| Kháng cholinergic | Giảm tiết, khát, da đỏ | Belladon, nấm,... |
| Chống tiết cholin |
Sốt, mê sảng Nhịp tim tăng, SHH |
Kháng Histamin,... |
|
Tiết Acetylcholine (Cholinergic) Muscarin Nicotine |
Tăng tiết dịch, nôn Co thắt phế quản, co đồng tử Nhịp tim tăng, co giật, hôn mê |
P. hữu cơ, trừ sâu Carbamate, nấm độc, thuốc lá,... |
|
Gây mê (thuốc ngủ) |
Ức chế thần kinh trung ương, hạ nhiệt độ, giảm huyết áp, giảm thông khí, co đồng tử | Gây mê, Heroin,... |
| Tăng chuyển hoá | Sốt, nhịp tim tăng, thở nhanh, co giật, nhiễm toan | Salicylate, chất diệt cỏ, Phenol, Aspirin |
|
Giống thần kinh giao cảm |
Kích thích, loạn tâm thần, nhiệt độ tăng, giãn đồng tử | Amphetamin, Cocaine, Theophylline, Cafein |
Difficult diagnosis: Must be based on two of the following three criteria:
Ask the patient carefully to find evidence: Using drugs, chemicals. Symptoms come on suddenly: The child was previously healthy. Toxicology testing consistent with clinical symptoms.
3. Characteristics of acute poisoning in children
Mainly due to the unconsciousness of adults in the preservation of drugs and chemicals in food for children to eat or drink: Because the family self-administers the drug without a prescription from a doctor or medical officer and uses it improperly. Age of acute poisoning: Any age, from birth to 15 years old. Common: 1 - 3 years old, boys see more than girls due to hyperactivity. Children under 5 years old account for 70%. Drug poisoning: Mainly children < 1 year old. Food and chemical poisoning: Mainly children > 6 years old. The cause of acute poisoning in young children is often easy to detect because it is not hidden, older children can be poisoned by trying to commit suicide because of conflicts with family, friends, teachers,... Need to be careful when taking medical history of children. Common poisoning routes: Gastrointestinal tract (70%), respiratory tract (5%), skin (7%),... Clinical features of acute poisoning in children are different from adults due to biological characteristics of the nervous system. The central part is not yet perfect and vulnerable. The liver and kidney are the two main detoxification organs, but their function is immature, so they are prone to drug accumulation. Therefore, small doses in children can cause acute poisoning; or there are drugs that inhibit adults but children cause irritation such as pipolphen, ...4. Treatment of acute poisoning
4.1. Principles Urgency and coordination of key measures:Maintain vital functions. Eliminate toxins from the body. Toxic neutralization. Specific detoxification. Homeostasis, symptoms and nutritional care. 4.2. Treatment measures 4.2.1. Emergency treatment Eliminate danger Maintain vital function, manage according to A.B.C. sequence. 4.2.2. Induce vomiting Advantages: Simple, easy to use, effective for poisoning < 6 hours. Indications: Children awake, poisoning < 6 hours. Contraindications: Poisoning with hydrocarbons (petroleum), strong corrosive substances (acids, bases), coma, convulsions in children. Method : Fingers, cotton swabs to stimulate throat.
Drink Ipeca 7 - 10% solution:
Children < 1 year old: 10 ml.
Children 1 - 10 years old: 15 ml.
Children > 10 years old: 30 ml.
After 15-20 minutes, most children vomit, remove 30-40% of the substance when eating < 1 hour.
Can be repeated after 20 minutes.
Apomorphine 0.01g/1ml dermal injection, dose from 1/3 to 1/2 ampoule depending on age, not for children < 5 years old.
4.2.3. Gastric lavage Simple and effective method. Indications: Poisoning < 6 hours, patients awake, comatose must be intubated first. Method: Warm water mixed with 5g salt/1 liter, 0.9% saline serum, 0.5% potassium permanganate solution, or 10g activated charcoal/1 liter. Or put a nasogastric tube to pump 10-20ml/kg/wash until the liquid is clear and the odor is gone. Contraindications: Poisoning with corrosive substances.

Be careful with children < 2 years old because of possible dehydration - electrolytes.
4.2.5. Diuresis more Indications: Poisoning but toxic waste through the kidney, good kidney function in young children. Method: Drink lots of water.
Glucose solution 10% + electrolyte solution: 120-150 ml/kg or 2-3 liters/m2 skin/24 hours.
Mannitol 1g/kg, Lasix 1 - 2 mg/kg
Causing alkalization or acidification of the urine:
Alkalizing: Bicarbonate 14%o, Protopam.
Acidification: Vitamin C, Ammonium Chloride.
4.2.6. Dialysis Modern, effective method, reducing mortality. Helps regulate water - electrolytes, acid-base. Indications: Poisoning with heavy metals, poisonous mushrooms. 4.2.7. Blood exchange Indications for patients with hemolytic poisoning, hepatocellular toxicity: Mushrooms, salicylic acid.
4.3. Detoxification 4.3.1. Non-specific Method of absorption: Use activated charcoal after gastric lavage, pump 10g mixed with 50ml water or 1g/kg every 8 hours. Some poisons: Give milk to drink. Chemical neutralization: Alkali poisoning using lemon and vinegar. Acid poisoning using alkaline. Heavy metal poisoning: Using egg whites,... 4.3.2. Specific detoxification
| Chất gây độc | Chất giải độc | Liều và cách dùng |
|
Atropin, Belladon Scopolamine, ức chế phó giao cảm |
Prostigmin. Pilocarpine |
0,5 mg/1 ống 0,25 mg/kg trung bình, chia nhiều lần. |
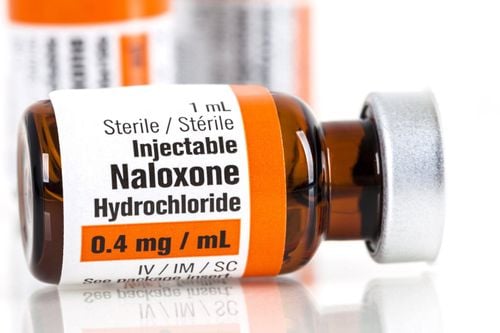
| Opi, morphin, codeine |
Nalorphine Lorphan Naloxon |
0,1 - 0,2 mg/kg 1 liều tĩnh mạch. 60 phút sau tiêm không đỡ thì nhắc lại. 0,01 mg/kg truyền TM. |
|
Muối kim loại nặng Hg, As, Au |
(B.A.L) Dimercaprol |
2 mg/kg. 4 giờ/1 lần. Trung bình 2 - 4 liều. Sau tăng lên 3 mg/kg. 4 giờ/1 lần/2 ngày. 3 mg/kg. 6 giờ/1 lần/1 ngày. 3 mg/kg. 12 giờ/1 lần/7 - 10 ngày. |
| Acetaminophen | N.A.C | 140 mg/kg liều đầu, tiếp 70 mg x 17 liều, cách 4 giờ. |
| Lân hữu cơ (Wofatox) |
Atropin PAM.(pralidoxime) |
0,05 mg/kg. Nhắc lại liều cách 2 - 5 phút. 10 - 20 mg/kg TM có thể lặp lại sau 30 phút - 1 giờ. |
| Fe | Deferoxamine | 50 mg trung bình cách 4 giờ hoặc 15 mg/kg/giờ. |
| Gây Met Hb | Vitamin C, coloxyl | 1 ống 0,1 g/10ml TM trong 5 - 10 phút. |
| Nấm độc | Atropin |
Rehydration - electrolytes, rehydration, correction of electrolyte disorders, anti-acidosis based on clinical, blood gas. Anti-respiratory failure: Absorb sputum widely, posture, breathe O2, support respiration. Anti-shock, vasoconstriction: IV fluid replacement, when blood pressure is low, use vasopressor Dopamine. Antipyretic, sedative, anticonvulsant. Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.