This is an automatically translated article.
Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease is a rare skin condition characterized by dark red, hard, painful papules. The disease is diagnosed by skin biopsy. Currently, the cause is still unknown, but it often occurs in cancer patients, especially blood cancer.
1. Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease
Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease also known as Swee t's syndrome is a rare dermatological condition. The disease causes skin lesions, especially in the extremities, head and neck, and is accompanied by fever. Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease can present with a variety of disorders and is generally classified into 3 types:
Classical form Combined with malignancies Drug-induced LEARN MORE: How to treat Sweet's syndrome and how to prevent disease
2. Symptoms of acute febrile neutropenic skin disease
2.1 Manifestations of skin symptoms neutropenic skin disease has the following symptoms:
Nodules or dark red patches: usually appear on the face, neck, upper extremities, especially the pubic hand. It can also appear in the mouth. Lesions such as pustules, pustules, or vesicles are rare. Fever: usually precedes skin lesions, and can last from days to weeks. Elevated neutrophils Pain in the patches Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease in patients with leukemia often presents under the skin, typically red blood clots often appear present in the limbs. In the lower extremities, the lesions present resembling erythema nodosum.
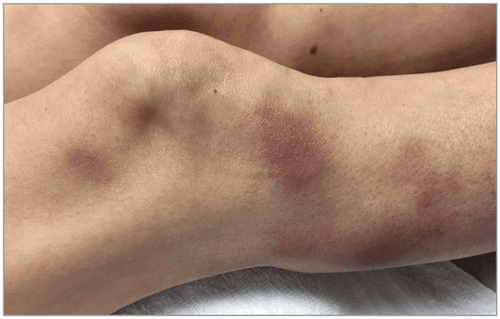
Tổn thương biểu hiện giống với hồng ban nút tại chi dưới của người bệnh
Eyes: conjunctivitis, scleritis, iritis Joints: arthralgia, inflammation joints , myalgias Internal organs: neutropenic alveolitis, aseptic osteomyelitis, neurological changes, psychiatric, impaired liver, kidney and pancreatic function,...
3. Causes of acute febrile neutropenic skin disease
Acute febrile neutropenic skin disease is currently unknown cause. However, the disease often occurs in cancer patients and especially blood cancer. About 25% of patients have cancer, of which 75% are blood cancer, especially myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia. The classic form is mainly seen in women aged 30 to 50 years. In contrast, men with the disease are usually at an older age between 60 and 90 years old. In addition, Th1 cytokines, including IL-2 and interferon-gamma, predominate and may play a role in the formation of skin lesions of the disease. .
4. Methods of diagnosis and treatment
4.1 Diagnostic methods Diagnostic methods for acute febrile neutropenic skin disease include:
Clinical examination: based on disease symptoms and medical history. Subclinical: Skin biopsy is indicated when the diagnosis is unclear. Histopathology showed edema in the superficial dermis with dense neutrophil infiltration in the dermis. Vasculitis may be present but is secondary. The diagnosis is suggested by the presence of clinical lesions and reinforced by related diseases or medications. In addition, it is necessary to differentiate acute febrile neutropenic skin disease with diseases such as:
Erythema multiforme, Erythema persistently raised, acute lupus erythematosus, pyoderma gangrenosum, Erythema knot
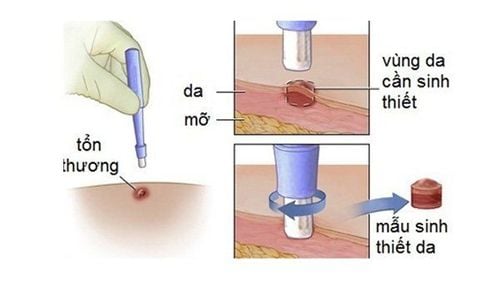
Người bệnh có thể được chỉ định sinh thiết da giúp chẩn đoán bệnh da tăng bạch cầu đa nhân trung tính có sốt cấp tính
Colchicine 0.5mg: 3 times a day dose Potassium iodide 300mg: taken 3 times a day In addition, antipyretic drugs are also recommended. Use intralesional corticosteroids for local treatment of skin lesions with triamcinolone acetonide. In difficult cases, some other drugs will be used such as dapsone, indomethacin, clofazimine, etanercept, infliximab, thalidomide, minocycline and mycophenolate mofetil.
In summary, acute febrile neutropenic skin disease is a rare skin disorder. The cause of the disease is unknown, but it is common in cancer patients, especially blood cancer. The disease has lesions on the skin that, if left untreated, can lead to infection. Therefore, when seeing abnormal symptoms, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility for examination and appropriate intervention measures.
In order for patients to detect acute febrile neutropenic skin disease early, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/ CT, SPECT/CT, MRI, ultrasound, skin biopsy, testing, ... are the most modern, meeting international standards to perform paraclinical tests.
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease, the stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always performed by a team of experienced doctors and nurses in close coordination with many specialties to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After going through the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the treatment is effective or not.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.