This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong- Gastrointestinal endoscopist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Duodenal cancer is a rare disease among gastrointestinal cancers. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of the disease are often difficult. If the patient notices the signs and risks of the disease, it is necessary to visit reputable medical institutions to perform screening and diagnosis of the disease, limiting the risk of possible complications.
1. Where is the duodenum located in the body?
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the jejunum, the next part of the small intestine. The duodenum is shaped like a horseshoe and is responsible for taking digested food from the stomach.
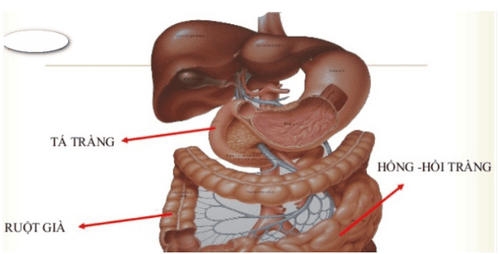
The duodenum plays an important role in the digestive process. Because digestive juices, bile, and pancreatic juice combine in the duodenum to help break down food. Here, vitamins and other nutrients begin to be absorbed into the body before food reaches the jejunum.
Duodenal cancer, although rare, can affect digestion and prevent the body from absorbing the minerals it needs to function properly.
2. Overview of duodenal cancer
Primary duodenal adenocarcinoma is an extremely rare disease. Kleinerman J. and Cs found an incidence of 0.03% per 500,000 autopsies. Deba P. Sarma and Cs had a rate of 0.048 % in 6227 autopsies. In the small bowel tumor group, duodenal adenocarcinoma accounts for only 1-1.6%. Besides, the diagnosis is also very difficult, even though there are modern imaging tools like today because people pay little attention to the disease due to its low frequency. According to the literature, X-ray and endoscopic methods are not enough to make a diagnosis.
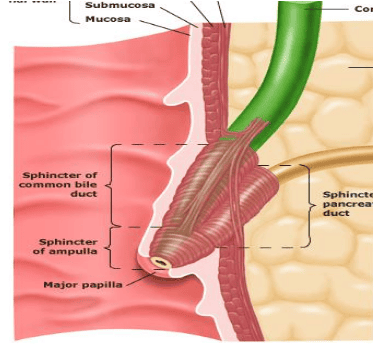
In the reports of duodenal cancer, cancer in the Vater papilla is often excluded because of the peculiarities of the tumor in this region, because it is the junction of the three bile ducts, pancreas and duodenum.
3. Causes of duodenal cancer
Currently some of the main causes of duodenal cancer are:
Alcohol Tobacco Helicobacter pylori bacteria Stress Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids. In addition, some health conditions such as belching, heartburn, peptic ulcers also increase the risk of disease.
4. Clinical symptoms of duodenal cancer
There are no specific symptoms for this disease. Currently, duodenal cancer is a fairly rare form of cancer in the digestive tract. In the early stages of the disease, the patient may have no symptoms, the patient can only be discovered by chance through routine physical examination, screening endoscopy... So when cancer cells begin to form In the duodenum, tumors can prevent food from passing through the digestive tract. And when food cannot pass through the small intestine or when the body cannot absorb the necessary vitamins, the person may experience some of the following symptoms:
Acid reflux. Weight loss. Bloody stools. Constipation . Vomiting. Stomachache. Nausea. In most cases, symptoms appear in the later stages, when the tumor has grown large enough to block food. At that point, the person may notice a lump in the abdomen.
5. Stages of duodenal cancer
Duodenal cancer can be diagnosed in five different stages, namely:
Stage 0: Cancer cells are present in the walls of the duodenum. Stage 1: The cancer cells are only in the duodenum and have not spread to the lymph nodes. Stage 2: The cancer has grown through the layers of the intestine, to the connective tissues, muscles, and lymph nodes. Stage 3: Cancer cells have spread to nearby organs or other parts of the small intestine. Stage 4: Cancer has spread throughout the abdomen, bones, or distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or pancreas.
6. Diagnosis of duodenal cancer
Until now, diagnosing duodenal cancer can be very difficult because symptoms often occur in later stages of the disease. Tests that produce detailed images of the digestive tract can diagnose diseases such as:
Magnetic resonance imaging Endoscopic computed tomography. Biopsy. Drink barium for X-rays to examine the upper digestive tract.
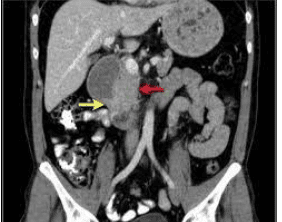
To date, gastrointestinal endoscopy is considered the most valuable for the diagnosis of this pathology. Endoscopy showed images around the ampulla of Vater, D2 of the duodenum, biopsy of the suspected lesion for histopathology.
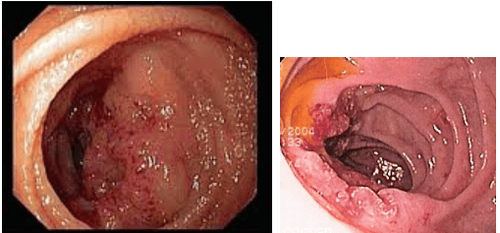
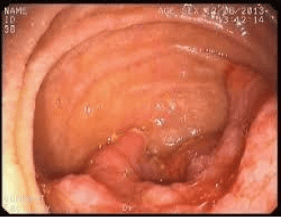
7. Treatment of duodenal cancer
7.1. Early stage
Excision of duodenal tumor by EMR (endoscopic mucosal resection technique) or ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection technique)
For duodenal lesions still localized in the mucosa, has not invaded the submucosa, the complete removal of tumor lesions, preserving organ functions, helping patients avoid a major surgery, improving the quality of life for patients. However, this technique requires early detection of the disease, a mature technique, because if not careful, it will cause bleeding complications, duodenal perforation, acute pancreatitis ....
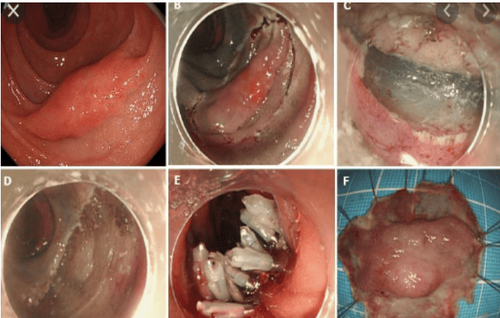
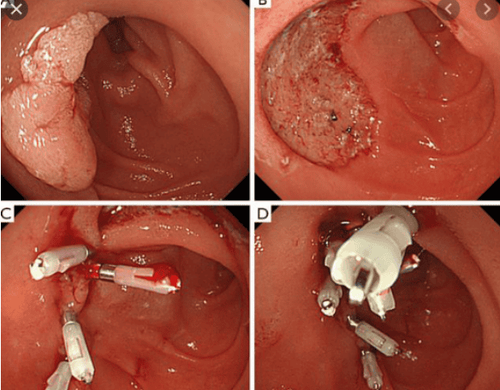
7.2. Late stage
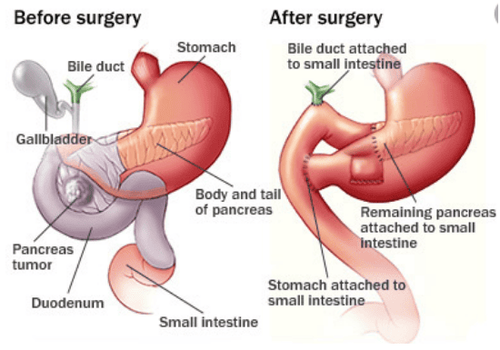
When the tumor has invaded the submucosa, surgery is the preferred option. The current commonly used method is resection of the entire pancreaticoduodenal mass (Wipple method), however the complications of this method are still quite high (death, pancreatic fistula, bleeding, anastomosis ...)
Usually treatment for duodenal cancer depends a lot on the stage at which the patient has been diagnosed. However, the most common and most effective treatment option in invasive disease is surgery with or without chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
In surgery, doctors will try to remove the tumor in the duodenum so that food passes through the stomach. In addition, another surgical option is the Whipple procedure. In this procedure, the doctor removes the duodenum, gallbladder, and part of the pancreas.
Currently, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital is equipped with the most modern digestive endoscope system of Olympus, one of the best brands today. In which, there are machines being used for treatment such as the Olympus CLV 190 endoscope, especially with a team of doctors who have extensive experience in early cancer diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract, trained through many training courses in the field of cancer treatment. and abroad on cancer diagnosis and treatment will help patients detect the disease at the earliest stage.
The advantage of these endoscopes is that in addition to the conventional white light endoscope, the system also has the function of narrow band light (NBI), magnified endoscope, with high resolution NBI endoscopic images and High contrast makes it easier to detect and screen and diagnose gastrointestinal cancer at an early stage. Accordingly, cancerous lesions detected at an early stage, depending on the nature of the lesions, will be cut by mucosal resection (EMR), or submucosal dissection (ESD) via flexible endoscopically. without having to undergo surgery. Not only that, in order to ensure sterility, the hospital endoscopes are also equipped with an automatic endoscope washing machine and RO water filtration system.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading hospitals in the country for examination, diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.