This is an automatically translated article.
Perennial pitted scars are often a permanent complication of fairly common acne, affecting aesthetics. The long-term experience of treating pitted scars depends on the opinion of each dermatologist as well as on the type of acne scar and the limitations of each available method. Therefore, there are many options for treating pitted scars, including chemical peels, dermabrasion, laser treatment to fat grafting or combination therapy with their own advantages and limitations for the patient to consider first. when deciding.
1. Scar treatment with chemical peels
Chemical peels are the process of applying chemicals to the skin to destroy the damaged outer layers. Thereby, the normal exfoliation process will be accelerated. Different agents used have different penetration, giving different response efficiency.
2. Glycolic acid treats pitted scars
Glycolic acid is the alpha hydroxyl acid most commonly used as an exfoliant. This ingredient can be used as a daily skin care product in concentrations as low as 5 to 15%. Greater concentrations of 30 to 70% are used for chemical peels.
Thus, with higher concentrations, the deeper the crust they create. Glycolic acid works by thinning the stratum corneum, promoting epidermal lysis and dispersing melanocytes in the basal layer. Glycolic acid is systemically safe, non-toxic, and creates a crust with potentially significant effects, but few complications, and is well tolerated by patients. The best results are achieved for perennial pitted scars, after five consecutive treatments of 70% glycolic acid every two weeks.
However, the downside is that the penetration is often uneven, neutralization is required, and there is a high risk of overload if the application time is too long or the skin becomes inflamed.
3. Jessner's solution helps to treat scars
Jessner's solution is used for light peels or to prepare a peel with trichloroacetic acid. This preparation is made of salicylic acid, resorcinol, lactic acid and ethanol, which is effective in destroying the epidermal barrier by disrupting individual epidermal cells.
The depth of the crust depends on the number of layers of solution used. Different aged pitted scars may require different amounts of coats to achieve the same degree of skin peeling. Thereby, the advantage of Jessner's solution is that the peeling process is superficial and safe, rarely going deeper, but can still cause erythema and skin discoloration.

Dung dịch Jessner’s được sử dụng cho những lần lột nhẹ để trị sẹo rỗ lâu năm
4. Scar treatment with pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid is an alpha-keto acid and an effective exfoliant that exhibits keratolytic, antibacterial and serum-suppressing properties as well as the ability to stimulate the production of new collagen, the formation of elastic fibers. . Therefore, using a solution with a concentration of 40 to 70% pyruvic acid helps to effectively treat perennial pitted scars.
The advantages of pyruvic acid are uniform penetration with uniform erythema, mild scabbing, short postoperative time, and applicability for all skin types. The downside is that it causes stinging and burning sensations, which need to be neutralized or possibly pungent and uncomfortable for the upper respiratory tract mucosa.
5. Treatment with Phenol
Phenol is a chemical for deep skin peeling, can also be an option for severe atrophic pitting scars but is used more rarely, because it requires a long recovery time and has a high potential for complications. .
To overcome these limitations, solutions for deep peels often require a combination of croton oil and phenol in different concentrations. Because phenol can cause cardiac arrhythmias, the patient should have their heart monitored during the procedure.
6. Skin grinding method
This is the first progressive treatment for pitted scars caused by acne. Dermabrasion and microdermabrasion are facial resurfacing techniques that mechanically abrade damaged skin to promote re-epithelialization.
Although they have the same physical principles, dermabrasion and microdermabrasion differ in the tools used and how the technique is performed. Specifically, dermabrasion is the complete removal of the epidermis and penetration to the level of the papillary or reticular dermis, which helps to regenerate the structural proteins of the skin. Meanwhile, microdermabrasion only removes the outer layer of the epidermis, promoting natural exfoliation. Both techniques are particularly effective in treating pitted scars and produce clinically significant improvements to the skin's appearance. Unlike microdermabrasion, microdermabrasion can be repeated in a short period of time, is painless, requires no anesthesia, and causes fewer complications, but also has a more limited effect, and does not treat severe scarring. deep.
Mài da và mài da vi điểm là một phương pháp trị sẹo rỗ lâu năm tiến bộ đầu tiên đối với sẹo rỗ do mụn
7. Laser method
Laser skin resurfacing is an effective, perennial pitted scar treatment that is easier to use than other modalities. There are different types of lasers, which make them useful in treating different acne scars. However, laser is also limited in the treatment of deep pitted scars8. Skin resurfacing with plasma
This technology uses pulses of ionized nitrogen gas to deliver thermal energy directly to the skin. Initially, the epidermis remains intact, only to then peel off when the healing process is complete. About 10 days after the treatment, new collagen and elastin deposition fibroblasts can be seen, improving the pitted scar area. Rare side effects may include temporary hyperpigmentation, erythema, edema, infection, and new scarring.
9. Method of using high frequency waves
Radio frequency is a type of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation, which runs through the skin and generates heat deep in the skin layer to cause skin damage. As a result, the skin will create a wound-healing response, stimulating collagen regeneration in the skin.
10. Drilling technique
Techniques of drilling or excision to the subcutaneous level are preferred to treat perennial pitted scars, effective in cases of deep pitted scars. The goal of this technique is to create a larger, deeper scar so that the old scar can fade over time.
Although surgical procedures are a one-time effective treatment, a major drawback of dermabrasion is that only treated scars have a chance to improve. In addition, this technique does not affect the irregularities or discoloration of the surrounding skin as much as is common with other acne scar treatments.
11. Fat grafting
Autologous fat is considered the ideal lifting material because of its low cost, availability, and no risk of rejection or allergy or adverse reactions to other tissues.
This technique consists of two stages: grafting and grafting. The doctor will inject small pieces of fat that both fill in the scarred area and maximize access to the skin's available blood supply. Most patients with long-standing pitted scars achieve maximum results about three months after this technique.
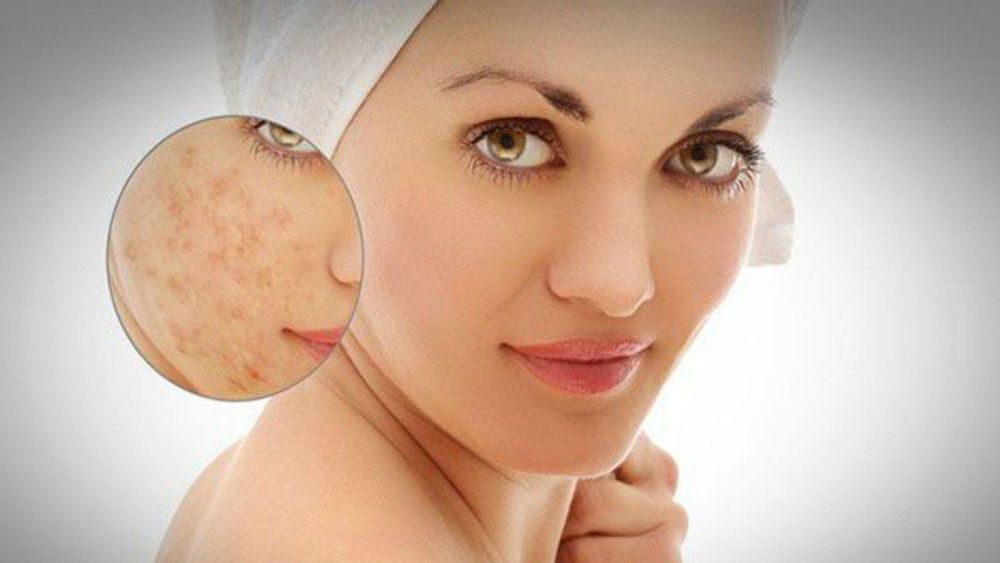

Hầu hết các bệnh nhân bị sẹo rỗ lâu năm đều đạt được kết quả tối đa khoảng ba tháng sau khi làm kỹ thuật cấy mỡ
12. Skin Needle Roller
This is also known as collagen induction therapy or needle dermabrasion. The mechanism of this technique is to roll a cylindrical device fitted with hundreds of needles, creating thousands of small holes in the skin from the papillary to dermal level. From there, the exposed skin layer initiates a complex chain of growth factors that eventually leads to collagen production.
The effect of microneedling can be seen after about six weeks but full effect can take at least three months, as new collagen deposition is slow, skin texture will continue to improve over a period of 12 month.
13. Stem Cell Therapy
Epidermal replacement is accomplished by adding epidermal cells to the skin structure to form a synthetic dermal layer with some particular biological activity. These replacement cells have the ability to proliferate and renew themselves, helping to repair the skin.
The technical way of stem cell therapy is to isolate stem cells from the patient, propagate and differentiate in vitro, and then re-inject the autologous cells into the patient. The role of epidermal stem cells has been demonstrated in contributing to the maintenance of skin homeostasis and general wound repair, not merely the treatment of pitted scars.
In short, with the great development of medical technology, dermatology has made many strides in the treatment and cosmetic problems of the skin. Accordingly, the long-term experience of treating pitted scars gradually achieves high satisfaction from patients with a variety of different therapies. Because of the diverse forms of perennial pitted scars on the skin, the multimodal combination always promises to bring the best treatment effect.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov