Laparoscopic surgery to remove kidneys and ureters due to urinary tract tumors
Urinary tract cancer is a transitional cell cancer mainly in the renal calyces and ureters. The disease can be effectively treated when it is detected early and has not passed the metastatic stage. Currently, the most optimal treatment option is laparoscopic ureterectomy.
1. Urinary tract cancer
Urinary tract cancer is a rapid and abnormal cell growth affecting the organs and structures of the male and female urinary systems, and the male reproductive system.
Some types of urinary tract cancer are located according to the structure or location they affect:
Bladder cancer: This is cancer that affects the cells in the urinary bladder gland, bladder. The bladder stores urine for excretion. Kidney cancer: This type of cancer forms in the small tubes that clean the blood of the kidneys. Pelvic cancer is a rare form of the disease. It occurs in the part of the kidney that connects to the bladder. Testicular cancer: This is a type of cancer that forms in the testicles and makes up a very small percentage of all cancers in men. Penile cancer: This cancer affects the penis, which is the male reproductive organ as well as part of the endocrine system. This type of cancer is extremely rare. Urethral cancer: It occurs in the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra passes through the penis, making this cancer more common in men than in women. Cancer treatment in general and urinary tract cancer in particular should be detected early before metastasis for the best treatment results. Today, laparoscopic surgery is the treatment of choice among surgeons. The principle of urinary tract cancer treatment is to remove the entire kidney and ureter.
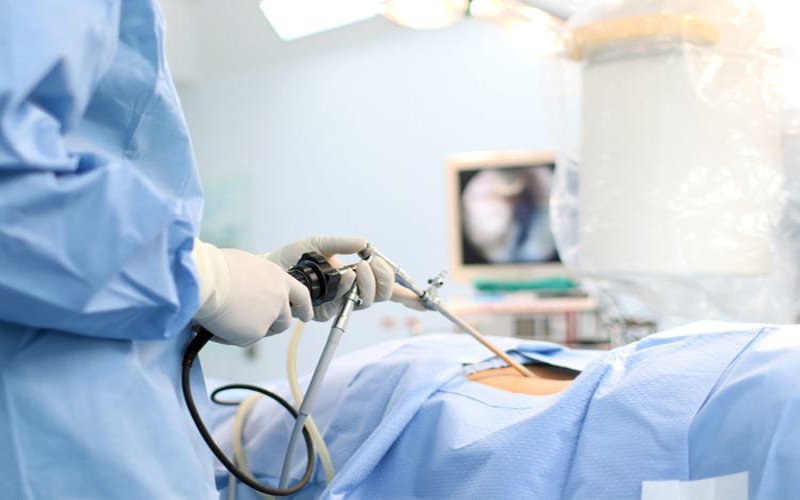
Phâu thuật nội soi là phương pháp điều trị tiên tiến mang lại hiệu quả cao
2. Laparoscopic surgery to remove kidneys and ureters due to urinary tract tumors
To perform this surgery, the doctor will perform a clinical examination to give an indication to proceed. Types of urinary tract cancer are used endoscopically for treatment such as: unilateral urinary tract cancer (invasive level is not deep), transitional cell cancer in the renal calyces,...
Previous For each surgery, in addition to preparing the patient, equipment, operating room, and surgeon, the preparation of records is extremely important. It includes: minutes of consultation, minutes of surgery approval, medical record, pre-anesthesia and written commitment of the patient's family.
2.1. Laparoscopic surgical procedure for nephrectomy and ureterectomy. The patient is under endotracheal anesthesia, the urethral catheter is also placed before surgery. The patient's position is also adjusted to suit the surgical process. And locate the trocar.
The process of laparoscopic nephrectomy and ureterectomy has two stages:
The first phase: Laparoscopic ureterectomy. The patient's position is the obstetric posture. The instrument is placed through the urethra and into the bladder, and then the urethra is cut from the ureteral orifice along the direction of the side of the ureter with the tumor. Then move the patient to the second-stroke position. Second stage: Laparoscopic surgery to remove the kidney and ureter through the peritoneum. The patient was placed on a 45-degree side, with the first trocar placed just at the left edge of the umbilicus (inflated endoscopically for examination). Two other trocars are placed under the camera along the left flank. Next, the surgeon will completely release the ureter (including the part of the ureter that looks up to the bladder wall). Simultaneously, the genital veins are released to the point where they enter the kidney. Lumbar vein and adrenal vein are dissected separately. Continue, dissect the renal artery. Release the entire kidney including the kidney, peri-renal fat layer and adrenal gland. This specimen is removed by bag through the junction of the two trocars. Thereafter, surgical drainage was inserted, the abdomen was closed, and the urinary catheter was kept for 24 h. Similar to the nephrectomy, the technician continues the ureterectomy. Complete release of the ureter, including the ureter to the bladder wall, release of the pyelonephritis, and then the renal vein as well as the renal artery. Renal artery and renal vein dissection.

Bệnh nhân được gây mê để ca phẫu thuật được diễn ra thuận tiện
2.2. Postoperative monitoring and management of complications After surgery, bleeding secondary to hemostasis may occur due to inadequate hemostasis or bodily tissue detachment (this is rare). If bleeding can be uncontrolled, surgery may need to be repeated to improve hemostasis.
Temporary urine leakage can be due to the unsatisfactory suture of the urinary tract or due to a urinary tract arrest. It is these causes that cause urine to flow into the surgical site, which can cause wound infection.
Urinary tract cancer is a dangerous disease, but the disease can be effectively treated if it has not passed the metastatic stage. Accordingly, laparoscopic nephrectomy and ureterectomy is the optimal surgical method to treat this cancer. To achieve the best treatment results, patients should choose reputable places to perform this surgery, which not only minimizes the risk of complications but also ensures long-term health for the patient. long.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment, prevention, screening and screening of urological diseases with high efficiency. With a team of qualified, well-trained medical doctors and quality medical services, it will bring satisfaction as well as the best treatment results for customers.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.






