This is an automatically translated article.
The cause of thin facial skin can be sun exposure, genetic factors or the use of certain medications for a long time... Thin facial skin is not a sign of a medical condition The problem is serious but cosmetic-related, so you should see a dermatologist for proper advice.
1. What is thin skin?
Thin skin is the appearance of bruises or peeling, easy to tear. Sometimes, the skin is so thin that it looks like tissue paper. Thin skin is common on the face, arms, and hands, affecting appearance and quality of life, especially in women.
Causes of thin skin are very common, including:
Skin aging: Collagen is a structural component of the skin that helps prevent wrinkles, sagging and loss of moisture. As the body ages, less collagen is produced, which makes it difficult for your skin to repair itself, leading to thinning skin. Ultraviolet Exposure: Much of the thinning of facial skin is usually associated with prolonged sun exposure. This is the part of the body that is rarely covered by clothing. Medications: You can thin your skin with long-term use of certain medications, most commonly topical and oral corticosteroids, over-the-counter aspirin, prescription blood thinners, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs). Lifestyle: People who smoke, use alcohol, are sedentary, and eat a lot of sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to thinning skin.
2. What to do with thin facial skin?
2.1. Treatment at a medical facility
In-office thin facial treatments include:
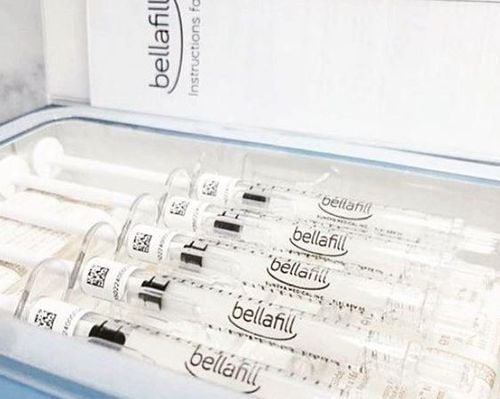
Microneedling: Microneedling can be done at home or in a medical facility to rejuvenate the skin. The doctor will apply local anesthetic to the skin and use a hand-held roller with very small needles attached to the surface of the skin. The needles cause minor bleeding but do not damage the skin. Repeating this treatment over time will help boost collagen production in the skin. Dermal fillers: Many types of dermal fillers provide a more youthful appearance. Laser Resurfacing Treatments: Several laser treatments are available in the clinic that will help reduce the signs of skin aging caused by UV exposure. Ablative lasers will vaporize tissue and produce dramatic results, but require a longer recovery time. Non-ablative lasers produce moderate results with little or no downtime. Therefore, your dermatologist will help you decide on the best laser options for your skin's needs. Photodynamic therapy and intense pulsed light: This is a light-based skin rejuvenation treatment. It focuses a specific wavelength of light onto the skin. First, the skin is covered with a topical photosensitive product, then repeat and monitor many times to get results. This treatment will stimulate collagen production and may help minimize sun damage.
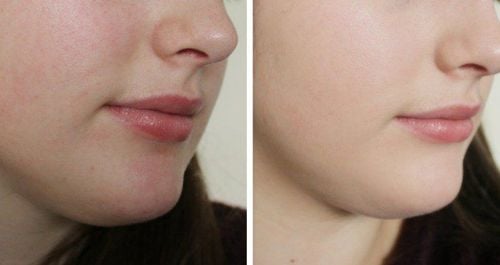
Tái tạo bề mặt bằng laser, lăn kim, tiêm chất làm đầy là các phương pháp điều trị da mặt mỏng tại phòng mạch.
2.2. Treatment of thin facial skin at home
Treatments for thinning skin that can be done at home include:
Using topical retinoids: Retinoids are a group of medications derived from vitamin A. Prescription topical retinoids are very effective in reducing and prevent signs of skin damage caused by UV exposure. Your doctor can discuss specific products or retinoids that are right for your skin type. Diet and nutritional supplements: A balanced diet is an important point in the home treatment of thin facial skin. Many of the ingredients needed for healthy skin are found in fruits, vegetables, fish, oils, and meats. The nutritional supplements vitamin C, gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), collagen peptides, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-aging effects on the skin. However, some supplements can interact with medications you're taking, so you should talk to your doctor before deciding to take any product.

Chế độ ăn uống cân bằng là điểm quan trọng trong quá trình điều trị da mặt mỏng tại nhà.
3. Measures to prevent thin skin
It is not possible to completely reverse the symptoms of skin damage caused by the sun. However, to prevent premature skin aging or further damage, the American Academy of Dermatology recommends the following:
Apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to unprotected skin. Avoid natural sunbathing. Quit smoking. Maintain a balanced diet. Drink less alcohol. Exercise regularly to strengthen the immune system and bring back younger looking skin. Cleanse skin gently and often, especially after sweating. Apply moisturizer daily and stop using products that cause skin stinging or burning, unless directed by your doctor. Besides, people with thin skin will appear bruises, scratches or abrasions. To reduce your risk of these injuries, you can:
Wear clothing to protect vulnerable body parts such as hands and feet, where you can easily collide with surrounding objects home. Consider wearing gloves to protect delicate skin. Move slowly and carefully to prevent bruises and scratches caused by accidents. Cover sharp edges of furniture and doorways with soft cushions. Trim your pet's fingernails. Good moisturizing for the skin. In summary, thin, weak skin, veins and veins are not a sign of a serious medical condition but related to a cosmetic problem, so you should see a dermatologist for proper advice. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Mayoclinic.org, Healthline.com