This is an automatically translated article.
Abdominal ultrasound is one of the most popular and important imaging tools for accurate diagnosis of biliary tract conditions such as biliary dilatation and focal liver lesions. So what are the features of intrahepatic biliary tract disease on ultrasound? Let's find out through the following article.
1. What is abdominal ultrasound?
Abdominal ultrasound is an imaging method performed through the abdomen to help provide information about the structure of the internal organs of the abdomen. This is a cost-effective, safe and effective technique for evaluating the hepatobiliary system, especially the gallbladder and biliary tract. However, ultrasound does not provide information about the function but only the structure of the organs. Abdominal ultrasound is indicated in the following cases:
Screening for hepatobiliary disease Evaluate intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tracts Differentiate intrahepatic and extrahepatic jaundice Investigate liver tumors Investigate spleen size to suggest abnormalities case of portal hypertension. In some cases, patients with obesity, abdominal distension can interfere with ultrasound, at this time, endoscopic ultrasound combines an ultrasound probe into the end of the endoscope for images with greater resolution even when the bowel is distended.
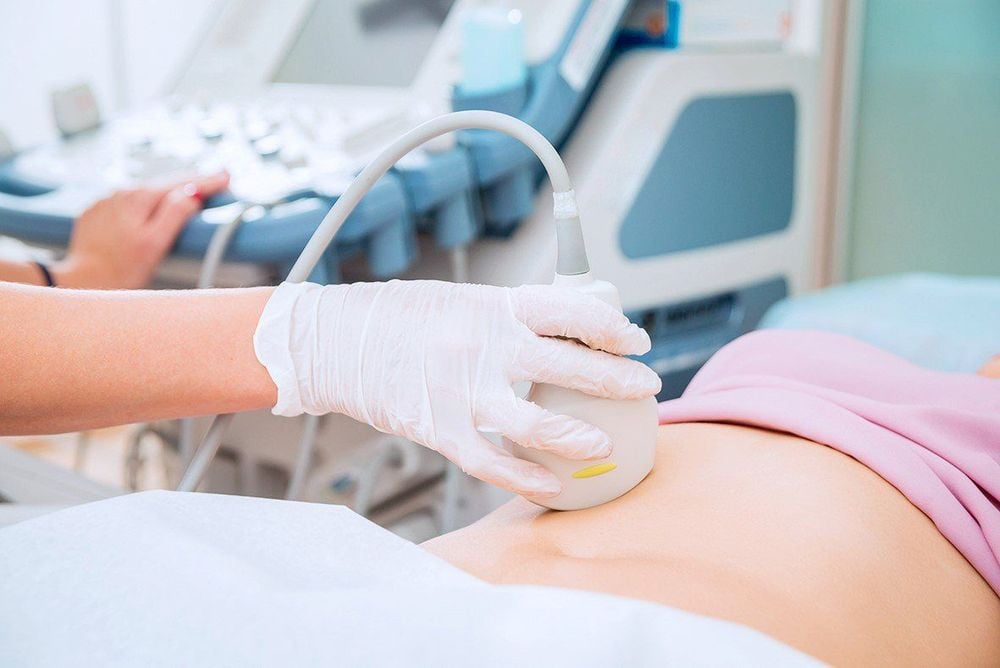
Siêu âm ổ bụng được chỉ định trong trường hợp giãn đường mật trong gan
The genetic cause of the disease is a recessive gene mutation that is common in men. The disease is characterized by segmental, rhomboid or non-obstructive biliary dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts. Patients with dilated intrahepatic biliary tract often have the following manifestations:
Fever Abdominal pain Enlarged liver Comorbidities: Polycystic kidney, cholangitis, biliary tract abscess, gallstones, sepsis, cirrhosis, kidney failure and cholangiocarcinoma. 3. Image of intrahepatic biliary dilatation on abdominal ultrasound On abdominal ultrasound, the biliary tree is normal with a hollow structure, the diameter is usually less than 7mm, but this is not a constant number that can be larger in humans old age, a history of old biliary tract surgery or old gallstones,... Ultrasound images of biliary tract dilatation may be suggestive signs of cholelithiasis, cholangiocarcinoma or pancreatitis. Thus, images of intrahepatic biliary dilatation on ultrasound in some cases are only suggestive of obstruction in the biliary tract, while the definitive diagnosis of the disease needs to be based on other specific signs on ultrasonography. sounds such as:
Gallstones: Hyperechoic image with shadow behind Biliary worms : Tri-layer image with two outer layers of parallel-sounding worm shell without shadowing like a “rail” and a reduced middle layer Yin is the intestines of worms. In summary, biliary tract dilatation on ultrasound may be suggestive of cholelithiasis, cholangiocarcinoma, or pancreatitis. Thus, images of intrahepatic biliary dilatation on abdominal ultrasound in some cases are only suggestive of obstruction in the biliary tract, while the definitive diagnosis of the disease needs to be based on other specific signs. on ultrasound..
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.