What tests are needed to diagnose congenital megacolon?
Posted by Doctor Dam Thi Quynh - Pediatrician - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Congenital megacolon is in about 15% of diseases and birth defects requiring surgery in children. The disease can affect any child, both male and female. So what tests should be done to diagnose congenital megacolon?
1. What is congenital megacolon?
Congenital megacolon, also known as Hirschsprung or congenital colonic agranulomatosis, is caused by a congenital lack of ganglion cells of the intestinal plexus, with the beginning always starting with the internal sphincter, the diseased segment of the intestine. Causes of frequent contractions and no peristalsis lead to stagnation of stool and gas in the upper bowel, causing this segment of intestine to gradually dilate.
Characteristic of congenital megacolon is difficulty in defecation more and more even when defecation is soft. The disease will cause children to anorexia, slow growth, many cases encounter dangerous complications such as severe enteritis, intestinal obstruction, making it more difficult to care for children with congenital megacolon at this time.

Phình đại tràng bẩm sinh khiến trẻ chán ăn và gây ra nhiều bệnh lý khác
2. Congenital megacolon manifests like?
The narrow segment of the colon is the nodal segment, the average length of the non-ganglionic segment is 6-10cm. This length is related to the clinical manifestations of the disease. The clinical forms of congenital megacolon are as follows:
2.1. Acute form
The acute form seen in the neonatal period corresponds to the pathological pathology of the nodal segment 15-20cm long. Diagnostic signs similar to those of intestinal obstruction include:
The child is delayed in passing meconium after 24 hours. Vomiting of milk or bile and intestinal juices. The abdomen is distended with collateral circulation and the abdominal skin is distended. butt and abdomen completely flattened. These findings allow clinical diagnosis and require further confirmation by colonoscopy or rectal biopsy. Some infants have very poor symptoms and are only present at 2 or 3 weeks onwards.
Trẻ chậm đi phân su là dấu hiệu của phình đại tràng bẩm sinh thể cấp tính
2.2. Subacute form
Occurs at breast-feeding age corresponding to the average length of the agranuloma (6-10cm). Therefore, children are admitted to the hospital mainly because of constipation and diarrhea alternating with each other and persisting for a long time. In addition, in this form of disease, the child also has the following symptoms:
Abdominal distension with floating bowel loops, palpable stool tumor in the left iliac fossa. Children with growth retardation, anemia, malnutrition. Abdomen with recurrent episodes of semi-obstruction. Rectal examination showed fecal polyps due to stasis. Rectal biopsy and colonoscopy for definitive diagnosis.
2.3. Chronic form
Occurs in older children corresponding to a short amygdala length (< 6cm). The child is admitted to the hospital with the following conditions:
Persistent long-standing semi-obstruction. Malnutrition, physical and mental retardation. The abdomen is distended, the stool tumor is very large due to stagnation. History of constipation persisting from birth. X-rays and biopsies for definitive diagnosis.

Phình đại tràng bẩm sinh thể mạn tính khiến trẻ suy dinh dưỡng
3. What tests are needed to diagnose congenital megacolon?
Unprepared abdominal X-ray shows low bowel obstruction (the bowel loops are most markedly dilated in the sigmoid, left colon, and transverse colon), with absence of pelvic air, in older children. Spotty stools in the pelvic cavity.
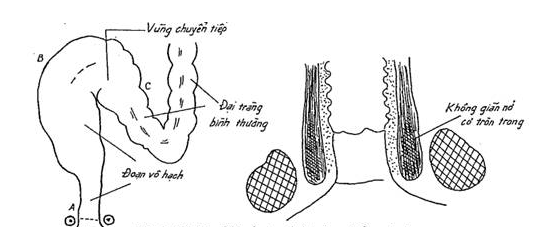
Barium-enhanced colonoscopy shows dilated sigmoid colon, atrophied rectum, and medial colon resembling a funnel or pig's tail. In addition, there are other additional images such as colon lengthening, irregular drug absorption in the nodal segment, and drug retention in the colon for more than 24 hours.
Contrast colonoscopy is the basic test to help confirm the diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease with an accuracy rate of 85%. This test has no diagnostic value in cases of total colonic agranulomatosis, ultra-short agranulomatosis, or in pediatric patients undergoing colostomy.
Rectal biopsy: no ganglion cells of the intrinsic plexus were seen. Pathological tests give an accuracy rate of 95-100%.
Measurement of rectal - anal balloon pressure: No relaxation of the internal sphincter was found, this test is usually applied only in newborns from day 12 onwards. The accuracy of this method is quite high from 85-100%.

Chụp đại tràng giúp chẩn đoán phình đại tràng bẩm sinh
4. Treatment of congenital megacolon
Thorough treatment of Hirschsprung's disease is mainly surgical resection of the lymph node and re-establishment of gastrointestinal circulation on the basis of respecting the anatomical structure to ensure the function of defecation, urination and genital function later. .
4.1. Temporary treatment
Treatment is mainly care:
Enema 2 times a day with warm isotonic saline mixed with oil and large enough pine (16 or 18), combined with instructions for family members to be able to perform the operation at home for a long time. long after discharge. Diet rich in nutrients and laxatives. Follow up monthly to assess the effectiveness of treatment. If internal treatment does not work, an colostomy must be performed. A colostomy in the following situations:
When the neonatal bowel obstruction is evident and the contrast-enhanced colonoscopy shows the length of the narrow passage beyond the sigmoid colon on radiographs: enema will not be effective. When complications of the disease occur: small bowel inflammation, sepsis, intestinal perforation.
4.2. Thorough treatment
In the classics, the authors choose an age of over 1 year or a weight of 10kg or more. With advancements in the field of anesthesia and pediatric surgery, the age of surgery has been lowered to less than 6 months or earlier.
Surgical methods include 4 common methods:
Swenson method: Removal of the entire nodal segment. Connect the healthy colon to the anal canal at a distance of 0.5-2cm from the anal margin. Duhamel method: Leaving a non-ganglionic rectal balloon. Connect the healthy colon to the anal canal in the posterior wall above the dentate line. Soave method: Leaving part of the rectal bulb without lymph nodes, removing the entire mucosa, leaving only the sigmoid duct of the rectum. The healthy lower colon passes through the sphincter and connects to the anal canal above the dentate line. Rehbein and State method: Apply as in Resection anterieure surgery, connecting the healthy colon and rectum about 5cm from the anal margin.
Phương pháp Swenson trong điều trị phình đại tràng bẩm sinh nhằm cắt bỏ toàn bộ đoạn vô hạch
Recently, along with the development of laparoscopic surgery, most hospitals have deployed and applied it in the treatment of Hirschsprung's disease with very good results. Therefore, when a child shows signs of delayed meconium excretion (> 24 hours), regurgitation of yellow fluid, abdominal distension, prolonged constipation, delayed physical and mental development, the child should be taken to a specialized medical facility. clinic for the most thorough examination and treatment.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious and knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






