This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is based on clinical symptoms and family history. Treating atopic dermatitis requires trying different treatments for months or years. Even if atopic dermatitis is successfully treated, the disease can still recur.
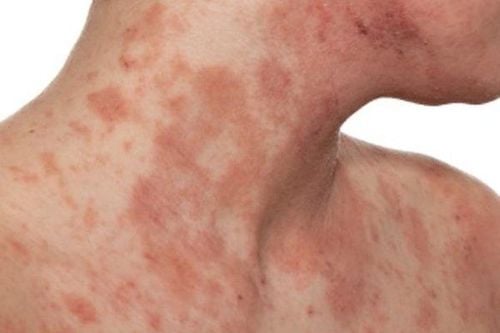
Atopic dermatitis is a skin disease that makes the skin red and itchy. The disease can occur at any age but is most common in children. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition and may be accompanied by asthma attacks or pollen allergies.
1. Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is mainly based on clinical symptoms and family history.Itching of the inflamed area; Chronic and recurrent dermatitis; Typical lesion morphology and location: In children, eczema is localized in the face, extensor region; in older children and adults, keratosis, lichen in the folds; Personal or family history of treatment for atopic dermatitis, asthma, allergic rhinitis; Other clinical symptoms such as: Dry skin, cheilitis, recurrent eye conjunctivitis and irritation, red or pale facial color, food allergies, eczema on the palms or backs of the hands, IgE increased, positive type 1 immediate skin reaction, white scales;

2. Treatment of atopic dermatitis
Here are ways to prevent and treat atopic dermatitis at home as well as a treatment regimen of a dermatologist.2.1 Home treatment Before examining or taking medicine, there are several ways to treat atopic dermatitis at home to help relieve symptoms as follows:
Warm bath: You can add a little baking soda or oatmeal grind into warm water, soak for 10-15 minutes, then dry your body, use moisturizer right after; Do not scratch the itchy area: You can use your fingertips to gently press the itchy area to relieve discomfort; Use a band-aid: Bandaging the itchy area will help protect the skin and limit scratching to damage the skin; Use mild soaps: Fragrance-free and detergent-free soaps will avoid irritating your skin. After using soap, the skin in contact with soap should be washed thoroughly; Use a humidifier: Hot and humid environments can make itchy and flaky skin worse. Therefore, use a humidifier in combination with an air conditioner to keep the indoor air cooler and more humid; Wear comfortable clothing: In the treatment of atopic dermatitis, skin irritation should be reduced by avoiding tight and stiff clothing. Instead, choose clothes that are soft and absorb sweat well; Avoid stress and anxiety: Stress and psychological disorders can make atopic dermatitis worse. Therefore, improving mental health will help reduce itchy skin. 2.2 Use of drugs Treatment of atopic dermatitis needs to be started early. If regular moisturizing and self-care at home don't work, your doctor may prescribe a number of medications including oral, topical, or even injectable medications to help reduce inflammation and relieve itching:
Topical creams relieve itching and help heal the skin: Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids help fight bacteria and reduce itching. Apply cream as directed by your doctor after moisturizing. A side effect of overuse of these creams is possible thinning of the skin, so they should only be used as directed by your doctor. Medicines such as Protopic and Elidel can be used to treat atopic dermatitis in children over 2 years old, when applying the drug (under the guidance of a doctor) should avoid strong sunlight; Anti-infectives: Antibiotic creams are used when the skin is infected, or the wound is open or cracked. You may also need to take antibiotics for a short time to treat the infection; Oral medications: In more severe cases, oral corticosteroids such as Prednisone are more effective, but can cause serious side effects if used long-term.

Bandage: In severe cases, bandages are the treatment. efficient and in-depth. This therapy is usually done in the hospital, which involves dressing the inflamed area with topical corticosteroids and wet dressings; Light therapy: For cases where the disease does not respond to topical medications or the disease often recurs, light therapy will be applied, which is exposing the skin to certain natural light. Some other forms of this therapy are the use of artificial UVA and UVB rays, which can be combined with drugs to treat atopic dermatitis. However, long-term use of this therapy can lead to side effects including premature skin aging and also an increased risk of skin cancer. Therefore, light therapy is limited in use in young children and should not be used in infants at all; Psychotherapy: Relaxation therapies, behavior modification, and biofeedback can help reduce scratching. In addition, to prevent disease outbreaks and help improve dry skin, the following ways can be applied:
Moisturize the skin: Apply a moisturizer suitable for the skin at least twice a day; Avoid and limit harmful agents to the skin: Factors such as sweat, anxiety, stress, overweight, obesity, exposure to soaps, harsh detergents, smog and pollen can aggravate atopic dermatitis. Note, for babies and young children, it is possible to get atopic dermatitis when eating certain foods such as eggs, milk, soy and wheat; Limit bathing for too long: Taking a warm bath for 10-15 minutes is reasonable; Use mild soaps: Choose soaps that are gentle on the skin. Soaps with deodorants and antibacterials can dry out the skin by stripping the skin of its natural oils; Dry the body thoroughly after bathing: After bathing, gently pat the skin with a soft towel to absorb the water, avoiding rubbing the towel with the skin too hard. 2.4 What should people with atopic dermatitis eat? Diet can greatly affect skin inflammation. Therefore, besides treating atopic dermatitis, patients should learn what foods should and should not be eaten to improve their condition:
Foods to eat: Omega-rich fish such as tuna, mackerel, salmon, sardines and herring (helps with inflammation); fermented foods such as yogurt, miso soup... contain many probiotics (helps with antibacterial); Colorful fruits and vegetables such as apples, cherries, broccoli, spinach or kale contain many flavonoids (anti-inflammatory) that support the treatment of atopic dermatitis; Foods to avoid: Eggs, tomatoes, soybeans, nuts, citrus fruits, dairy products, foods containing gluten, spices like vanilla, cloves and cinnamon, foods containing a lot of nickel such as black tea, chocolate, canned meat, shellfish such as snails, oysters, crabs..., legumes such as soybeans, lentils, peas,...; Abstain from some allergenic foods: such as pears, carrots, hazelnuts, celery, green apples.

3. Where is the best treatment for atopic dermatitis?
Clinical Dermatology at Vinmec Times City International Hospital is one of the leading medical facilities in the examination, diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis. The specialty is comprehensive in both professional quality and service, with modern medical equipment, ensuring the best support when performing simple to complex treatments.When visiting Vinmec Times City Clinical Dermatology Specialist, patients will be diagnosed and consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Thu - with more than 30 years of studying and working in the field of Dermatology. diseases and intensive treatment of dermatological diseases, including atopic dermatitis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.