This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by CCII Doctor Bui Thu Huong - Head of Emergency, Day Treatment Unit - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Acute abdominal pain in children is a very common phenomenon, appearing suddenly and most of them are not dangerous for children, the pain can go away on its own without the need for treatment intervention. However, when children have acute abdominal pain, it is necessary to rule out surgical causes for appropriate management.
1. Definition of acute abdominal pain in children
Acute colic is an emergency diagnosis that occurs suddenly, immediately, and has an acute impact on the child's functioning.
May combine symptoms of a medical or surgical cause.
2. Approach to the patient with acute abdominal pain
Approach the patient with acute abdominal pain by:
Asking about the nature of the abdominal pain How the pain occurs: Date and time associated with meals Sudden or gradual Location of abdominal pain at onset Intensity of pain: Severe, causing the child to wake up and stop playing. Factors that increase pain: Walking, coughing, taking a deep breath, urinating. Analgesic factors: Rest, vomiting, postprandial, analgesic positions Immediate pain progression: Decreased, increasing pain, constant Progression persists, alternating, intermittent.

Bác sĩ sẽ thăm hỏi cha mẹ về tình hình đau bụng cấp ở trẻ
3. Signs accompanying abdominal pain
When a child has acute abdominal pain, it may be accompanied by the following signs:
General condition: Fever, anorexia, fatigue, weight loss Digestive symptoms: Nausea, vomiting blood Movement disorders: Constipation , bowel obstruction Diarrhea (number of stools, loose stools, with bloody mucus) Respiratory: Runny nose, cough Urinary: Painful urination, anuria, blood in urine, dark color. Neurological: Headache, bipolar disorder Joint pain, muscle pain Rash or bleeding Signs of puberty: First period Family background: Family conflict Child's social relationships School children have Learning difficulties History: Acute abdominal pain or similarity to previous pediatric pain History of surgery

Trẻ bị đau bụng cấp có thể kèm theo triệu chứng biếng ăn
4. Guide to examining the abdomen when the child is in pain
Observation: Abdominal distention, abdominal mobility Scarring of abdominal wall Abdominal palpation: Assess degree of tenderness, focal pain point Abdominal wall stiffness, abdominal wall response and peritoneal touch Abdominal percussion: abdominal distension, low-grade percussion, loss of pre-hepatic opacity Listen to the abdomen to assess bowel movements Stimulating the abdominal wall for signs of snakes, floating intestinal loops Rectal examination
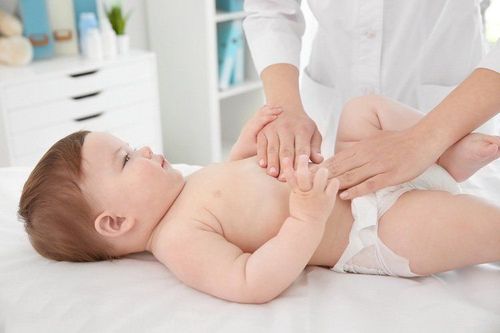
Sờ bụng để thăm khám đánh giá điểm đau khu trú
5. Guidelines for full body examination when children have abdominal pain
Need systematic physical examination Manifestations of infection Mucosal skin: Pale skin, jaundice, anemia, hemorrhage, rash Assessment of shock: Pulse, blood pressure, refill Respiratory examination: Rhythm breathing, listening to the lungs Joint examination: Find purpura joints Ear, nose and throat examination In addition, to prevent diseases that young children often suffer from, parents should pay attention to nutrition to improve the resistance of children. At the same time, add supporting foods containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins,... snacks and less digestive problems.
Parents can learn more:
Why do you need to supplement Lysine for your baby?
The role of zinc - Guidelines for reasonable zinc supplementation
Please visit the website Vinmec.com regularly and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.