This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc Duong Xuan Loc - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 12 years of experience as a Gastroenterologist.When cirrhosis has turned to cirrhosis, ascites, the patient's health will decrease, the pain and discomfort appear more and more. At this time, the method of aspiration of abdominal fluid is used by doctors to prevent abdominal distention, making it difficult for patients to breathe, and rupture of esophageal veins.
1. Indication for aspiration of the abdominal cavity
Abdominal aspiration is a procedure to remove fluid from the peritoneal cavity. Normally, this fluid is just enough to smooth the peritoneum, secreted and absorbed into the lymphatic system, but in the process of cirrhosis ascites, the amount of fluid in the cavity is too large, called ascites.Normally, the ascites is serum-like, clear and light yellow, can aspirate the abdominal cavity to make laboratory specimens and reduce intra-abdominal pressure due to the presence of too much fluid. The doctor must perform this procedure with the assistance of a nurse and follow strict aseptic procedures.
Determine ascites in the case of little fluid, unclear clinical manifestations, still discreet. Know the nature of ascites fluid: Fibrin, pus, blood; This helps to diagnose the cause of abdominal fluid obstruction. Amniocentesis when the ascites is too tight due to a lot of fluid so that the patient can breathe easily and the doctor can examine the patient easily. Abdominal sinus aspiration is indicated for all patients with ascites due to heart, kidney, and liver disease. When a small amount of fluid is removed, it is called a puncture, when a large amount is taken, it is called a peritoneal puncture. Inject the drug into the peritoneal cavity in cases requiring treatment.
2. Procedure for performing abdominal aspiration technique
2.1 Patient preparation
Explain to the patient the purpose of the abdominal aspiration procedure. Instruct the patient on necessary things such as defecation, urination before the procedure... Check pulse, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate. If the procedure for aspiration is performed at the hospital bed, there must be a screen so as not to affect other patients.2.2 Preparation of tools
Nurses wear masks, hats, wash hands, and wear gloves. Sterile instruments are prepared in sterile trays and covered with sterile towels. Two needles to probe or remove:Needle probe 1mm in diameter, 5-8cm long. Needle to remove 1.5 - 2mm in diameter, 5 - 9cm long. Prepare sterile instruments: One 5ml syringe for anesthesia, one 20ml syringe for fluid aspiration, one cannula with holes, two pliers, one Kocher clip with tab, one Kocher clip without tab, pliers for pressing post-needle puncture, a Michel stapler.
Prepare clean tools: Vial of iodine alcohol, alcohol 700, anesthetic novocaine or lidocaine 1-2%, glass beaker containing 100ml distilled water mixed with 2 drops of acetic acid to do the rivalta reaction. Rack for 3 labeled test tubes, including one sterile tube, clearly stating the patient's name, department, and room.

2.3 Perform the technique of aspiration of the abdominal cavity
Place the patient in a lying position depending on the condition of the disease and at the request of the doctor; usually lie on your back on the side of the puncture close to the bed, put a pillow under the back of the opposite side so that the puncture side is lower; or half-lying, half-sitting position; or place the patient in a recliner, feet resting on a baby chair.Disinfect the puncture area: Draw a line from the navel to the anterior upper iliac spine, divide this line into 3 parts, disinfect the outer 1/3 point. Patients are usually poked on the left side, rarely on the right side to avoid puncture of the cecum. However, sometimes poking on the right side is prescribed by a doctor. Disinfect 2 times, first with alcohol iodide, next time with alcohol 700.
Pour alcohol 700 to disinfect doctor's hands. Prepare anesthetics for the doctor to smoke smoothly and aseptically. When the doctor anesthetizes, the nurse monitors the patient's facial expression, pulse, and encourages the patient. The nurse disinfects hands, gently pours the needle into the doctor's palm. When the fluid begins to flow, insert the needle tube so that the doctor can clear the tube, place the bean tray to catch the first few drops of liquid.

Collect into 3 tubes: cell, bacteriological and biochemical tests. Bacterial culture tube must be sterile, burn the mouth of the test tube before and after taking the solution with alcohol lamp. Do the Rivalta reaction at the bed
Method: Put 2 - 4 drops of the solution into a beaker containing 100ml of distilled water and acetic acid. Result: if a cloud like cigarette smoke settles to the bottom of the cup, the Rivalta test is positive. If no cloudiness is observed in the beaker, the Rivalta reaction is negative. Positive Rivalta test: is exudate, the amount of protein in the fluid is more than 30g/liter. Negative Rivalta reaction: is permeable fluid, the amount of protein in the fluid is less than 30g/liter. Regularly monitor the patient's facial expression and pulse while draining the fluid. When the doctor removes the needle, the nurse disinfects the puncture site, puts a gauze, and bandages it.
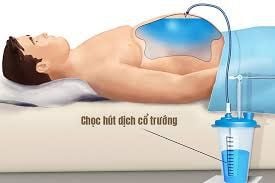
Facial expression, pulse, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate. The amount, nature, and color of the fluid that flows out. Signs of abdominal pain or distention. Faint. Infection status. Accurately label specimens and send them immediately to the laboratory. People with cirrhosis and ascites are often used this procedure to avoid serious complications in the abdomen. Usually, the specialist will appoint a regular schedule to aspirate fluid in the abdominal cavity. Abdominal sinus aspiration is a common method used by specialists to reduce fluid pressure in people with cirrhosis and ascites.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Is cirrhosis of the liver ascites contagious? Treatment of advanced cirrhosis: What you need to know Manifestations of cirrhosis and ascites?