This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tran Thanh Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.The urinary tract is the organ system responsible for filtering blood, forming and excreting urine as well as toxins and products of metabolism. Urinary tract infections cause discomfort and sometimes lead to dangerous complications, sepsis. Learning and having a way to prevent this disease is a way to keep yourself and your loved ones healthy.
1. What is UTI?
The urinary system consists of two organs: two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder and a urethra. The kidneys have the function of filtering blood and filtering waste products out of the blood, protein metabolism products, and electrolytes to form urine. Urine passing through the filter tubes in the kidneys becomes gradually concentrated, following the ureters to the bladder. When the bladder is full, the bladder muscles reflexively contract, causing a feeling of needing to urinate, signaling we have to urinate, releasing urine through the urethra.Under normal conditions, urine is completely sterile. The presence of bacteria in the urine is evidence of a urinary tract infection, also known as a urinary tract infection.
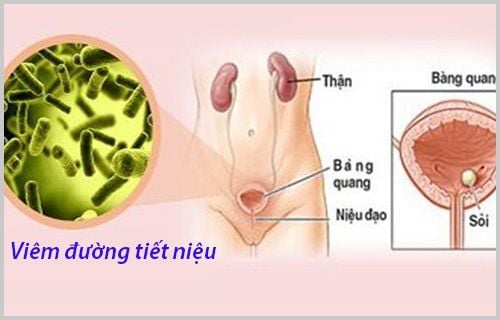
Urinary tract infections have many classifications:
Classification by location: Upper urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis - acute pyelonephritis, pyelonephritis - chronic pyelonephritis, retrograde nephritis, renal abscess, kidney purulent discharge) and lower urinary tract infections (including cystitis, urethritis, orchitis, prostatitis). Classification by course: Uncomplicated and complicated UTIs are recurrent urinary tract infections, common in people with urinary system abnormalities, catheter placement, and neurological disorders. menstrual bleeding, these patients are often in the hospital. Classification according to the degree of recurrence: isolated bacteriuria, recurrent bacteriuria, recurrent bacteriuria, recurrent bacteriuria.
2. Common objects and causes
Newborn to less than 5 years old: This period is less likely to occur UTIs. If so, then boys have a higher rate due to abnormalities of the urinary tract, which makes urine easy to stagnate and is an ideal environment for bacteria to reside. School-going children: The rate of UTIs is higher in the group of children who just started school than in the general population, probably related to hygiene problems. Adults up to 65 years of age: In this group, the rate of urinary tract infections in men is quite low, often due to anatomical abnormalities of the urinary system, urinary stone disease, prostate disease, and urinary system interventions. such as catheterization. Meanwhile, urinary tract infections in women are common. About 10% of women in this age group have a UTI once in their life due to sexual activity or pregnancy. In addition, because the anatomical structure of the urethra is shorter in women than in men, bacteria are also easier to penetrate. Age group over 65: The rate of urinary tract infections did not differ between the sexes.
3. What are the manifestations of urinary tract infections?
Local manifestations Urinary tract infections sometimes have no symptoms but are discovered by chance during a urine test for a general physical examination. Common subjects in this situation are women of sexually active age, pregnant women, people with diabetes,...
If there are symptoms, the patient has uncomfortable symptoms on the urinary system. when urinating, such as the need to urinate, the urge to urinate, the urge to urinate often, or the feeling that there is still urine in the bladder even though you have just finished urinating. Patients with cloudy urine, purulent urine, urine with blood or strong odor. In addition, the patient can also go to the doctor because of the pain in the lower abdomen when cystitis or pain in the hip and back when the urinary tract infection is in the kidney. If the kidney has stones that cause fluid retention, infection or kidney abscess, examining this area will be very painful.

Systemic manifestations Because the kidney is an organ in direct contact with the blood. Every day, the kidneys have to receive a huge amount of blood to filter and form urine. Therefore, when bacteria enter the urinary system, it is also very easy to enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. At this time, the patient has a high fever, intermittent chills, dry lips, dirty tongue, and emaciated face. Signs of infection and intoxication are evident.
4. How to treat urinary tract infections
Antibiotics are the mainstay therapy in the treatment of urinary tract infections. If the patient has only local symptoms due to urethritis, the doctor usually prescribes oral antibiotics for 5 to 7 days. If the patient has fever, chills, symptoms of sepsis, and inflammation in the upper urinary tract, they need to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
In cases of recurrent urinary tract infections, patients with urinary tract abnormalities or urinary catheters, it is necessary to culture bacteria to find the right antibiotic sensitive to that strain of bacteria.
In addition, oral antiseptics on the urinary system have also been reported to be effective in eradicating bacteria, which can be prescribed in conjunction with antibiotics. However, the evidence for these drugs is still unclear.
Besides, if the infection is not controlled by drugs or complications in the kidney, pyelonephritis, kidney abscess, surgical intervention is required. Similar to urinary system malformations, without complete surgical correction, patients are prone to recurrent urinary tract infections, which can lead to serious complications for a long time.
5. Complications of urinary tract infections
Lower urinary tract infections in women without abnormalities of the urinary system or renal tissue are likely to be benign, and the disease is usually curable.
In contrast, UTIs occurring in patients with pre-existing predisposing factors can lead to serious, sometimes life-threatening, complications. The risks and complications of UTIs are many, including virulence of bacteria causing host destruction of renal tissue, renal papillary necrosis, obstruction or impaired renal function. If this condition persists, it can lead to permanent kidney failure or the need to remove the kidney.
If the persistent presence of bacteria in the urinary system is not treated correctly and with an adequate dose of antibiotics, bacteria can easily enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis, septic shock and death.
Urinary tract infections in men can progress to prostate abscess, orchitis, epididymitis, ... blocking the vas deferens, increasing the risk of infertility.
Urinary tract infection in pregnant women increases the risk of amniotic fluid infection, fetal infection, increased risk of premature rupture of membranes, premature birth, ...

6. How to prevent urinary tract infections
Must drink enough water, every day 2 - 2.5 liters to help the kidneys increase urine excretion, increase the expulsion of germs out, limit infection upstream. Maintain hygiene of the genitourinary system. For women, menstrual hygiene is required. Patients who have had or are suffering from kidney - urological stones must regularly examine and screen for UTIs for early treatment and intervention to remove stones when indicated. Urinary tract infections must be treated properly and thoroughly from the very beginning to prevent recurrence. Urinary tract infections can be prevented and treated if the patient detects early signs and actively goes to the doctor for treatment. Absolutely do not self-medicate without a doctor's instructions because it can make the condition worse, causing unnecessary consequences. Currently, Vinmec International Hospital always provides screening packages for urinary tract diseases, this is an effective method to help patients screen for diseases and protect their own health. For pregnant mothers, regular checkups and tests with accurate diagnoses will help detect abnormal signs early and have a thorough treatment.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.