This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Hung Cuong - Gastroenterologist, Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Stomach cancer is a malignant lesion that develops from the layers of the stomach wall. Usually the mucosal layer is the most likely site to develop malignant lesions. According to Globocan-2018, in Vietnam, the number of new cases of stomach cancer is 17,527, accounting for 10.6% of new cancer cases, ranking fourth after liver cancer and lung cancer.
1. Situation of gastric cancer in Vietnam
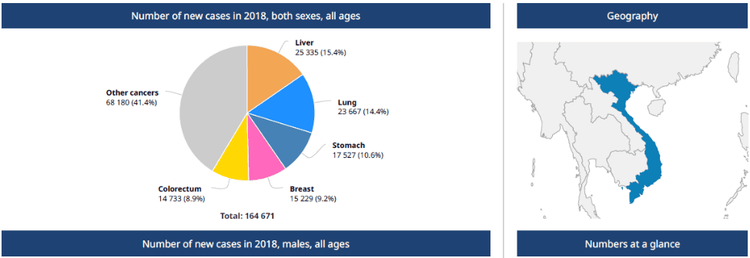
Số ca mắc mới ung thư tại Việt nam năm 2018
For men, the number of cases is 11,161 cases, ranking third after liver cancer and lung cancer, accounting for 12.3%. Stomach cancer in women is 6,366 cases, accounting for 8.6%, the total number of new cases and ranks fourth after breast cancer, colorectal cancer and lung cancer.
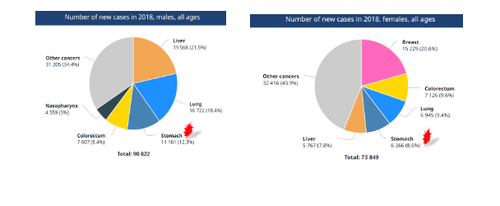
Số ca mắc mới của nam giới và nữ giới
With the 2018 census of 96,491,142 in which women: 48,735,730 and men: 47,755,412, the rate of stomach cancer in women is: 13 cases per 100 thousand people and for men is: 23.3 cases per 100 thousand people.
2. Causes of stomach cancer
Although the understanding of the specific causative factors of these factors is still unclear, studies and community observations show that: Stomach cancer is caused by a combination of factors from environmental changes environment in the stomach, eating habits and genetic causes.
Predisposing factors for stomach cancer:
2.1 Diet high in nitrate compounds (Nitrates) Foods rich in nitrates include: canned food, smoked meat-fish, salted foods , fermented, pickled tomato,...
Solution:
Limit foods containing a lot of nitrate: salted meat, pickled cucumbers, smoked foods. Eating more fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins C, E, and beta carotene helps prevent the metabolism of nitrate and nitrogen metabolism products. 2.2 Smoking Many studies have shown that smoking increases the risk of stomach cancer (increased by 60% in men and 20% in women).
Solution: Quit smoking
2.4 Abuse of alcohol, alcoholic beverages Alcohol is not only a cause of liver cancer but also a risk factor for recurrent gastritis causing cancer gastric cancer, especially gastric cancer.
Solution: Give up alcohol and alcoholic beverages
2.5 H.P (Helicobacter Pylory) The role of H.P. was demonstrated in 1982 by Marshal and Warren. By 1984, the international agency for cancer research This bacteria is the cause of stomach cancer. That also explains stomach cancer more and more appearing in young people (under 40 years old).
Solution:
Treatment of H.P is recommended in combination with treatment of gastritis- H+ proton pump inhibitor combined with 2 of 3 drugs (Amoxicillin, Clarythromycin and Metronidazole). If this treatment is not successful, it will be used: proton pump inhibitors H +, metronidazole, tetracycline combined with drugs Bismuth) Use pain relievers, anti-inflammatory regularly, uncontrolled.
Vi khuẩn H.P là một trong các nguyên nhân gây bệnh ung thư dạ dày
In addition, other risk factors also play a role in the formation of stomach cancer: obesity, stomatitis after gastrectomy, worker exposure, exposure to dust, nitrogen-containing gases , radiation,....
Early detection of modifiable or non-modifiable risk factors is very important in the prevention of primary gastric cancer.
The modifiable risk factors that account for the incidence of stomach cancer are as follows:
+ Depends on the patient:
Maintain a balanced diet Quit smoking and risky foods and drinks Maintain normal weight + Depend on doctor:
Diagnosis and treatment of gastritis and H.P. Consider controlled use of analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs Unmodifiable risk factors: Occupational exposure career and family factors.
3. Classification of stomach cancer
3.1 Classification according to histopathology (the type of cancer cell) + Adenocarcinoma: accounting for 85%-90% of total stomach cancers
+ Cancer of connective tissue: Occupying rate 5 -ten%.
+ Other types of cancer: lymphoma 2%-5%, myoma 0.5%-1%, carcinoid tumor 3%.
3.2 Classification according to lesions + Early gastric cancer: Cancer that the extent of damage is only localized in the mucosa, submucosa of the stomach. Stomach cancer early treated thoroughly, has a better prognosis. + Advanced gastric cancer: is cancer that has penetrated deep into the muscular layers of the stomach, which can metastasize to the lymph nodes and other organs.
In Vietnam, it is common to see cancer at an advanced stage.
Most early gastric cancer symptoms are similar to gastritis, but gastritis often recurs, so we are still subjective, buying drugs without going to the doctor, without a gastroscopy. for diagnosis. People still do not have the habit of going for regular health check-ups, screening for cancer, especially stomach cancer 3.3 Classification by stage Like other cancers, cancer is often evaluated on 3 factors:
+ T (primary Tumor): The degree of invasion of the original tumor.
+ N (regional lymph node nodes): whether or not cancer cells have spread to regional lymph nodes, number of lymph nodes.
+M (distance M etastasis)- Distant metastasis to other organs.
Another more common classification with specific prognostic factors, which helps in treatment, is the staging classification, which is based on the following factors:
T - Primary tumor
Tx: Mass Primary tumor cannot be assessed
+ To: Unprovable primary tumor
+ Tis: Cancer in situ or superficial cancer, intraepithelial tumor has not invaded the mucosa.
+ T1: Tumor invades mucosa and submucosa
+ T2: Tumor invades muscle layer or subserosal layer
+ T3: Tumor invades serosa but has not invaded into tissues around.
+ T4: Tumor invades surrounding tissues

Ung thư dạ dày theo từng giai đoạn
The smaller the T, the better the prognosis, the higher the cure. N1: There is metastasis in 1 to 6 regional lymph nodes
+ N2: There is metastasis in 7 to 15 regional lymph nodes
+ N3: There is metastasis in more than 15 regional lymph nodes
N the smaller, the better the prognosis, the possibility of cure higher disease
M - Distant metastasis
+ Mx: Distant metastasis cannot be determined
+ Mo: No distant metastasis
+ M1: Has distant metastasis
Mo has a better prognosis than M1
4. Diagnosing stomach cancer
Diagnosis of gastric cancer after minimal surgery:
What type of cell cancer? What are the TNM indicators? The following symptoms may be signs of stomach cancer:
Poor appetite, loss of appetite Feeling of abdominal pain, sluggishness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, decreased working capacity, dizziness, dizziness . Skinny, weight loss for no reason Feel the mass, lump in the abdomen Passing bloody or black stool When having one of the above signs, the patient needs to go to the hospital for examination or consult a doctor do not buy drugs on their own.
What tests are used to diagnose stomach cancer?
When stomach cancer is suspected, you will be examined and do more tests:
+ Gastroscopy, tumor biopsy if malignant lesions are suspected.

Hình ảnh ung thư dạ dày trên nội soi
+ Chest and abdomen computed tomography
+ PET/CT scan

Hình ảnh tăng chuyển hóa trên phim chụp PET ở vùng dạ dày do ung thư
+ Do a blood test: To evaluate the degree of anemia, and cancer markers in the blood.
After the examination and the test results, the doctor will diagnose the stage of the disease for you.
5. Treatment methods for stomach cancer
After being diagnosed with gastric cancer and related factors including physical condition, tumor factors, lymph nodes and assessment of distant metastases, the doctor will decide on the treatment method:
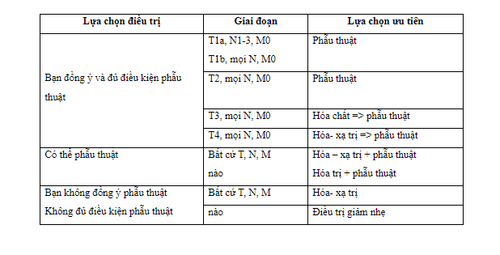
A panel consisting of: surgeons, chemotherapy doctors, radiation therapists, pathologists, radiologists, will discuss and agree on how to treat for you and offer advice on a case-by-case basis.
Treatment of stomach cancer
Surgery is always the first priority for stomach cancer, depending on the disease and health conditions, surgery can be done before or after chemotherapy treatment . Surgery can be curative, or it can be symptomatic or palliative.
A: Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be used before and after surgery or can be combined with radiation therapy after surgery
Commonly used drugs are:
5-FU and Cisplatin ECF (Epirubicin, Cisplatin). and Fluorouracil) Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Fluorouracil Epirubicin, Cisplatin and Capecitabine Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine B: Radiotherapy
Postoperative radiotherapy is adjuvant and has been shown to reduce local recurrence for cancer stomach. Radiation therapy helps improve the effectiveness of treatment in cases where surgery cannot completely solve the disease.
C: Surgery
Radical surgery: is a method of removing the damaged part of the stomach containing the original tumor, along with removing the surrounding lymph nodes
Depending on the location of the tumor in the stomach, the doctor The doctor will decide to remove part or all of the damaged stomach.
+ Gastric mucosal resection: Only applied to early lesions, still localized to the surface of the gastric mucosa without invading the lower layers
+ Total gastrectomy: Performed when Elevated, proximal, or extensive tumor lesions necessitate resection of organs with invasive tumors.

Khối dạ dày kèm lách và một phần đuôi tụy bị cắt bỏ
+ Partial gastrectomy, also known as gastrectomy: A part of the stomach with a tumor is removed according to the principle so that the nearest section of the tumor is larger than 4cm, accompanied by more than 15 lymph nodes removed. lymphocytes according to their respective locations.
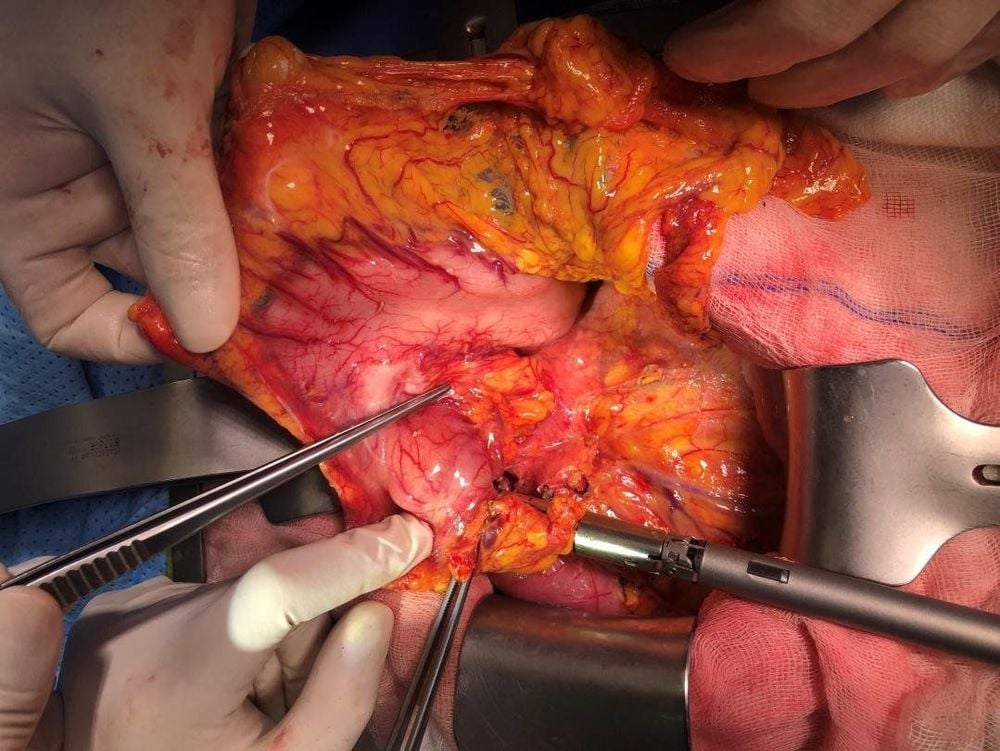
Khối u mặt sau dạ dày xâm lấn ra lớp thanh mạc

Hình ảnh ung thư dạ dày qua phẫu thuật robot (các tổn thương đã xâm lấn ra ngoài thanh mạc)

Khối u mặt sau dạ dày được lấy bỏ kèm các hạch lân cận
After the stomach is removed, the remaining stomach will be connected to the intestine to restore digestive circulation.
Gastric surgery can be performed by open surgery (brake surgery), laparoscopic surgery, robotic surgery.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, robotic gastric bypass surgery has been performed on a routine basis, combined with the ERAS (enhanced recovery after surgery) program to help:
Enhance treatment capacity Limited abdominal wall damage after surgery and the risk of intestinal obstruction due to postoperative adhesions Increased aesthetics Patients less pain Less blood loss Ability to recover quickly => short hospital stay (only 3-5 days) => Due to That reduces the cost of treatment for the patient. + Palliative surgery: Open the small intestine to nourish: in case radical surgery is not possible, over time food will not pass through the stomach anymore. At this point, the doctor will insert a small tube into your intestine, this tube goes out into the abdominal wall to pump nourishing food.
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for gastric cancer examination and treatment at Vinmec Times City International Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination and 50% discount on Esophageal and Stomach Cancer Screening Package
- 50% off cost for customers who have indications for post-examination treatment. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.
Articles refer to sources: nccn.org, gco.iarc.fr