This is an automatically translated article.
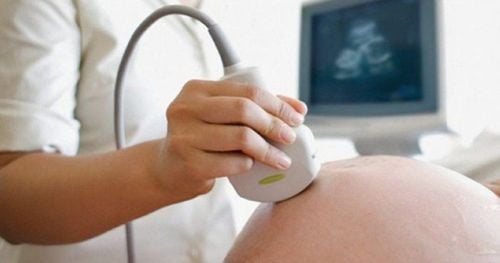
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Amniotic fluid surrounds the fetus and is responsible for protecting and maintaining a stable temperature, water and electrolyte balance, etc. to help the fetus develop well in the womb. Evaluation of amniotic fluid by ultrasound is one of the methods to diagnose and detect abnormalities of amniotic fluid early.
1. Amniotic fluid
1.1 Origin of amniotic fluid Origin of amniotic fluid is formed from:Amniotic membrane: Amniotic membrane is a part that covers the placenta and umbilical cord, it also has the function of secreting amniotic fluid Fetal: The fetal skin has related to the formation of amniotic fluid appears in the early stages of pregnancy from the 20th week, to the 28th week to terminate. However, from the 16th week of pregnancy, amniotic fluid is released from the urinary tract when the fetus urinates into the amniotic chamber. In the 20th week from the trachea, amniotic fluid is secreted, due to the permeation of fetal plasma through the respiratory mucosa. Maternal Blood: Nutrients from maternal blood and amniotic fluid are exchanged across the amniotic membrane. 1.2 Functions of amniotic fluid Amniotic fluid surrounds the fetus and is responsible for protecting the fetus from external influences. In addition, amniotic fluid helps the fetus maintain a stable temperature, water and electrolyte balance. Moreover, this is also a nutrient-rich environment with the ability to regenerate and exchange, which plays an important role in the life and development of the fetus.
Amniotic fluid has the function of nourishing the fetus from the beginning of pregnancy through the reabsorption of amniotic fluid, which is carried out through the fetal digestive system. After the placenta appears, amniotic fluid plays a role in keeping the metabolism of water and other substances to ensure the life and development of the fetus. From the 20th week of pregnancy, the fetus begins to drink amniotic fluid. In addition, amniotic fluid is also reabsorbed through the amniotic membrane, umbilical cord and fetal skin. The fetus absorbs 300-500ml of amniotic fluid per day after the 34th week of pregnancy. The amount of amniotic fluid will enter the bloodstream to help balance the fluids in the fetus's body, and part of the amniotic fluid to form urine. Amniotic fluid enters the intestines to make meconium.
Besides, amniotic fluid has a protective function, creating an environment for the fetus to develop harmoniously. In the last months of pregnancy, the amniotic fluid normalizes to the fetal position in the mother's genital tract. Amniotic fluid protects the fetus from the trauma of uterine contractions and infections during labor. Amniotic fluid helps facilitate cervical dilation by establishing the amniotic sac to dilate the mother's cervix. After the water breaks, the amniotic fluid is oily, which helps to lubricate the mother's genital tract, making it easier to deliver the baby.

8-12 weeks of pregnancy: Amniotic fluid volume is about 50ml; Week 28 of pregnancy: Amniotic fluid volume at most about 1000ml; The 30th week of pregnancy: The volume of amniotic fluid decreases gradually, to about 900ml; Week 40 of pregnancy: Amniotic fluid volume from 600-800ml. 1.4 Color of amniotic fluid In the early stages of pregnancy, amniotic fluid is white and clear, and will gradually turn cloudy as the fetus grows because it contains many substances. By the 38th week of pregnancy, the fetus is mature enough, the amniotic fluid will be milky white.
2. Evaluation of amniotic fluid by ultrasound
2.1 Assessment of the volume of amniotic fluid There are many ways to measure the volume of amniotic fluid:Measurement of the largest amniotic cavity: Measure the largest amniotic cavity in the vertical depth, without the umbilical cord inside. Amniotic index AFP measurement: Divide the uterus into 4 parts, using two intersecting lines at the belly button of the pregnant woman. Measure the depth of the largest amniotic cavity in each chamber and calculate the sum of the above measurements. Measure the largest amniotic cavity in both longitudinal and transverse directions, calculate the area of that amniotic cavity. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of amniotic fluid volume:
Qualitative assessment: Increase or decrease, subjectively according to the doctor doing ultrasound (>2 and <8 are normal) Amniotic index AFI: Divide the uterus into 4 parts, two transverse lines at the navel. Measure the depth of the largest amniotic cavity in each chamber and calculate the sum of the measurements in the longitudinal profile of the mother (12-13 cm is normal) Measure the amniotic area: DDo the horizontal and vertical dimensions of an amniotic sac 2.2 Measurement Largest amniotic cavity To find the largest amniotic sac, measure the depth of the largest amniotic cavity vertically, without the umbilical cord. The AFI is an index that measures the measurements of the largest amniotic sac according to the following table:
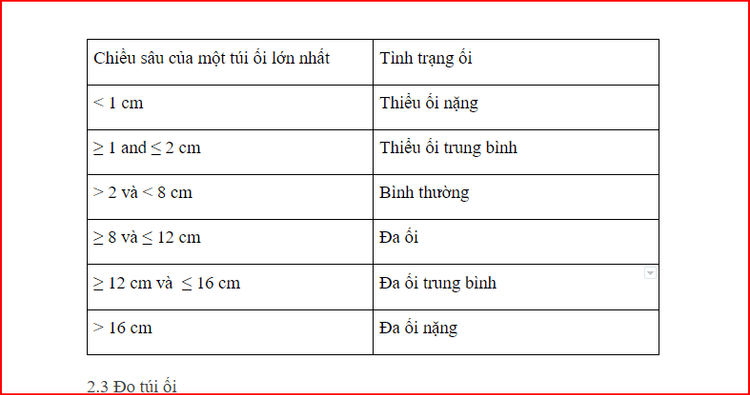

2.4 Measure the area of the amniotic fluid Measure the largest amniotic cavity horizontally and vertically. AFV index is an index to assess the volume of amniotic fluid:
Normal: 15-50cm2 Polyhydramnios: >50cm2 Oliguria: <15cm2 In short, amniotic fluid is one of the important parts for healthy fetal development. Evaluation of amniotic fluid by ultrasound is the best imaging method, helping to detect abnormalities such as polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, etc. Therefore, in addition to regular antenatal check-up, when you see the signs, Abnormalities need to go to a medical facility to be examined and detected in time.
During pregnancy, in addition to evaluating amniotic fluid by ultrasound through each stage, to monitor the comprehensive development of the fetus, pregnant women need:
Comprehensive fetal malformation screening by ultrasound technique outstanding 4D sound. Screening for gestational diabetes, avoiding many dangerous complications for both mother and baby. Control the mother's weight reasonably to assess the health status of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. Understand the signs of threatened early delivery (especially in those carrying multiple pregnancies or having a history of miscarriage or premature birth) so that they can receive timely treatment to maintain pregnancy. To protect mother and baby during pregnancy, Vinmec provides a comprehensive Maternity service to monitor the health status of mother and baby, periodical antenatal check-ups with leading Obstetricians and Gynecologists. enough tests, important screening for pregnant women, counseling and timely intervention when detecting abnormalities in the health of mother and baby.
For detailed information about all-inclusive maternity packages, please contact the hospitals and clinics of the Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.